In the world of medicine, the human body holds countless mysteries waiting to be unraveled.
From the delicate movements of internal organs to the precision of surgical techniques, every procedure offers a glimpse into the complexity of our anatomy.
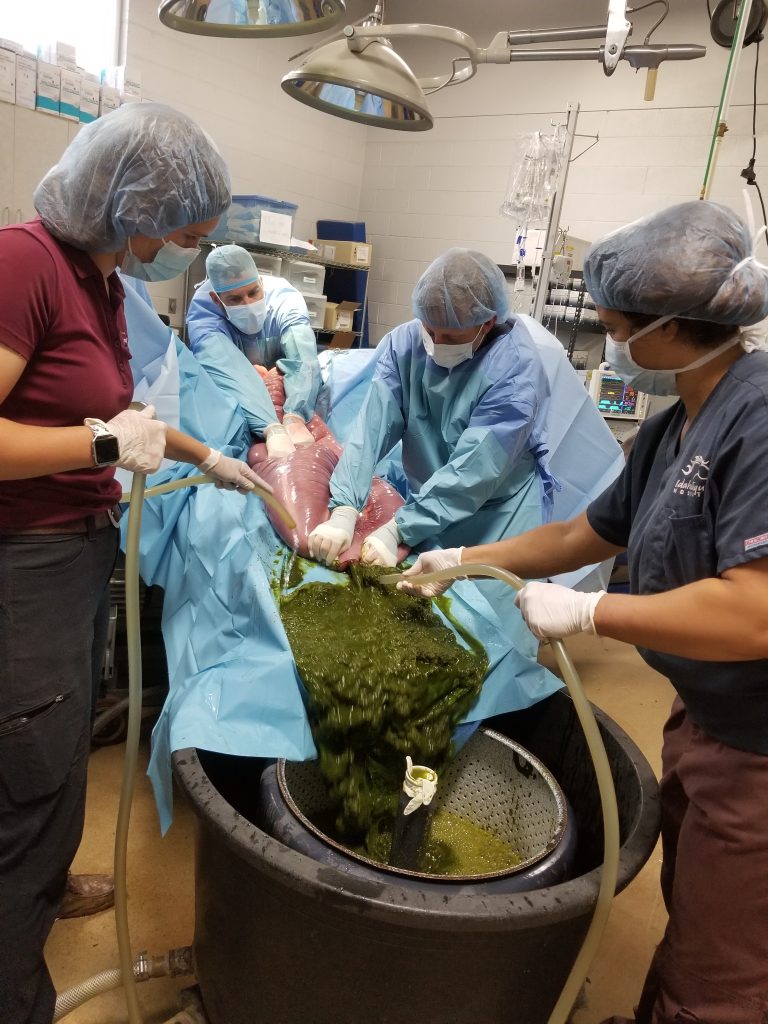
Among the myriad of surgeries performed, one particularly intriguing procedure stands out – the abdominal cellotomy.
Join us as we delve into the world of abdominal surgeries, unveiling the secrets held within the incisions, and discovering the intricate dance of healing and recovery.
abdominal cellotomy
Abdominal cellotomy refers to a surgical procedure performed on the abdomen.
It can be performed through various methods, including laparotomies and laparoscopic surgeries.
The purpose of this procedure is to address various conditions such as a ruptured appendix, cesarean sections, inguinal hernia surgery, exploratory laparotomy, cholecystectomy, appendectomy, exploratory celiotomy, diagnostic tests, biopsies, ventral midline incisions, and linea alba interventions.
Throughout the procedure, essential steps include skin clipping, accessing the abdominal cavity, addressing specific organs or structures, and potential interventions such as the placement of drains or feeding tubes.
Abdominal cellotomy is also relevant to procedures involving the lower urinary tract and mammary chain.
Key Points:
- Abdominal cellotomy is a surgical procedure performed on the abdomen.
- It can be done using different methods, including laparotomies and laparoscopic surgeries.
- The procedure is used to address various conditions, such as a ruptured appendix, cesarean sections, and inguinal hernia surgery.
- Essential steps of the procedure include skin clipping, accessing the abdominal cavity, and addressing specific organs or structures.
- Potential interventions during the procedure may involve the placement of drains or feeding tubes.
- Abdominal cellotomy is also relevant to procedures involving the lower urinary tract and mammary chain.
abdominal cellotomy – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The term “abdominal cellotomy” refers to a surgical procedure in which a specific type of cells within the abdomen are targeted and removed.
2. One interesting fact is that abdominal cellotomy was first performed in the late 19th century as a technique to treat certain abdominal disorders before advanced imaging technology was available.
3. Did you know that abdominal cellotomy is rarely performed today due to the development of less invasive procedures, such as laparoscopic surgeries, which have proven to be more effective and have shorter recovery times?
4. In some cases, abdominal cellotomy may involve the removal of cells from specific organs, such as the liver or intestines, in order to treat diseases like cancer or gastrointestinal disorders.
5. Interestingly, advancements in cellular biology and regenerative medicine have led to studies exploring the potential use of stem cells derived from abdominal cellotomy to promote tissue repair and regeneration, offering new possibilities for medical treatments in the future.
Abdominal Surgery
Abdominal surgery encompasses a range of surgical procedures aimed at addressing medical conditions and concerns related to the organs and structures within the abdomen. This category covers surgeries specific to the stomach, liver, intestines, appendix, and reproductive organs. When these vital organs suffer from dysfunction or damage, abdominal surgery becomes a crucial intervention for restoring health and function.
Laparotomies
Laparotomies are a type of abdominal surgery that involves making a large incision in the abdomen to gain access to the internal organs. This technique allows surgeons to have a wide field of view and direct access to the organs, making it suitable for complex or emergency cases.
Laparotomies are commonly used for procedures such as exploratory surgeries, removal of tumors or cysts, and extensive repair of damaged organs. However, due to the large incision and extensive tissue dissection required, laparotomies typically require a longer recovery period compared to minimally invasive techniques.
Laparoscopic Surgeries
Laparoscopic surgeries, also known as minimally invasive surgeries, have revolutionized the field of abdominal surgery. Instead of making a large incision, laparoscopic surgeries involve the use of small incisions and specialized instruments equipped with a camera. This camera allows surgeons to visualize the surgical site on a monitor, eliminating the need for a direct view.
Laparoscopic surgeries offer several advantages over traditional open surgeries, including:
- Reduced scarring
- Shorter recovery times
- Decreased risk of infection
- Less postoperative pain
Common laparoscopic procedures include:
- Cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal)
- Appendectomy (appendix removal)
- Hernia repairs
“The shift towards laparoscopic surgeries has greatly improved patient outcomes and quality of life.”
Ruptured Appendix
A ruptured appendix is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate surgical intervention. Appendicitis, inflammation of the appendix, can lead to a rupture if left untreated. This condition necessitates the removal of the entire appendix to prevent the spread of infection within the abdominal cavity, which can be life-threatening.
Traditionally, a ruptured appendix would be addressed through an open laparotomy. However, advancements in laparoscopic techniques now allow for the minimally invasive removal of the appendix. Laparoscopic appendectomy offers faster recovery times and decreased risk of complications compared to open surgery.
- A ruptured appendix requires immediate surgical intervention.
- Appendicitis can lead to a rupture if left untreated.
- The condition necessitates the removal of the entire appendix.
- This prevents the spread of infection within the abdominal cavity, which is life-threatening.
“Laparoscopic appendectomy offers faster recovery times and decreased risk of complications compared to open surgery.”
Cesarean Sections
Cesarean sections, also known as C-sections, are surgical procedures that involve delivering a baby through an incision made in the mother’s abdomen and uterus. This procedure is necessary when vaginal delivery poses risks to the mother or baby. Some reasons for opting for a C-section include complications during labor, fetal distress, breech presentation, or multiple pregnancies.
During a C-section, a low transverse incision is typically made in the abdomen. This type of incision facilitates faster healing and lowers the chances of complications, like uterine rupture, in subsequent pregnancies.
In summary:
–Cesarean sections involve delivering a baby through an incision in the abdomen and uterus
–They are performed when vaginal delivery is not feasible or safe
–Reasons for a C-section may include complications during labor, fetal distress, breech presentation, or multiple pregnancies
–A low transverse incision is typically made, enabling easier healing and reducing the risk of complications in future pregnancies.
A C-section may be recommended when complications arise during labor or when there are concerns for the well-being of both the mother and the baby. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the best course of action.
Inguinal Hernia Surgery
Inguinal hernias occur when a portion of the intestine or abdominal tissue pushes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall, resulting in a bulge or swelling. Surgery is often necessary to repair the hernia and prevent potential complications such as bowel obstruction or strangulation.
Inguinal hernia surgeries can be performed using either open or laparoscopic approaches.
The open technique involves making an incision in the groin area and manually repairing the hernia.
The laparoscopic technique utilizes small incisions and specialized instruments to place a mesh to reinforce the weakened area.
Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair offers a quicker recovery time and less risk of postoperative complications.
- Inguinal hernias occur when intestine or abdominal tissue pushes through weak spot in lower abdominal wall
- Surgery required to repair hernia and prevent complications like bowel obstruction or strangulation
- Two approaches: open and laparoscopic
- Open technique involves incision in groin area and manual repair of hernia
- Laparoscopic technique uses small incisions and specialized instruments to place mesh for reinforcement
- Laparoscopic repair offers quicker recovery time and less risk of postoperative complications.
Note: Inguinal hernias occur when a portion of the intestine or abdominal tissue pushes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall, resulting in a bulge or swelling. Surgery is often necessary to repair the hernia and prevent potential complications such as bowel obstruction or strangulation.
Exploratory Laparotomy
An exploratory laparotomy is a surgical procedure used to visualize and evaluate the organs and structures within the abdomen. It is commonly performed to diagnose and determine the extent of various abdominal conditions such as tumors, infections, or trauma.
During an exploratory laparotomy, the surgeon makes a large incision in the abdomen and carefully examines the organs and tissues. Depending on the findings, surgical intervention may be performed during the same procedure.
Exploratory laparotomies are important in providing valuable information for accurate diagnosis and can guide subsequent treatment plans*.
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. This procedure is commonly performed to treat gallbladder-related conditions, such as gallstones or inflammation.
A cholecystectomy can be performed either through an open laparotomy or laparoscopic approach.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy involves making several small incisions,
- while an open cholecystectomy requires a larger incision.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the preferred method due to its minimally invasive nature, resulting in:
- minimal scarring,
- less pain, and
- shorter recovery times.
Appendectomy
Appendectomy is the surgical removal of the appendix, usually due to inflammation caused by appendicitis. This condition is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate attention to prevent the appendix from rupturing.
Appendectomies can be performed through open or laparoscopic techniques. Laparoscopic appendectomy involves making small incisions and using specialized instruments to remove the inflamed appendix. Open appendectomy requires a larger incision and direct visualization of the appendix.
Laparoscopic appendectomy is preferred when possible, as it offers faster recovery and reduced risk of complications compared to open surgery.
Exploratory Celiotomy
Exploratory celiotomy, also known as an open exploratory laparotomy, is a surgical procedure that involves making a large incision in the abdomen to visually inspect and evaluate the abdominal organs. It is primarily used to diagnose and treat complex or extensive abdominal conditions, such as tumors, adhesions, or trauma.
During an exploratory celiotomy, the surgeon carefully examines the organs, takes biopsies if necessary, and performs interventions to address the identified issues. Although an open procedure, exploratory celiotomy remains an invaluable tool in certain scenarios where a comprehensive assessment of the abdominal cavity is required.
Abdominal celiotomy encompasses various abdominal surgeries, from open laparotomies to minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures. Each procedure has specific indications and advantages based on the medical condition at hand. With advancements in surgical techniques and technology, the focus has shifted towards minimally invasive approaches to decrease patients’ discomfort and accelerate their recovery. Understanding these different techniques can help patients make informed decisions and alleviate concerns when faced with the possibility of abdominal surgery.
💡
You may need to know these questions about abdominal cellotomy
What’s the difference between Celiotomy and laparotomy?
Celiotomy and laparotomy are two terms used interchangeably to describe a surgical procedure that involves making a large incision in the abdomen to access the peritoneal cavity. The main difference between the two lies in their technical approach. Celiotomy refers to a general term used to describe any surgical incision in the abdominal wall, while laparotomy specifically refers to a sagittal, midline incision along the linea alba. This standardized approach in laparotomy allows for consistent access to the peritoneal cavity in a reliable manner. Although both procedures achieve the same goal, the use of the term laparotomy implies a more standardized and defined incision technique.
What is a Celiotomy?
A celiotomy, also known as a laparotomy, is a surgical procedure that involves making an incision into the abdominal cavity. This procedure allows surgeons to access and examine the organs within the abdomen, and perform various surgical interventions if needed. Celiotomy is typically performed when less invasive methods are not sufficient to diagnose or treat abdominal conditions. During the procedure, the surgeon carefully opens the abdominal wall, providing direct access to the organs for thorough examination, repair, or removal of any diseased tissue. Celiotomy is a vital technique in modern medicine, enabling surgeons to address a wide range of abdominal conditions and improve patient outcomes.
What are the two types of abdominal surgery?
Abdominal surgeries are categorized into two types: open laparotomies and minimally invasive laparoscopic surgeries. Open laparotomies involve a substantial incision in the abdomen, resulting in a longer recovery period and considered a major operation. On the other hand, laparoscopic surgeries are performed using smaller incisions, providing a minimally invasive approach with shorter recovery times.
What are the indications for Celiotomy?
Celiotomy, a surgical procedure involving opening the abdomen, may be indicated for various conditions. These include the presence of foreign bodies, masses, abscesses, or granulomas within the abdomen. Additionally, it may be necessary in cases of uncontrolled abdominal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal or urinary tract obstruction, or radiographic evidence of pneumoperitoneum. Moreover, if a patient experiences persistent symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain without a detectable cause, or if there are abnormal findings on cytologic or laboratory tests, celiotomy may be warranted.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525961/
https://swvetsurgery.com/services/soft-tissue-and-oncologic-surgery/celiotomy/
https://www.farnorthsurgery.com/blog/what-is-abdominal-surgery-an-overview
https://www.cliniciansbrief.com/article/celiotomy-abdominal-surgery