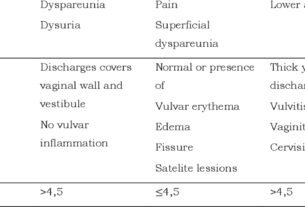
In the realm of women’s health, there exists a mysterious condition that some may have heard of but few truly understand – amenorrhea.
The absence of menstrual periods can be a perplexing and concerning occurrence, warranting a deeper delve into its intricacies.
Unlock the gate to knowledge as we explore a collection of terms surrounding this enigmatic issue, from the complexities of hormones to the potential remedies found within medical procedures.
Prepare to embark on a journey that will unravel the secrets of amenorrhea.
amenorrrhea
Amenorrhea refers to the absence of menstrual periods.
It can be caused by various factors, such as hormonal imbalances, pregnancy, breastfeeding, certain medications, excessive exercise, stress, or medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome or primary ovarian insufficiency.
Diagnosis of amenorrhea involves a thorough evaluation of medical history, physical examination, and possibly hormone testing.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve lifestyle changes, hormonal therapy, or surgical intervention.
It is important to consult with an obstetrician-gynecologist for proper diagnosis and management of amenorrhea.
Key Points:
- Amenorrhea is the absence of menstrual periods.
- Causes of amenorrhea include hormonal imbalances, pregnancy, breastfeeding, medications, excessive exercise, stress, and certain medical conditions.
- Diagnosis involves evaluating medical history, physical examination, and possible hormone testing.
- Treatment varies depending on the underlying cause and may involve lifestyle changes, hormonal therapy, or surgery.
- Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
- Amenorrhea can be managed through hormonal therapy, surgical intervention, or lifestyle changes.
amenorrrhea – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Amenorrhea, the absence of menstrual periods, can occur as a result of excessive physical exertion, such as intense exercise or participating in endurance sports.
2. Prolonged amenorrhea can lead to a decrease in bone density, putting individuals at a higher risk for osteoporosis.
3. Certain medications, such as antidepressants and antipsychotics, can cause amenorrhea as a side effect.
4. Amenorrhea can occur in individuals with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age.
5. Stress and certain psychological conditions, such as eating disorders like anorexia nervosa, can also cause amenorrhea by disrupting the hormonal balance in the body.
Amenorrhea Explained: The Absence Of Menstrual Periods
Amenorrhea, defined as the absence of menstrual periods, is a condition that affects many women worldwide. It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options for this condition.
Amenorrhea can occur for various reasons, including hormonal imbalances, certain medical conditions, and lifestyle factors.
There are two types of amenorrhea: primary and secondary. Primary amenorrhea refers to the absence of menstrual periods in a woman who has never had a period by the age of 16. Secondary amenorrhea, on the other hand, occurs when a woman who has previously had normal periods stops menstruating for three or more consecutive months.
There can be several causes of amenorrhea, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hormonal imbalances, hypothalamic dysfunction, thyroid disorders, excessive exercise, and stress. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment approach.
Symptoms of amenorrhea may also include other signs of hormonal imbalance, such as acne, weight gain or loss, breast discharge, and changes in libido. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience amenorrhea or any concerning symptoms.
- Hormonal imbalances
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Hypothalamic dysfunction
- Thyroid disorders
- Excessive exercise
- Stress
“It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience amenorrhea or any concerning symptoms.”
Understanding Androgen Insensitivity: The Condition That Causes Physical Traits Of A Woman But Male Sex Chromosomes
Androgen insensitivity is a genetic condition in which a person has physical traits of a woman but male sex chromosomes. This condition occurs when the body is unable to respond to certain male hormones, called androgens.
Individuals with androgen insensitivity typically have external genitalia that appear female at birth. However, internally, they possess undescended testes instead of ovaries. This condition is caused by a mutation in the androgen receptor gene, which is responsible for the body’s response to androgens.
The severity of androgen insensitivity can vary. Some individuals may have complete androgen insensitivity, where the body is completely unresponsive to androgens, while others may have partial androgen insensitivity, where the body’s response is partially impaired.
Androgen insensitivity does not typically cause amenorrhea, as individuals with this condition do not have a uterus. However, understanding this condition is vital in comprehending the complexities of reproductive health and hormonal imbalances that can lead to amenorrhea.
- Androgen insensitivity is a genetic condition
- Inability to respond to male hormones
- External genitalia appear female
- Internal presence of undescended testes
- Caused by a mutation in the androgen receptor gene
- Varying severity: complete androgen insensitivity and partial androgen insensitivity.
Anorexia Nervosa: The Severe Eating Disorder That Leads To Food Restriction And Weight Loss
Anorexia nervosa is a severe eating disorder characterized by a distorted body image and an intense fear of gaining weight. People with anorexia nervosa often engage in extreme food restriction, leading to significant weight loss. This can have a profound impact on their overall health, including reproductive health and the occurrence of amenorrhea.
The hormonal disruption caused by anorexia nervosa can result in amenorrhea, as the body tries to conserve energy and prioritize vital functions. The lack of proper nutrition and low body weight can lead to hormonal imbalances, specifically affecting the menstrual cycle.
The Role Of Estrogen: The Female Hormone Produced In The Ovaries
Estrogen is a vital hormone produced in the ovaries that plays a significant role in regulating the menstrual cycle and reproductive health. It is responsible for the growth and development of the female reproductive organs, as well as the secondary sexual characteristics that distinguish women from men.
In terms of the menstrual cycle, estrogen is primarily responsible for the thickening of the uterine lining in preparation for possible pregnancy. It also plays a crucial role in the release of an egg from the ovary during ovulation.
Fluctuating estrogen levels can impact the regularity of menstrual periods throughout a woman’s life. Imbalances in estrogen levels can lead to amenorrhea, causing disruptions in the menstrual cycle and potentially affecting fertility.
- Estrogen is a vital hormone produced in the ovaries.
- It regulates the menstrual cycle and reproductive health.
- Estrogen is responsible for the growth and development of female reproductive organs.
- It also influences secondary sexual characteristics in women.
- Estrogen thickens the uterine lining for possible pregnancy.
- It plays a crucial role in the release of an egg during ovulation.
- Fluctuating estrogen levels can affect menstrual regularity.
- Imbalances in estrogen levels can cause amenorrhea.
- Amenorrhea disrupts the menstrual cycle and affects fertility.
“Estrogen is a vital hormone that regulates the menstrual cycle and reproductive health.”
Exploring Hormone Therapy: Treatment For Relieving Menopausal Symptoms
Hormone therapy, also known as hormone replacement therapy (HRT), is a common treatment option for menopausal symptoms. Menopause, defined as the permanent cessation of menstrual periods, occurs as a natural part of aging in women. During this time, estrogen and progesterone levels decline, leading to various symptoms such as hot flashes, mood changes, and vaginal dryness.
Hormone therapy involves the administration of estrogen and/or progesterone to alleviate these symptoms. It can be delivered through different methods, including:
- Pills
- Patches
- Creams
- Vaginal rings
Although hormone therapy can effectively relieve menopausal symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable approach. The benefits and risks of hormone therapy should be carefully considered, as it may not be appropriate for every woman, particularly those with a history of certain medical conditions.
It is crucial to seek medical advice before starting hormone therapy to ensure it is the right choice for you.
Demystifying The Hymen: The Membrane At The Entrance Of The Vaginal Opening
The hymen is a thin, elastic membrane that partially covers the entrance of the vaginal opening in females. It has often been associated with virginity and societal expectations of intactness. However, it is essential to understand that the presence, shape, and state of the hymen do not indicate a woman’s sexual experience or reproductive health.
The hymen can naturally vary in appearance and size, and it can also be stretched or torn during various activities that do not necessarily involve sexual intercourse, such as physical exercise or using tampons. Therefore, the hymen should not be directly linked to the occurrence or absence of amenorrhea.
It is important to approach discussions about the hymen with sensitivity and debunk any misconceptions surrounding its appearance and significance. Open and informed conversations can help promote a better understanding of female reproductive health and break down harmful societal norms.
Linking Amenorrhea And Inflammatory Bowel Disease: The Connection Between The Absence Of Periods And Intestinal Inflammation
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) refers to chronic conditions that cause inflammation in the digestive tract, specifically Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Interestingly, there is a link between IBD and amenorrhea, as inflammation in the intestines can disrupt hormonal balance and menstrual regularity.
The chronic inflammation associated with IBD affects the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovary axis, which plays a vital role in regulating the menstrual cycle. This disruption can lead to hormonal imbalances, including reduced estrogen levels, ultimately resulting in amenorrhea.
It is important for individuals with IBD to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage the condition and address any potential reproductive health concerns, specifically amenorrhea. Treatment approaches may involve a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring hormone levels.
The Kidney’s Role In Amenorrhea: How This Organ Affects Menstrual Regularity
The kidneys, often associated with filtering waste from the blood, also play a role in menstrual regularity. The kidneys help regulate the balance of electrolytes and fluid levels in the body. Imbalances in these electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, can affect hormonal levels and menstrual regularity.
Conditions that affect kidney function, such as chronic kidney disease, can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance necessary for normal menstrual cycles. This disruption can lead to amenorrhea or irregular periods.
It is crucial for women with kidney conditions to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their kidney health and address any potential impact on menstrual regularity.
- Kidneys play a role in menstrual regularity.
- Imbalances in electrolytes can affect hormonal levels.
- Chronic kidney disease can disrupt hormonal balance.
- Women with kidney conditions should consult healthcare providers.
Menopause: The Permanent Cessation Of Menstrual Periods
Menopause refers to the permanent cessation of menstrual periods, marking the end of a woman’s reproductive years. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 to 55, but can happen earlier or later for some women.
During menopause, the ovaries produce fewer hormones, specifically estrogen and progesterone. This hormonal decline can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including hot flashes, mood changes, sleep disturbances, and vaginal dryness. Menopause is often associated with the onset of amenorrhea, as the ovaries no longer release eggs and the menstrual cycle ceases.
Managing menopausal symptoms and maintaining overall health during this transition is essential. Healthcare providers may recommend various treatments, including hormone therapy, lifestyle changes, and medications, to alleviate symptoms and support women through this life stage.
Understanding The Menstrual Cycle: Monthly Changes In A Woman’s Body For Possible Pregnancy
The menstrual cycle is a natural process in a woman’s body that involves a series of monthly changes in preparation for possible pregnancy. It generally lasts 28 days, although variations are common.
The menstrual cycle is divided into several stages, including:
- Follicular phase: Lasting about 14 days, this phase involves the stimulation of hormone production to develop an egg within the ovary.
- Ovulation: Occurring around day 14, this phase includes the release of the mature egg from the ovary.
- Luteal phase: This phase follows ovulation and prepares the uterus for possible pregnancy.
- Menstruation: If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining sheds during this phase, and the cycle starts again.
Throughout the menstrual cycle, hormone levels play a vital role in maintaining a healthy reproductive system. Disruptions in these hormonal fluctuations can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, amenorrhea, or other menstrual disorders.
Understanding the intricacies of the menstrual cycle contributes to a better grasp of women’s reproductive health and the potential causes and treatment options for amenorrhea.
- The menstrual cycle involves monthly changes in a woman’s body.
- It typically lasts 28 days, but there can be variations.
- Stages of the menstrual cycle include the follicular phase, ovulation, the luteal phase, and menstruation.
- Hormone levels are essential for a healthy reproductive system.
- Disruptions in hormone fluctuations can lead to menstrual disorders.
- Understanding the menstrual cycle is crucial for women’s reproductive health.
💡
You may need to know these questions about amenorrrhea
What is the main cause of amenorrhea?
The main cause of amenorrhea is often attributed to hormonal disruption. This disruption can arise from various factors such as emotional stress, severe weight loss, excessive physical activity, or particular reproductive disorders. These factors can interfere with the normal hormonal balance, leading to the absence of menstrual periods.
What can happen if you have amenorrhea?
Amenorrhea, the absence or cessation of menstrual periods, can have various consequences on a woman’s health and reproductive system. One potential outcome is hormonal imbalances, which can manifest in symptoms such as headaches, vision problems, or a reduced sexual desire. Moreover, amenorrhea may lead to difficulties in conceiving since it is often accompanied by anovulation, the lack of egg release from the ovaries necessary for pregnancy. Therefore, women with amenorrhea may face challenges in achieving pregnancy due to the absence of ovulation.
How many months does amenorrhea last?
The duration of amenorrhea can vary depending on the individual’s circumstances. In cases of a girl with previously normal periods, a healthcare provider may diagnose amenorrhea if there has been no menstrual bleeding for 3 months or more. However, if the girl had irregular periods before, amenorrhea may be diagnosed after 6 months or more without menstrual bleeding. Additionally, if a girl does not experience any menstrual bleeding by the age of 15, it may also be classified as amenorrhea. Therefore, the duration of amenorrhea can range from 3 months to 6 months or more, or until the age of 15, depending on the specific situation.
Is amenorrhea a serious problem?
While amenorrhea itself is not a disease, it can signify the presence of underlying health conditions that may require attention. In some cases, hormonal imbalances, genetic factors, or structural issues can result in amenorrhea. It is essential to identify and address the root cause as it can impact reproductive health and potentially lead to complications if left untreated. Although amenorrhea can be a natural occurrence during certain periods of a woman’s life, such as pregnancy or menopause, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if experiencing prolonged or unexplained amenorrhea to ensure proper care and management.
Reference source
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/amenorrhea-absence-of-periods
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/menstruation-amenorrhoea
https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/amenorrhea/conditioninfo/treatments
https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/menstrual-disorders-and-abnormal-vaginal-bleeding/absence-of-menstrual-periods