In the intricate world of childbirth, there is a fascinating condition that occasionally arises – the adherent placenta.
This mysterious and intricate phenomenon captivates medical professionals and expectant parents alike.
As we delve into the complexities of this condition, prepare to uncover the intriguing secrets hidden within the realm of childbirth complications.
adherent placenta
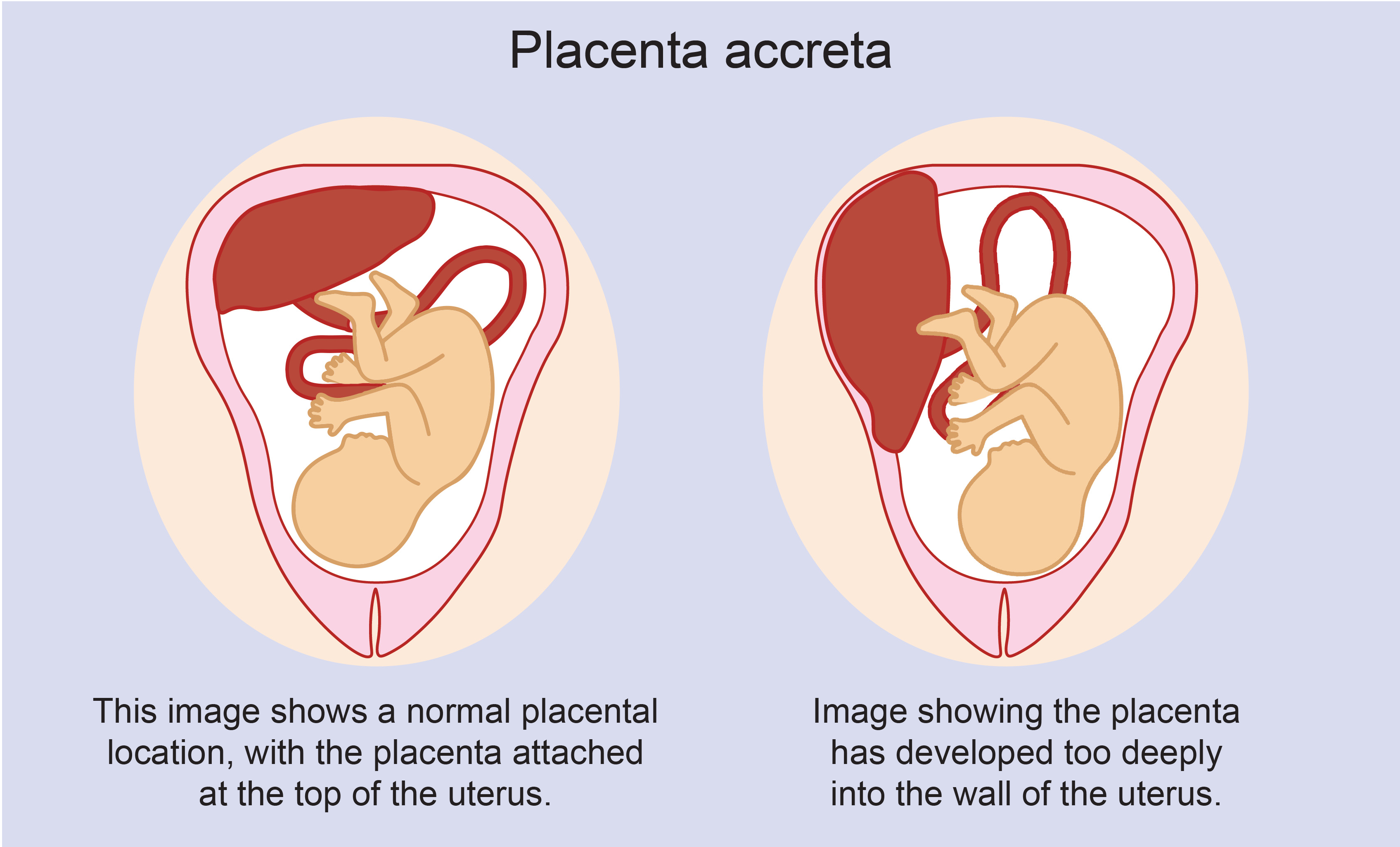
An adherent placenta refers to a condition where the placenta, specifically the chorionic villi, becomes deeply embedded and firmly attached to the uterine wall, making it difficult to separate during childbirth.
This condition, also known as placenta accreta, can lead to severe complications and increased risks for the mother, including excessive bleeding and the need for a hysterectomy.
Key Points:
- Adherent placenta refers to the attachment of the placenta to the uterine wall, making it hard to remove during childbirth.
- This condition is also known as placenta accreta.
- Adherent placenta can result in severe complications for the mother.
- Complications include excessive bleeding.
- A hysterectomy may be necessary to treat adherent placenta.
- Adherent placenta increases the risks involved in childbirth.
adherent placenta – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The adherent placenta is a rare condition that occurs when the placenta attaches too deeply into the uterine wall and is difficult to separate during delivery.
2. In some cases, an adherent placenta can lead to a condition called placenta accreta, where the placenta becomes abnormally attached to the uterine muscle, increasing the risk of severe bleeding during childbirth.
3. The risk factors associated with an adherent placenta include a history of previous cesarean deliveries, advanced maternal age, and certain uterine abnormalities.
4. An adherent placenta may require surgical intervention, such as a cesarean hysterectomy, to safely remove the placenta and avoid complications.
5. Despite advancements in medical technology, an adherent placenta remains a serious and challenging condition, often requiring a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Definition Of Adherent Placenta
Adherent placenta, also known as placenta accreta, is a serious medical condition that occurs during pregnancy when the placenta attaches too deeply into the uterine wall, making it difficult to detach during delivery.
In a typical pregnancy, the placenta naturally separates from the uterine wall after the baby is born. However, in the case of an adherent placenta, the placenta is tightly attached, and its removal can result in severe bleeding and other complications.
This condition is rare, occurring in approximately 1 in every 2,500 pregnancies, but its potential risks make it important to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Causes Of Adherent Placenta
The exact cause of adherent placenta is not yet fully understood, but several factors increase the risk of developing this condition.
Some common risk factors for adherent placenta include:
-
Previous uterine surgery, such as a cesarean section or the removal of fibroids. These procedures can leave scar tissue on the uterine wall, making it more difficult for the placenta to properly attach and detach.
-
Advanced maternal age.
-
Multiple pregnancies (such as twins or triplets).
-
A history of adherent placenta in previous pregnancies.
Identifying these risk factors early on is crucial for healthcare providers to provide appropriate monitoring and care throughout the pregnancy.
Blockquote: “It is important for healthcare providers to identify these risk factors early on to provide appropriate monitoring and care throughout the pregnancy.”
–
Signs And Symptoms Of Adherent Placenta
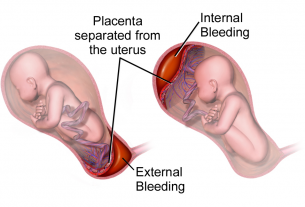
Adherent placenta, also known as placenta accreta, is a condition that may not exhibit noticeable symptoms during pregnancy. However, certain women may encounter abnormal bleeding throughout their pregnancy, specifically in the third trimester. In severe instances, there can be sudden and heavy bleeding during labor or delivery. Additional symptoms may comprise of pelvic pain, tender uterus, and an enlarged uterus that is not proportionate to the gestational age. Pregnant individuals must communicate any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider to guarantee early detection and appropriate management of this condition.
Diagnosis Of Adherent Placenta
Diagnosing adherent placenta can be challenging, as it does not always present obvious symptoms. However, healthcare providers may use various tests and imaging techniques to confirm this condition. These may include:
- Ultrasound scans
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Doppler flow studies
These diagnostic tools help visualize the position and attachment of the placenta, allowing healthcare providers to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the best course of action.
It is important to note that early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Complications Associated With Adherent Placenta
Adherent placenta is a condition that carries significant risks for both the mother and the baby. Severe bleeding during childbirth is one of the most worrisome complications, and it can become life-threatening if not promptly addressed. In some severe cases, this can necessitate blood transfusions, hysterectomy, or even lead to maternal death. Moreover, an adherent placenta raises the likelihood of other complications, including preterm birth, infections, and respiratory distress for the baby. These potential complications underscore the vital need for early diagnosis and proper management of this condition.
- Severe bleeding during childbirth is a major concern with adherent placenta
- Prompt management is essential to prevent life-threatening situations
- Possible interventions include blood transfusions and hysterectomy
- Adherent placenta increases the risk of preterm birth and infections
- The baby may experience respiratory distress due to this condition
“The potential complications emphasize the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate management of this condition.“
Treatment Options For Adherent Placenta
The treatment of adherent placenta depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition and the overall health of the mother and baby.
In some cases, a planned cesarean section may be recommended to minimize the risk of bleeding during delivery.
Before the birth, a multidisciplinary team, including obstetricians, radiologists, and anesthesiologists, may be involved to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
During delivery, specialized techniques may be employed, such as controlled cord traction or manual removal of the placenta, while closely monitoring for any signs of excessive bleeding.
In severe cases, a hysterectomy may be required to stop the bleeding and ensure the mother’s safety.
- Planned cesarean section to minimize bleeding risk
- Involvement of multidisciplinary team for comprehensive treatment plan
- Specialized techniques during delivery
- Hysterectomy in severe cases
“The treatment of adherent placenta requires a multidisciplinary approach to ensure the safety of both the mother and baby.”
Prevention Of Adherent Placenta
While it is not always possible to prevent adherent placenta, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk.
- Avoiding unnecessary uterine surgeries, particularly those that involve the removal of fibroids, can minimize the chances of developing this condition.
- Adequate prenatal care is crucial in identifying potential risk factors early on, allowing healthcare providers to closely monitor the pregnancy and take appropriate action if needed.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and regular exercise, may also contribute to a lower risk of developing placenta accreta.
Recovery And Prognosis For Adherent Placenta
The recovery process from adherent placenta can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the treatment options chosen.
- For some individuals, the recovery may be relatively straightforward, with no long-term complications.
- In more severe cases, however, the recovery process may be more challenging and require ongoing medical care and monitoring.
- Emotional support is also crucial during this time, as individuals may experience a range of emotions after going through such a difficult and potentially life-threatening experience.
- It is important for individuals to follow up with their healthcare providers regularly to ensure their overall well-being.
Support And Resources For Those With Adherent Placenta
Dealing with an adherent placenta can be overwhelming, and individuals may benefit from connecting with support groups or seeking professional counseling to help cope with the emotional aspects of the condition. Healthcare providers, such as obstetricians and midwives, can provide information and resources related to adherent placenta and offer guidance throughout the recovery process. Online platforms and forums may also serve as a valuable source of support and allow individuals to connect with others who have had similar experiences.
- Connecting with support groups or seeking professional counseling can help cope with the emotional aspects of an adherent placenta.
- Healthcare providers, such as obstetricians and midwives, can provide information and resources related to the condition.
- Online platforms and forums can serve as valuable sources of support and connection with others facing similar experiences.
“Dealing with an adherent placenta can be overwhelming… individuals may benefit from connecting with support groups or seeking professional counseling to help cope with the emotional aspects of the condition.”
Research And Advancements In Understanding Adherent Placenta
Researchers and medical experts are actively investigating adherent placenta to enhance prevention, diagnosis, and treatment options. Recent advancements in medical imaging technology, including three-dimensional ultrasound and MRI, have significantly improved the accuracy and early detection of this condition. Ongoing research endeavors aim to deepen our comprehension of the root causes and risk factors associated with adherent placenta. Moreover, medical professionals are dedicated to developing safer and more effective treatment techniques that reduce complications and optimize outcomes for both mothers and babies affected by this condition.
💡
You may need to know these questions about adherent placenta
What is an adherent placenta?
An adherent placenta is a condition in which the placenta remains attached to the uterine wall due to abnormal implantation. This can result in severe complications such as excessive bleeding, organ failure, and the need for emergency measures like blood transfusion or hysterectomy. In some cases, it can even be life-threatening.
What causes adherent placenta?
Adherent placenta, also known as placenta accreta, is primarily caused by the abnormal growth of the placenta into the uterine wall during pregnancy. This condition is more likely to occur when there is scarring in the uterus due to previous C-sections or other uterine surgeries. The scarring can disrupt the normal process of placental attachment, leading to the placenta becoming firmly attached to the uterine wall. This increases the risk of complications during delivery and may require medical intervention to safely remove the placenta after birth.
How do you treat adherent placenta?
The treatment for adherent placenta typically involves a multidisciplinary approach to minimize potential complications. After diagnosing placenta accreta during pregnancy or delivery, pregnancy care providers may opt for an early C-section and follow it with a hysterectomy. This procedure reduces the risk of severe complications by removing the uterus. Depending on the severity and individual circumstances, additional treatments like blood transfusions may be necessary to address any potential complications. Careful planning and collaboration between medical professionals are crucial in effectively managing adherent placenta.
What is the survival rate of morbidly adherent placenta?
The survival rate of individuals with morbidly adherent placenta can vary depending on various factors. Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) itself is a critical condition with a mortality rate that can reach up to 7%. However, it is essential to note that survival rates can be improved through timely and proper medical interventions, such as early detection, specialized surgical techniques, and access to adequate healthcare resources. While specific survival rates may vary, prompt diagnosis and appropriate management are key factors in enhancing the chances of survival for patients with morbidly adherent placenta.
Reference source
https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/uog.17417
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/placenta-accreta/symptoms-causes/syc-20376431
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17846-placenta-accreta
https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/aogs.14163