In the realm of childbirth, where the miracle of life unfolds, there lies an unpredictable force known as “abnormal labor”.
An enigma that challenges our understanding of the birthing process, every instance of abnormal labor opens up a world of curiosity and intrigue.
Join us as we dive into the mysteries that surround this fascinating phenomenon.
abnormal labor
Abnormal labor refers to the deviation from the normal progression and duration of the three stages of labor: early, active, and pushing.
It can be characterized by various factors, including inefficient or prolonged contractions, fetal malposition or malpresentation, and cephalopelvic disproportion.
Abnormal labor can lead to complications, such as prolonged labor, postpartum hemorrhage, and fetal distress, necessitating timely interventions such as pharmacological augmentation, cesarean section, or instrumental delivery to ensure a safe and successful birth outcome.
Key Points:
- Abnormal labor deviates from the normal progression and duration of the three stages of labor:
- early
- active
- pushing.
- Factors that characterize abnormal labor include:
- inefficient or prolonged contractions
- fetal malposition or malpresentation
- cephalopelvic disproportion.
- Abnormal labor can lead to complications such as:
- prolonged labor
- postpartum hemorrhage
- fetal distress.
- Timely interventions such as:
- pharmacological augmentation
- cesarean section
- instrumental delivery
may be necessary to ensure a safe and successful birth outcome in cases of abnormal labor.
abnormal labor – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Abnormal labor, known as dystocia, occurs in around 11% of all pregnancies.
2. According to a study, women who consume fish oils during pregnancy are less likely to experience abnormal labor.
3. One common cause of abnormal labor is cephalopelvic disproportion, where the size of the baby’s head is too large to fit through the mother’s pelvis.
4. An intervention used to treat abnormal labor is called a vacuum extraction, where a suction cup is attached to the baby’s head to assist with its delivery.
5. Certain factors can increase the risk of abnormal labor, such as maternal age over 35, obesity, and the use of certain medications during pregnancy.
Causes Of Abnormal Labor
Abnormal labor is a term used to describe labor and delivery that deviates from the normal progression. It is also known as dysfunctional labor or difficult labor. Various factors can contribute to abnormal labor, including:
- Maternal factors:
- Obesity
- Prior uterine surgery
- Maternal age
-
Medical conditions like diabetes or hypertension
-
Fetal factors:
- Abnormal position
- Macrosomia (large fetus)
-
Abnormal presentation
-
Environmental factors:
- Inadequate prenatal care
- Stress
It’s important to note that abnormal labor can sometimes occur spontaneously without any identifiable cause. This makes it a complex and challenging condition to effectively manage.
“Abnormal labor can also occur spontaneously without any identifiable cause, making it a complex and challenging condition to manage effectively.”
- Abnormal labor refers to labor and delivery that deviates from the normal progression.
- Various factors can contribute to abnormal labor, including maternal, fetal, and environmental factors.
- Maternal factors include obesity, prior uterine surgery, maternal age, and medical conditions such as diabetes or hypertension.
- Fetal factors such as abnormal position, macrosomia (large fetus), or abnormal presentation can also contribute to abnormal labor.
- Environmental factors like inadequate prenatal care or stress can play a role in the development of abnormal labor.
- Abnormal labor can sometimes occur spontaneously without any identifiable cause.
- It is a complex and challenging condition to manage effectively.
Signs And Symptoms Of Abnormal Labor
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of abnormal labor is crucial for early intervention and a successful outcome. Some common signs of abnormal labor include:
- Prolonged labor that exceeds 20 hours
- Inadequate contractions
- Lack of progress in cervical dilation
- Irregular or erratic uterine contractions
A woman may also experience:
- Severe pain
- Abnormal bleeding
- Abnormal fetal heart rate patterns during labor
Other signs may include:
- A sudden decrease in the level of amniotic fluid
- Meconium-stained amniotic fluid (indicating fetal distress)
- The presence of maternal fever
It is essential for healthcare providers to monitor these signs carefully during labor. Prompt action and intervention can help prevent complications and improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Complications Associated With Abnormal Labor
Abnormal labor can give rise to various complications that can negatively impact both the mother and the baby. Prolonged labor increases the risk of maternal exhaustion, infection, and postpartum hemorrhage. It can also lead to uterine rupture, which is a life-threatening condition for both the mother and the baby. In some cases, abnormal labor can result in fetal distress, meconium aspiration syndrome, or asphyxia. These complications can affect the baby’s health and increase the risk of neonatal morbidity and mortality.
The consequences of abnormal labor can have long-lasting effects on the psychological and emotional well-being of the mother. She may experience feelings of disappointment, anxiety, and sometimes even depression due to the unexpected challenges encountered during the labor process.
Medical Interventions For Abnormal Labor
When faced with abnormal labor, healthcare providers have various medical interventions at their disposal to manage and mitigate risks. One common intervention is the use of oxytocin to augment labor contractions and facilitate cervical dilation. Oxytocin is a synthetic hormone that mimics the effects of natural oxytocin, which stimulates uterine contractions. This intervention helps regulate the progress of labor and can be adjusted as necessary to achieve optimal outcomes.
In some cases, if vaginal delivery is not possible or safe, a cesarean section may be performed. A cesarean section is a surgical procedure in which the baby is delivered through an incision in the mother’s abdomen and uterus. This intervention is often necessary when there is a risk to the mother or the baby’s health during a vaginal delivery.
Other medical interventions may include the use of forceps or vacuum extraction to assist in the delivery process, episiotomy (surgical incision to enlarge the vaginal opening), or manual rotation of the baby’s position. These interventions aim to ensure a safe delivery and reduce the risks associated with abnormal labor.
Preventive Measures For Abnormal Labor
While not all cases of abnormal labor can be prevented, there are certain preventive measures that can help reduce the risk. Adequate prenatal care plays a significant role in identifying and managing potential risk factors before labor begins. Regular prenatal visits allow healthcare providers to monitor the mother’s health and the baby’s development closely. Timely interventions, such as managing pre-existing medical conditions, can help minimize the risk of abnormal labor.
Furthermore, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and attending childbirth education classes, can contribute to a smoother labor process. Educating pregnant women about the signs and symptoms of abnormal labor empowers them to seek timely medical attention and intervention, which can help prevent complications.
Management Of Abnormal Labor
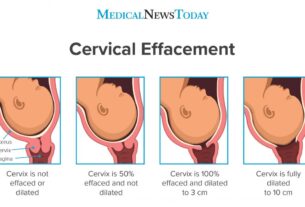
The management of abnormal labor involves a multidisciplinary approach, with healthcare providers working together to address the specific needs of each individual case. Close monitoring of maternal vital signs, fetal heart rate, and uterine contractions is essential to assess the progress of labor and identify any deviations from the normal course. Regular vaginal examinations are performed to evaluate cervical dilation and effacement, helping to determine the appropriate course of action.
Clear and effective communication between the healthcare team and the laboring woman is vital in managing abnormal labor. Women should be involved in decision-making regarding interventions and informed of the risks and benefits of each option. Emotional support, pain management strategies, and effective laboring positions can contribute to a more positive experience for the woman.
Understanding The Stages Of Abnormal Labor
Abnormal labor, which follows a similar progression to normal labor, is characterized by three main stages: the latent phase, the active phase, and the second stage of labor.
- The latent phase is marked by irregular contractions and early cervical dilation.
- The active phase is characterized by rapid cervical dilation, along with more frequent and regular contractions.
- The second stage is when full cervical dilation is achieved and the woman experiences an urge to push as the baby descends through the birth canal.
In instances of abnormal labor, one or more stages may be prolonged, or there may be a lack of progress altogether. Therefore, close monitoring and timely interventions are crucial during each stage to ensure a safe outcome for both the mother and the baby.
- It is important to closely monitor the progression of labor.
- Timely interventions should be implemented, if necessary, to assist with the labor process.
“Close monitoring and timely interventions are crucial during each stage to ensure a safe outcome for both the mother and the baby.”
Maternal And Fetal Risks In Abnormal Labor
Abnormal labor presents risks to both the mother and the baby. Maternal risks include fatigue, infection, postpartum hemorrhage, and an increased likelihood of needing instrumental delivery or a cesarean section. The prolonged labor process can also cause psychological distress and lead to postpartum depression or anxiety.
Fetal risks associated with abnormal labor include a higher chance of fetal distress, meconium aspiration syndrome, birth injuries due to instrumental delivery, or difficulties adapting to the stress of labor. The severity of these risks depends on the specific circumstances surrounding the abnormal labor.
Psychological Impact Of Abnormal Labor
Experiencing abnormal labor can have a profound psychological impact on women. The unexpected challenges, pain, and feelings of loss of control can lead to increased anxiety, fear, and disappointment. Postpartum depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can also be consequences of a difficult labor experience.
Recognizing and addressing the psychological impact of abnormal labor is crucial for the well-being of the mother. Supportive counseling, access to mental health resources, and appropriate follow-up care can help women cope with their emotions and adjust to their new role as mothers.
– Supportive counseling
– Access to mental health resources
– Appropriate follow-up care
Role Of Healthcare Providers In Abnormal Labor
Healthcare providers play a vital role in the management of abnormal labor. Their expertise, knowledge, and ability to recognize signs of abnormal labor are crucial for early intervention and prevention of complications. Prompt and effective decision-making, clear communication with the woman and her support team, and continuous monitoring of both the mother and the baby contribute to safe and successful outcomes.
Healthcare providers must provide appropriate emotional support and be sensitive to the psychological needs of women experiencing abnormal labor. Empathy, compassion, and understanding can help alleviate anxiety and build trust between the woman and the healthcare team.
Abnormal labor is a complex condition that can arise from various factors and pose risks to both the mother and the baby. Early recognition, prompt intervention, and a collaborative approach between healthcare providers and the laboring woman are essential for effective management. By understanding the causes, signs, and complications of abnormal labor, healthcare providers can provide the necessary support and medical interventions to ensure the best possible outcomes.
💡
You may need to know these questions about abnormal labor
What is abnormal labor?
Abnormal labor refers to a deviation from the normal progression of childbirth in any stage, whether it be the second or third stage. This can manifest as a prolonged, protracted, or arrested labor, indicating a delay or difficulty in the delivery of the fetus or placenta. It is important to promptly identify and manage abnormal labor to ensure the safety and well-being of both the mother and the baby. Complications arising from abnormal labor may require medical intervention, such as assisted delivery or cesarean section, to ensure a successful outcome for mother and child.
What are the examples of abnormal labor?
Abnormal labor can manifest in various ways, including a prolonged latent phase where the early phase of labor extends beyond the expected duration. Another example is a protracted active phase dilation, wherein the cervix takes longer than normal to dilate. Additionally, secondary arrest of dilation can occur, which refers to the halt in cervical dilation after previously progressing adequately. Another abnormal pattern is a prolonged deceleration phase, where there is a delay in the descent of the fetal head. Moreover, protracted descent occurs when the baby takes an extended period to descend into the pelvis. Lastly, an arrest of descent happens when the baby fails to progress through the birth canal despite sufficient contractions and pushing efforts.
How is abnormal labor diagnosed?
Abnormal labor can be diagnosed through the use of a labor curve, which plots the patient’s labor progress in terms of cervical dilation versus duration in hours. By comparing the patient’s labor curve to established norms, healthcare providers can identify deviations that may indicate abnormal labor. Additionally, other diagnostic tools such as fetal monitoring and pelvic examinations may be employed to further evaluate the progress and potential complications during labor. Overall, the use of a labor curve provides a valuable visual representation for healthcare professionals to assess abnormal labor and make informed decisions regarding intervention or further medical management when necessary.
What is the medical term for abnormal labor or childbirth?
The medical term for abnormal labor or childbirth is “dystocia.” Dystocia refers to the difficult or prolonged labor and delivery that may result from various factors such as inadequate contractions, fetal malposition, or maternal pelvic abnormalities. Aiming to reduce the number of cesarean deliveries, organizations like ACOG and SMFM have highlighted the importance of identifying and addressing labor dystocia to promote safer and more successful births. Through their joint consensus statement, they seek to prevent unnecessary interventions and ensure optimal maternal and fetal outcomes.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459260/
https://www.glowm.com/section-view/heading/Abnormal%20Labor:%20Diagnosis%20and%20Management/item/132
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/273053-workup
https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/products/labor-dystocia/research-protocol