Imagine a secret world hidden within a woman’s body, where the delicate lining of her uterus rebels against its boundaries.
Adenomyosis, a captivating condition, takes center stage, weaving a tale of pain, heavy periods, and an enigmatic swollen uterus.
Join us on an exploration into this disorder and the mysteries it unravels.
adenomyosis
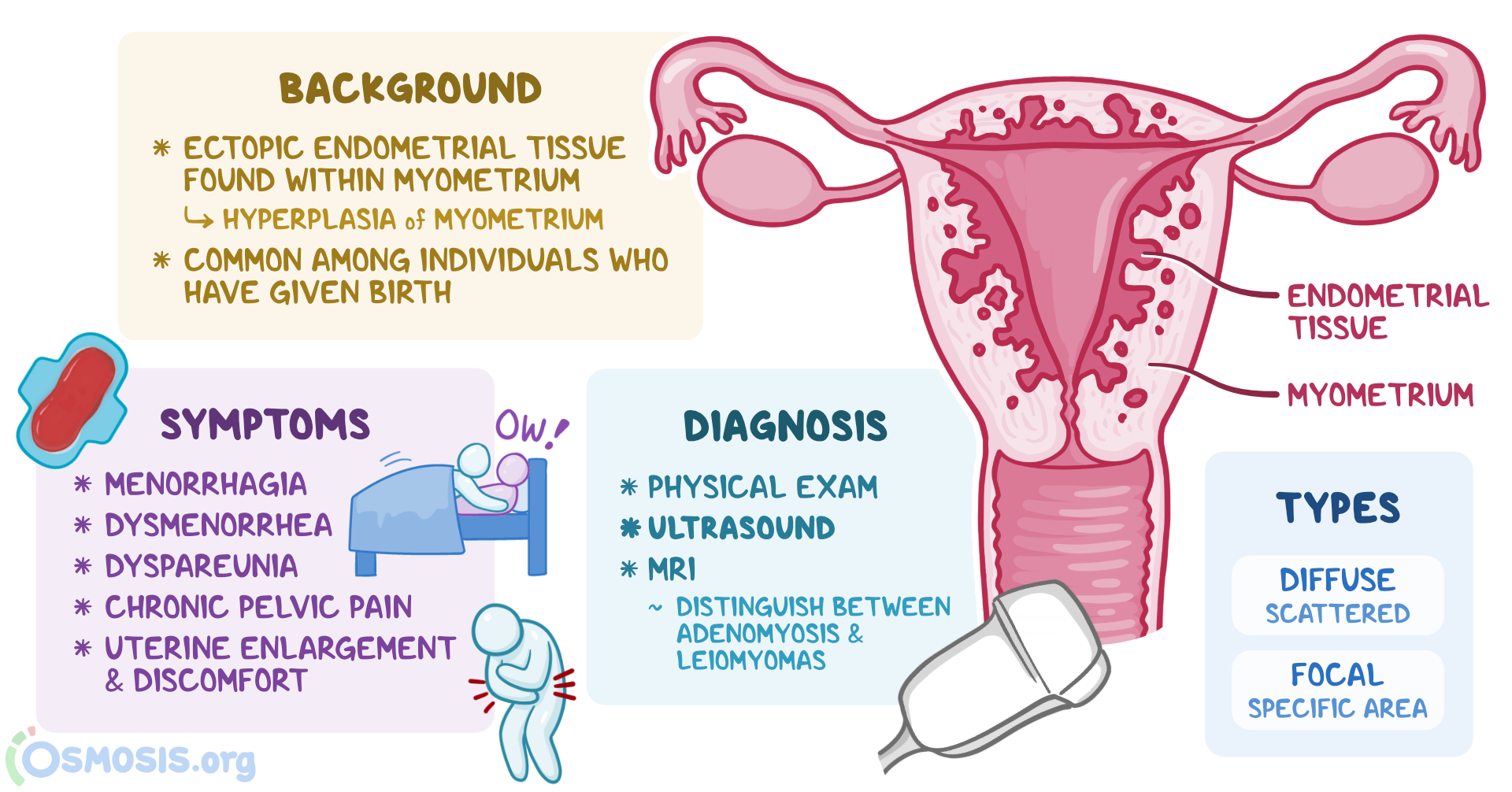
Adenomyosis is a condition in which the tissue that normally lines the uterus, called the endometrium, begins to grow into the muscular wall of the uterus.
This can result in the thickening of the uterine wall and the breaking down of this tissue during menstrual cycles, leading to bleeding.
Adenomyosis often leads to an enlarged uterus, and it is commonly associated with painful and heavy periods.
The exact cause of adenomyosis is unknown, but it typically resolves after menopause.
Hormonal treatments can help manage the symptoms, but in severe cases, a hysterectomy may be necessary for a cure.
Key Points:
- Adenomyosis is a condition where the endometrium grows into the muscular wall of the uterus.
- This can cause the thickening of the uterine wall and bleeding during menstrual cycles.
- Adenomyosis often leads to an enlarged uterus and is associated with painful and heavy periods.
- The exact cause of adenomyosis is unknown, but it usually resolves after menopause.
- Hormonal treatments can help manage symptoms of adenomyosis.
- In severe cases, a hysterectomy may be required for a cure.
adenomyosis – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Adenomyosis is a little known condition that primarily affects women, where the cells that normally line the uterus start growing into the muscular walls of the uterus.
2. Adenomyosis is often misdiagnosed as other conditions such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids, due to similar symptoms like heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and abdominal bloating.
3. Adenomyosis is more commonly found in women who have had children and is thought to be caused by the stretching of the uterus during pregnancy, allowing the endometrial cells to invade the muscular walls.
4. While the exact cause of adenomyosis is unknown, hormonal imbalances, genetics, and inflammation are believed to play a role in its development.
5. Adenomyosis can sometimes cause fertility issues, as the abnormal growth of endometrial cells can interfere with the implantation of an embryo in the uterus. However, many women with adenomyosis still go on to have successful pregnancies with appropriate management and treatment.
Adenomyosis – An Overview
Adenomyosis is a condition that affects the tissue of the uterus, specifically the muscular wall. It is characterized by the thickening of this tissue and its subsequent breaking down during menstrual cycles, leading to bleeding. One of the key indicators of adenomyosis is an enlarged uterus, which can cause painful and heavy periods.
While the exact cause of adenomyosis remains unknown, it is believed to resolve itself after menopause. However, for those who experience severe discomfort, there are hormonal treatments available. In extreme cases, a hysterectomy may be the only option for a cure.
- Adenomyosis affects the tissue of the uterus, particularly the muscular wall.
- It leads to thickening and breaking down of the tissue, resulting in bleeding during menstrual cycles.
- An enlarged uterus is a key indicator of adenomyosis, causing painful and heavy periods.
- The exact cause of adenomyosis is unknown, but it may resolve itself after menopause.
- Hormonal treatments are available to alleviate severe discomfort.
- In extreme cases, a hysterectomy may be necessary for a cure.
“Adenomyosis is a condition characterized by the thickening and breaking down of the tissue of the uterus, leading to bleeding. It is often accompanied by an enlarged uterus and can cause painful and heavy periods. While the exact cause is unknown, it is believed to improve after menopause. Hormonal treatments can help manage symptoms, but in severe cases, a hysterectomy may be necessary.”
Understanding Adenomyosis: Causes and Symptoms
Adenomyosis is a condition that primarily affects women of childbearing age. While the exact cause is still unknown, several theories have been proposed. Some experts believe that it may be caused by the invasion of endometrial cells into the muscular wall of the uterus, while others suggest that it may result from a hormonal imbalance or genetic predisposition.
Regardless of the cause, adenomyosis can lead to a range of symptoms. Painful periods, also known as dysmenorrhea, are a common complaint among individuals with adenomyosis. The pain experienced during menstruation can be severe and often radiates to the lower back and thighs. Heavy menstrual bleeding, known as menorrhagia, is another symptom associated with adenomyosis.
Impact On The Uterus: Thickening And Breaking Down Of Tissue
In adenomyosis, the tissue within the muscular wall of the uterus becomes thickened and starts to break down during each menstrual cycle. This process can result in bleeding, which can be painful and lead to the formation of blood clots. The repeated thickening and breaking down of tissue can cause inflammation, leading to the symptoms associated with adenomyosis.
The presence of adenomyosis can lead to structural changes in the uterus as well. The continuous thickening of the tissue causes the uterus to enlarge, which can be detected through medical imaging techniques such as ultrasound. An enlarged uterus is often an important indicator for diagnosing adenomyosis and differentiating it from other conditions with similar symptoms.
- Adenomyosis is a condition where the tissue within the uterine wall becomes thickened and breaks down during each menstrual cycle.
- This can cause painful bleeding and the formation of blood clots.
- Inflammation may also occur, leading to the symptoms associated with adenomyosis.
- Adenomyosis can also cause structural changes in the uterus, resulting in an enlarged uterus that can be detected through ultrasound.
Adenomyosis: Link To Painful And Heavy Periods
One of the most prominent symptoms of adenomyosis is painful and heavy periods. The invasion of endometrial cells into the muscular wall of the uterus leads to increased uterine contractions during menstruation, resulting in intense pain. This pain can also radiate to other areas of the body, causing further discomfort.
Additionally, the thickened tissue and the increased vascularity of the uterus can lead to heavy bleeding during periods. Women with adenomyosis often experience prolonged bleeding and the passing of blood clots. The combination of painful and heavy periods can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and may require medical intervention to manage.
Enlarged Uterus: A Key Indicator of Adenomyosis
One of the key indications of adenomyosis is an enlarged uterus. During the menstrual cycle, the excess endometrial tissue causes the uterus to expand and become larger than normal. This enlargement can often be detected during a physical examination or through imaging studies such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
An enlarged uterus, in combination with other symptoms such as painful and heavy periods, can help doctors differentiate adenomyosis from other conditions such as uterine fibroids or endometriosis. It is essential to accurately diagnose adenomyosis to determine the most appropriate treatment options.
- Key feature: enlarged uterus
- Diagnosis methods: physical examination, ultrasound, and MRI
- Differentiation from other conditions: presence of painful and heavy periods
It is important to accurately diagnose adenomyosis in order to determine the most suitable treatment options.
Mysterious Origins: Adenomyosis and Its Unknown Cause
Despite significant progress in medical research, the exact cause of adenomyosis remains unknown. Several theories have been proposed, but none have been definitively proven. It is believed that a combination of factors, such as hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, and invasive endometrial cells, may contribute to the development of adenomyosis.
- Further research is needed to unravel the mysteries surrounding adenomyosis and to discover its precise origins.
- Understanding the cause of this condition is crucial for the development of more effective preventive measures and targeted treatment options.
It is important to note that adenomyosis is a complex condition with multifactorial causes, and ongoing research is essential to expand our understanding and improve patient outcomes.
Adenomyosis and Menopause: Resolving the Condition
Fortunately, adenomyosis often resolves itself after menopause as hormone levels naturally decline. This leads to an improvement or complete disappearance of the associated symptoms such as pain and heavy bleeding.
For women nearing menopause who still experience severe symptoms, hormonal treatments may be an effective option. These treatments aim to regulate hormone imbalances and reduce the thickening of uterine tissue. By managing symptoms, hormonal therapy can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with adenomyosis.
Hormonal Treatments for Adenomyosis: A Viable Option
Hormonal treatments are commonly used in the management of adenomyosis. These treatments aim to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce the thickening and breaking down of tissue within the uterus. The most commonly used hormonal therapies include oral contraceptive pills, progestogen-only therapies, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists.
Oral contraceptive pills and progestogen-only therapies work by altering hormone levels and preventing the growth of uterine tissue. GnRH agonists, on the other hand, temporarily suppress the production of certain hormones, leading to a reduction in symptoms.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of hormonal treatments may vary from person to person. Individualized treatment plans, in consultation with a healthcare professional, will help determine the most suitable options for each individual.
Debilitating Discomfort: Adenomyosis and Severe Symptoms
Some individuals with adenomyosis may experience mild to moderate symptoms, while others may suffer from severe discomfort. The pain and heavy bleeding associated with adenomyosis can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Severe symptoms may require more aggressive treatment options.
For individuals who do not respond to hormonal therapies or other conservative treatments, more invasive procedures may be considered. These can include endometrial ablation, which involves the removal of the uterine lining, or myomectomy, which aims to remove the adenomyosis-affected tissue while preserving the uterus. In extreme cases, when all other options have been exhausted, a hysterectomy may be recommended as a last resort for a cure.
- Adenomyosis symptoms can range from mild to severe
- Pain and heavy bleeding are common symptoms
- Conservative treatments may not work for everyone
- Endometrial ablation and myomectomy are invasive procedures
- Hysterectomy is considered a last resort option.
Hysterectomy: A Last Resort for Adenomyosis Cure
A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and, in some cases, the cervix. For individuals with severe and debilitating symptoms of adenomyosis, a hysterectomy may be the only option for a cure. This procedure effectively eliminates the source of the condition, resolving the pain and heavy bleeding associated with adenomyosis.
However, a hysterectomy is a major surgical procedure that should not be taken lightly. It is irreversible and has implications for future fertility. Therefore, it should only be considered after careful discussion with a healthcare professional and consideration of other treatment options.
In conclusion, adenomyosis is a complex condition that affects the tissue of the uterus, leading to symptoms such as painful and heavy periods. While the exact cause remains unknown, several treatment options are available, ranging from hormonal therapies to more invasive interventions. For those with severe symptoms, a hysterectomy may be recommended as a last resort for a cure. It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms of adenomyosis to consult with their healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their individual needs and circumstances.
💡
You may need to know these questions about adenomyosis
Is adenomyosis a serious problem?
Adenomyosis, though typically not considered a serious problem, can still have significant implications for individuals affected by it. While it may not lead to life-threatening complications, it can contribute to challenges conceiving or increase the risk of miscarriage. Moreover, the symptoms associated with adenomyosis can considerably disrupt one’s daily life, underscoring the importance of appropriate management and support for those affected.
What triggers adenomyosis?
The exact triggers of adenomyosis remain uncertain, yet evidence indicates that prolonged exposure to estrogen plays a significant role. Factors such as shorter-than-average menstrual cycles or multiple pregnancies may expose women to higher levels of estrogen, potentially contributing to the development of adenomyosis. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, these hormonal factors are believed to play a role in triggering this uterine condition.
What does adenomyosis lead to?
Adenomyosis, characterized by thickened uterine walls and distorted blood vessels, tends to result in significant symptoms for those affected. Primarily, individuals with this condition often experience heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding, accompanied by intense pain. Moreover, adenomyosis contributes to discomfort during sexual intercourse and can be associated with infertility.
Is adenomyosis as bad as endometriosis?
While both adenomyosis and endometriosis can cause similar symptoms such as pelvic pain and abnormal menstrual bleeding, the severity of the conditions may vary from person to person. Adenomyosis specifically involves the abnormal growth of uterine tissue into the uterine muscle, which can cause significant discomfort. On the other hand, endometriosis refers to the growth of uterine tissue outside the uterus, potentially impacting other organs as well. Given that individuals can have both conditions simultaneously, the experience and impact of each condition may differ for each person.
Reference source
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/adenomyosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20369138
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14167-adenomyosis
https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/uterine-adenomyosis
https://www.healthline.com/health/adenomyosis