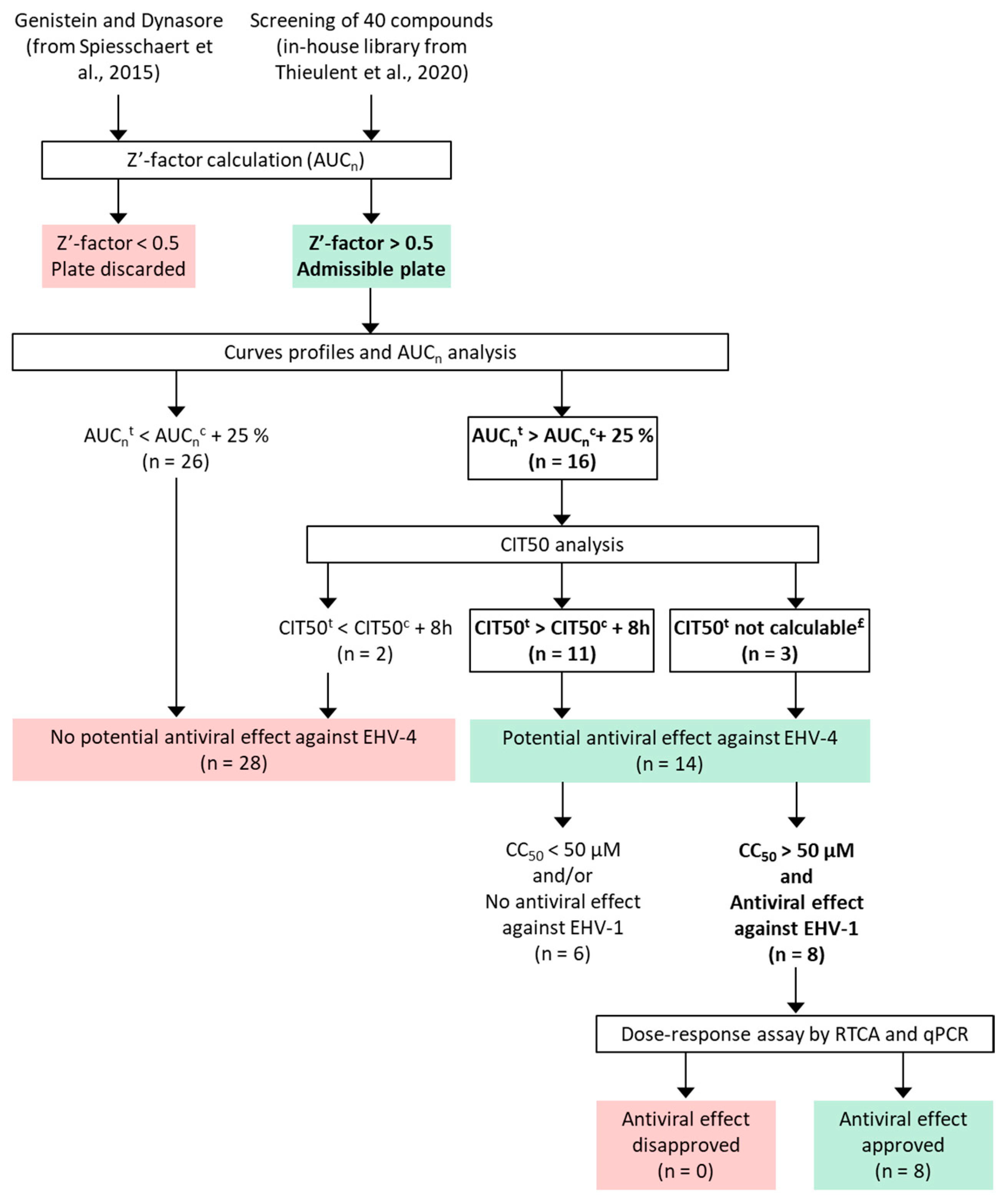
From the moment of conception, the journey of life begins for a tiny, vulnerable embryo.
But in the vast tapestry of existence, there are hidden dangers lurking, known as abortigenic substances.
These insidious culprits have the power to derail the miracle of life itself, jeopardizing both the expectant mother and the precious new life growing within.
In this gripping exploration, we delve into the mysterious world of abortigenic phenomena, shedding light on the risks that haunt expecting parents.
Brace yourself to uncover the truth and embark on a compelling quest for understanding, as we unravel the enigma of abortigenic substances.
abortigenic
“Abortigenic” refers to substances or factors that have the ability to induce abortion or terminate pregnancy.
It can include substances like abortifacients, which are drugs or agents that induce premature expulsion of the fetus, or teratogens, which are substances that cause birth defects or abnormal development of the embryo.
Abortigenic factors pose a risk of miscarriage or harm to the developing fetus, and are considered contraindicated in pregnancy due to their adverse effects on reproductive health.
Key Points:
- “Abortigenic” refers to substances or factors that induce abortion or terminate pregnancy.
- Abortifacients are drugs or agents that induce premature expulsion of the fetus.
- Teratogens are substances that cause birth defects or abnormal development of the embryo.
- Abortigenic factors pose a risk of miscarriage or harm to the developing fetus.
- Abortigenic substances are considered contraindicated in pregnancy.
- Abortigenic substances have adverse effects on reproductive health.
abortigenic – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Abortigenic substances refer to certain medications, chemicals, or environmental factors that can cause the termination or miscarriage of a pregnancy.
2. One little-known abortigenic substance is a plant called Pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium), which has been historically used as a traditional herbal remedy to induce abortion.
3. The pharmaceutical drug Misoprostol, originally developed to prevent stomach ulcers, is also an abortigenic substance and is commonly used in some countries for medical abortions.
4. Certain species of spiders produce abortigenic venom, which can induce fetal resorption (the loss of an unborn animal) in some animals.
5. Exposure to high levels of radiation, such as that from a nuclear disaster or certain medical procedures, can potentially have abortigenic effects on pregnant women.
Abortifacient Effects
When discussing pregnancy, it is important to familiarize oneself with the term “abortigenic,” which pertains to substances capable of causing abortion or ending a pregnancy. A specific group of such substances is known as abortifacients. Abortifacients, whether in the form of drugs or natural compounds, are capable of stimulating contractions in the uterus, ultimately resulting in the expulsion of the fetus. It is crucial to emphasize that the use of abortifacients must be closely monitored and regulated by medical professionals. Misuse or incorrect dosage can expose pregnant women to serious health hazards.
- Abortigenic substances are substances that induce abortion or terminate a pregnancy.
- Abortifacients are drugs or natural compounds that can cause uterine contractions, leading to the expulsion of the fetus.
- The use of abortifacients should be strictly regulated and controlled under medical supervision to avoid health risks to the pregnant woman.
“The use of abortifacients should be strictly regulated and controlled under medical supervision, as misuse or incorrect dosage can pose severe health risks to the pregnant woman.”
Teratogenic Risks
Teratogens are substances or agents that can cause malformations or abnormalities in the developing fetus. While abortifacients specifically focus on terminating the pregnancy, teratogens can have detrimental effects on the fetus if exposure occurs during certain stages of development. Teratogenic substances can include medications, chemicals, infections, or even environmental factors. It is essential for pregnant individuals to be aware of these risks and consult with healthcare professionals to avoid exposure to teratogenic agents.
Embryotoxicity Factors
Another aspect of abortigenic substances is their potential to be embryotoxic, which means they can harm or disrupt the growth and development of the embryo. Embryotoxic agents can interfere with essential processes such as cell division, differentiation, and organ formation, leading to the loss of pregnancy or congenital anomalies.
It is crucial for individuals planning or currently undergoing pregnancy to be cautious about exposure to any substances that have the potential to cause embryotoxicity.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Embryotoxic substances can harm the growth and development of the embryo.
- They can interfere with important processes like cell division and organ formation.
- Exposure to these substances can result in the loss of pregnancy or the development of congenital anomalies.
- Individuals planning or undergoing pregnancy should be cautious about their exposure to substances that may be embryotoxic.
“It is crucial for individuals planning or currently undergoing pregnancy to be cautious about exposure to any substances that have the potential to cause embryotoxicity.”
Understanding Pregnancy Termination
Pregnancy termination, whether induced or spontaneous, refers to the ending of a pregnancy before the fetus becomes viable.
-
Induced pregnancy termination involves the deliberate use of medical procedures, medications, or surgical interventions to end the pregnancy.
-
In contrast, spontaneous pregnancy termination, commonly known as miscarriage, occurs naturally due to various factors, including genetic abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, or maternal health conditions.
It is vital for individuals considering or experiencing pregnancy termination to seek medical guidance and support.
Unveiling The Risk Of Miscarriage
Miscarriage is a common occurrence and refers to the spontaneous termination of a pregnancy. There are several factors that contribute to the risk of miscarriage:
- Advanced maternal age: The risk of miscarriage increases as a woman gets older. Women above 35 years of age have a higher risk compared to younger women.
- Chromosomal abnormalities: Most miscarriages occur due to chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. These abnormalities commonly happen by chance during the formation of reproductive cells or early development.
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), diabetes, thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and uterine abnormalities can increase the risk of miscarriage.
- Exposure to environmental toxins: Chemicals, radiation, and certain medications can have harmful effects on pregnancy and increase the risk of miscarriage.
While some risk factors are beyond an individual’s control, there are measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of miscarriage:
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to a healthy pregnancy.
- Regular prenatal care: Seeking regular prenatal check-ups and following medical advice can help detect and manage any potential risk factors early on.
- Avoiding teratogenic or abortigenic agents: It is important to avoid exposure to substances known to be harmful during pregnancy. These include certain medications, recreational drugs, and toxic substances.
In conclusion, while the risk of miscarriage cannot be eliminated entirely, adopting a healthy lifestyle, seeking regular prenatal care, and being aware of potential harmful agents can help reduce the risk and promote a healthier pregnancy.
“A healthy lifestyle, regular prenatal care, and avoiding known teratogenic or abortigenic agents may help reduce the risk of miscarriage.”
Potential Fetal Harm
Exposure to abortigenic or teratogenic substances can lead to potential fetal harm. Fetal harm refers to any damage or adverse effects on the developing fetus, including physical abnormalities, cognitive impairments, or developmental delays. Pregnant individuals must be aware of potential hazards and take necessary precautions to safeguard the health and well-being of their unborn child.
Some important points to remember:
- Exposure to abortigenic or teratogenic substances can be harmful to the fetus.
- Fetal harm can manifest as physical abnormalities, cognitive impairments, or developmental delays.
- Pregnant individuals need to be informed and take necessary precautions to protect their unborn child from potential hazards.
Examining Reproductive Toxicity
Reproductive toxicity is the term used to describe the harmful effects certain substances can have on reproductive health. This includes impacts on fertility, pregnancy, and fetal development. It is important to note that substances with reproductive toxicity can lead to abortifacient, teratogenic, or embryotoxic effects.
Such effects are risky not only for the pregnant individual but also for the developing child. Therefore, it is crucial to understand and address reproductive toxicity to safeguard reproductive health and promote healthy pregnancies.
Some key points to consider about reproductive toxicity:
- It refers to the harmful effects substances can have on reproductive health.
- It encompasses impacts on fertility, pregnancy, and fetal development.
- Substances with reproductive toxicity can have abortifacient, teratogenic, or embryotoxic effects.
- Reproductive toxicity poses risks to both the pregnant individual and the unborn child.
“Understanding and mitigating reproductive toxicity is paramount to protect reproductive health and ensure healthy pregnancies.”
Contraindication In Pregnancy
Due to the potential risks associated with abortigenic substances, many medications, chemicals, or procedures are contraindicated during pregnancy. Contraindication means that the use of certain substances or procedures is strongly advised against during pregnancy to avoid harm to the fetus. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to have comprehensive knowledge of abortigenic substances and their contraindications to provide accurate guidance and protect the health of pregnant individuals.
Adverse Effects On Pregnancy
Exposure to abortigenic substances can have various adverse effects on pregnancy. These effects can range from an increased risk of pregnancy complications, such as preterm birth or low birth weight, to serious health risks for the pregnant individual, including maternal mortality or severe morbidity.
Understanding and minimizing exposure to abortigenic substances is essential to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Improvements:
- Use markdown bold to highlight important information
- Clarify the term “abortigenic substances”
- Emphasize the range of adverse effects on pregnancy
- Mention the seriousness of health risks
- Highlight the need to understand and minimize exposure to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy
Exposure to abortigenic substances can have various adverse effects on pregnancy. These effects can range from an increased risk of pregnancy complications, such as preterm birth or low birth weight, to serious health risks for the pregnant individual, including maternal mortality or severe morbidity.
Understanding and minimizing exposure to abortigenic substances is essential to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.
- Increased risk of pregnancy complications
- Serious health risks for the pregnant individual
- Maternal mortality or severe morbidity
“Understanding and minimizing exposure to abortigenic substances is essential to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.”
Abortive Properties Explored
Abortive properties refer to the ability of substances, often natural compounds, to induce abortion or terminate a pregnancy.
These substances may have been historically used for this purpose, but their use in modern medicine is strictly regulated. Caution must be exercised to prevent endangering the health of the pregnant individual.
Exploring the abortive properties of certain substances requires thorough research and scientific understanding to ensure safe, informed choices when considering pregnancy termination options.
Understanding the risks and safety measures associated with abortigenic substances is crucial for individuals planning or experiencing a pregnancy. From abortifacient effects to teratogenic risks, embryotoxicity factors, and the potential for adverse effects, comprehensive knowledge is necessary to make informed decisions regarding pregnancy termination.
This knowledge is also important to safeguard the health and well-being of both the pregnant individual and the developing fetus. Healthcare professionals should remain up-to-date on these matters and provide accurate guidance and support to individuals navigating pregnancy and related challenges.
💡
You may need to know these questions about abortigenic
What does abortigenic mean?
Abortigenic refers to anything that has the potential to induce abortion or cause miscarriage. It is commonly used to describe substances or medications that have abortifacient properties, meaning they can trigger the termination of pregnancy. These substances work by interrupting the normal hormonal processes involved in pregnancy, leading to the expulsion of the developing embryo or fetus. Abortigenic factors can vary, ranging from natural compounds found in certain plants to synthetic drugs specifically designed to induce abortion. While the term abortigenic primarily relates to the medical and pharmaceutical fields, it also encompasses various environmental factors that may pose a risk to pregnancy and result in spontaneous abortion.
1. What are some common abortigenic substances or medications that should be avoided during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, it is crucial to avoid certain substances and medications that have been found to be abortifacients or have potential risks to the developing fetus. Some common abortigenic substances to avoid include alcohol, tobacco, illicit drugs, and excessive caffeine consumption. These substances can increase the risk of miscarriage, premature birth, low birth weight, and developmental issues in the baby.
Certain medications should also be avoided during pregnancy as they can pose risks to the fetus. Examples include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, certain antibiotics, certain acne medications (such as isotretinoin), anticoagulants, and some herbal remedies. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication during pregnancy to ensure its safety for both the mother and the baby.
2. Are there any natural remedies or alternative therapies considered abortigenic that pregnant women should be aware of?
While there are no scientifically proven natural remedies or alternative therapies that are considered abortifacient (capable of inducing abortion) and safe for pregnant women, it is crucial for expectant mothers to be cautious and consult with their healthcare professional before considering any form of treatment. Some herbs, such as black cohosh and tansy, have been associated with potential abortifacient properties and are therefore advised to be avoided during pregnancy. Acupuncture, massage, and certain essential oils may also have the potential to cause contractions or stimulate the uterus, posing risks of complications during pregnancy. To ensure the well-being of both the mother and the unborn child, it is essential to rely on medical advice and avoid experimenting with unproven natural remedies or alternative therapies without professional guidance.
3. Can certain abortigenic factors, such as maternal age or pre-existing health conditions, increase the risk of pregnancy loss?
Yes, certain abortigenic factors can increase the risk of pregnancy loss. Maternal age is one such factor that has been identified as a risk factor for miscarriages. Women who are older, typically above the age of 35, have a higher chance of experiencing miscarriages compared to younger women. This is believed to be due to the increased likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities in eggs as women age.
Similarly, pre-existing health conditions can also increase the risk of pregnancy loss. Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases can interfere with the normal development and functioning of the placenta, leading to complications that can result in miscarriages. It is essential for women with these conditions to receive proper medical management and care to minimize the risk of pregnancy loss.
Reference source
https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/abortogenic
https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/abortigenic
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34600470/
https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/abortigenic