Discover the intriguing and little-known world of ampullary pregnancy, a rare condition that challenges conventional notions of conception.
Delve into the complexities of this unique phenomenon and unlock the secrets of this captivating medical mystery.
Embark on a journey of discovery and be captivated by the enigmatic wonders of ampullary pregnancy.
ampullary pregnancy
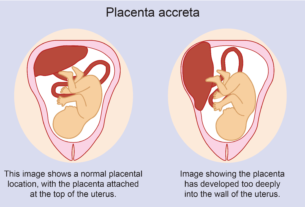
Ampullary pregnancy refers to the implantation of a fertilized egg within the ampulla, which is the widest part of the Fallopian tube.
This type of ectopic pregnancy is specifically located in the ampulla and poses potential risks to the health of the woman.
Key Points:
- Ampullary pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the widest part of the Fallopian tube called the ampulla.
- It is a type of ectopic pregnancy, meaning the embryo develops outside the uterus.
- Ampullary pregnancy poses risks to the woman’s health.
- The ampulla is the specific location where the embryo is implanted in this type of pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancies in the ampulla can be dangerous and may require medical intervention.
- Ampullary pregnancy requires careful monitoring for potential complications.
ampullary pregnancy – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Ampullary pregnancy, also known as tubal pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants and develops outside of the uterus, specifically in the fallopian tube.
2. Ampullary pregnancy is the most common type of ectopic pregnancy, accounting for approximately 70-80% of all ectopic pregnancies.
3. One of the major risk factors for ampullary pregnancy is a history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause scarring and blockage of the fallopian tubes.
4. Ampullary pregnancy can be potentially life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated promptly. The fallopian tube can rupture as the embryo grows, leading to severe internal bleeding.
5. While the chances of having an ampullary pregnancy in any given pregnancy are relatively low, women who have previously experienced an ampullary pregnancy have a higher risk of having another one in the future.
Causes Of Ampullary Pregnancy
Ampullary pregnancy, also known as tubal pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus. The exact cause of ampullary pregnancy is not always clear, but several factors may increase the risk.
One of the leading causes is damage or inflammation of the fallopian tube, which can result from previous pelvic infections or surgeries. Other risk factors include a history of previous tubal pregnancy, certain contraceptive methods, and reproductive abnormalities. Hormonal imbalances and conditions affecting the fallopian tubes, such as endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease, can also contribute to ampullary pregnancy.
The journey of a fertilized egg from the ovary to the uterus relies on the fallopian tubes’ ability to transport it. However, in cases of ampullary pregnancy, the egg fails to reach the uterus and becomes implanted in the tube, leading to complications and possible rupture. Understanding the causes of ampullary pregnancy is crucial in identifying high-risk individuals and implementing preventive measures or early interventions.
– Damage or inflammation of the fallopian tube
– Pelvic infections or surgeries
– History of previous tubal pregnancy
– Certain contraceptive methods
– Reproductive abnormalities
– Hormonal imbalances
– Conditions affecting the fallopian tubes (endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease)
Symptoms Of Ampullary Pregnancy
Early signs and symptoms of ampullary pregnancy are often similar to those of a normal pregnancy, making them difficult to discern. However, as the pregnancy progresses, certain symptoms may arise, indicating a potential ampullary pregnancy. These include:
- Abdominal pain, often on one side
- Vaginal bleeding, which may be light or heavy
- Sharp shoulder pain due to the irritation of the diaphragm by blood from a ruptured fallopian tube
- Other common signs may include dizziness, faintness, or a racing heart, indicating possible internal bleeding.
It is important to note that not all women will experience the same symptoms, and some may exhibit no symptoms at all until a rupture occurs.
The timely recognition of symptoms is crucial for the early diagnosis and treatment of ampullary pregnancy. Any woman experiencing unexplained abdominal pain or abnormal vaginal bleeding, especially in conjunction with pregnancy, should seek immediate medical attention to rule out the possibility of an ampullary pregnancy.
Diagnosis And Testing For Ampullary Pregnancy
When a woman presents with symptoms suggestive of an ampullary pregnancy, healthcare providers will employ various diagnostic methods to confirm the condition and determine its severity. The process typically begins with a thorough physical examination, including a pelvic exam, to assess the patient’s overall condition and identify any abnormalities. Blood tests may also be performed to measure the levels of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which is produced during pregnancy. In cases of ampullary pregnancy, hCG levels may be lower than expected for the gestational age.
To further diagnose ampullary pregnancy, imaging techniques, such as transvaginal ultrasound or pelvic ultrasound, are commonly used. These imaging tests provide detailed pictures of the reproductive organs, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize the location and viability of the pregnancy. A definitive diagnosis of ampullary pregnancy is made when an embryo or gestational sac is identified within the fallopian tube during an ultrasound examination.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial in ensuring prompt intervention, reducing the risk of complications associated with ampullary pregnancy.
Complications Associated With Ampullary Pregnancy
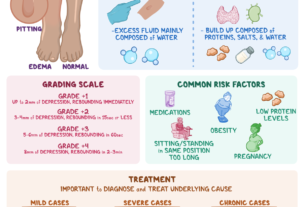
Ampullary pregnancy can lead to various complications if left untreated, including life-threatening emergencies. One of the most serious and potentially fatal consequences is the rupture of the fallopian tube. As the embryo grows, it can cause the tube to stretch and eventually rupture, resulting in severe internal bleeding. This condition, known as a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, requires immediate medical intervention to control the bleeding and prevent further complications.
Other complications include anemia from blood loss, infection from the rupture, or damage to the fallopian tube, leading to long-term fertility issues. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital in minimizing the risk of complications and preserving reproductive health.
Treatment Options For Ampullary Pregnancy
The treatment strategy for ampullary pregnancy depends on various factors, including:
- Location of the pregnancy
- Extent of damage to the fallopian tube
- Patient’s desire for future fertility
In cases where the pregnancy is diagnosed early and no rupture or significant bleeding has occurred, a medical approach can be considered.
- Medication, specifically methotrexate, may be administered to stop the growth of the embryo and facilitate its absorption by the body.
This non-surgical intervention is most effective when the pregnancy is small and the patient’s overall condition is stable. Careful monitoring and follow-up are necessary to ensure the success of medical treatment.
If a ruptured ampullary pregnancy or heavy bleeding is detected, surgical intervention is necessary.
- Laparoscopic surgery is commonly performed to remove the ectopic pregnancy and repair any damage to the fallopian tube.
In severe cases or if the fallopian tube is severely damaged, a more invasive surgical procedure, such as a salpingectomy (removal of the fallopian tube), may be required.
The choice of treatment method depends on individual circumstances and should be discussed with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action.
– Medication such as methotrexate may be used to stop the growth of the embryo.
– Laparoscopic surgery is commonly performed to remove the ectopic pregnancy and repair the fallopian tube.
– In severe cases, removal of the fallopian tube (salpingectomy) may be necessary.
– Individual circumstances should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Surgical Procedures For Ampullary Pregnancy
When surgical intervention is required for the treatment of ampullary pregnancy, different procedures may be employed based on the extent of the condition and the patient’s reproductive goals.
-
Salpingostomy: Involves creating a small incision in the fallopian tube to remove the pregnancy while preserving the tube’s integrity. This procedure is often favored when the fallopian tube is undamaged and the patient wishes to preserve future fertility.
-
Salpingectomy: In cases where the fallopian tube is severely damaged or if the patient’s fertility is not a concern, a salpingectomy may be performed. This procedure involves the complete removal of the affected fallopian tube to prevent future ectopic pregnancies.
The decision to perform a salpingostomy or salpingectomy depends on several factors, including the patient’s reproductive goals, the condition of the fallopian tube, and the presence of any additional risk factors.
- Blockquote: “The decision to perform a salpingostomy or salpingectomy depends on several factors, including the patient’s reproductive goals, the condition of the fallopian tube, and the presence of any additional risk factors.”
Recovery And Follow-Up Care For Ampullary Pregnancy
Following treatment for ampullary pregnancy, patients will require a period of recovery and close monitoring to ensure optimal healing and minimize any potential complications. The length of the recovery period may vary depending on the type of treatment received, the extent of the condition, and individual factors.
After a surgical procedure, such as salpingostomy or salpingectomy, patients should expect some discomfort and may be prescribed pain medication. It is essential to follow all post-operative instructions provided by the healthcare team, including any restrictions on physical activity and care for the surgical wound.
Regular follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor the patient’s recovery and evaluate the success of treatment. During these visits, healthcare professionals may:
- Conduct physical examinations
- Perform blood tests to monitor hCG levels
- Conduct imaging tests to ensure complete resolution of the ectopic pregnancy.
Patients should adhere to their follow-up appointments and communicate any symptoms or concerns to their healthcare team.
Fertility Considerations After Ampullary Pregnancy
After experiencing an ampullary pregnancy, the impact on future fertility can be a significant concern for many individuals. The ability to conceive naturally may be affected, especially if the fallopian tube on the affected side was removed or damaged during the treatment process.
However, it is important to note that ampullary pregnancy does not necessarily mean total infertility. In some cases, the remaining fallopian tube may still allow for ovulation and fertilization to occur. Additionally, assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), may offer alternative options for individuals seeking to conceive after ampullary pregnancy.
It is advisable for individuals who have undergone treatment for ampullary pregnancy and desire future fertility to consult with a reproductive specialist. These experts can provide individualized guidance and explore available options based on the specific circumstances and goals.
Prevention And Risk Reduction For Ampullary Pregnancy
While ampullary pregnancy may not always be preventable, there are steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk. Regular gynecological check-ups, including comprehensive pelvic examinations and screenings for sexually transmitted infections, can help detect any abnormalities early on. Adequate management of conditions, such as endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease, can also play a role in reducing the risk of ampullary pregnancy.
Additionally, it is essential to use contraceptive methods correctly and consistently. Barrier methods, hormonal contraceptives, and intrauterine devices (IUDs) are effective means of preventing unplanned pregnancies and can contribute to reducing the risk of ampullary pregnancy.
Education and awareness about ampullary pregnancy and its associated risk factors can empower individuals to make informed choices and take appropriate steps to minimize their risk.
Research And Advances In Ampullary Pregnancy Management
Ongoing research and advances in medical science are continuously improving the management of ampullary pregnancy. The development of diagnostic techniques, such as improved ultrasound imaging and more sensitive hCG tests, enables earlier detection and intervention. This early diagnosis, in turn, allows for less invasive treatment options and better outcomes for patients.
Innovations in surgical techniques, such as the use of minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures, have also contributed to reduced hospital stays, decreased post-operative pain, and faster recovery times.
Furthermore, research efforts are focused on identifying novel medical interventions and exploring the potential use of medications other than methotrexate for the treatment of ampullary pregnancy. These advancements aim to improve patient outcomes, preserve fertility, and enhance the overall management of this challenging condition.
In conclusion, ampullary pregnancy is a complex condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and being aware of available treatment options are vital for managing ampullary pregnancy effectively. With ongoing research and advances in medical science, the management and outcomes of this condition continue to improve, offering hope to those affected and contributing to the field of women’s reproductive health.
- Early detection and intervention through improved diagnostic techniques
- Less invasive treatment options
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures for reduced hospital stays, decreased post-operative pain, and faster recovery times
- Research focused on identifying novel medical interventions and exploring alternative medications
- Improved patient outcomes, preservation of fertility, and enhanced overall management
💡
You may need to know these questions about ampullary pregnancy
Can pregnancy occur in the Ampulla?
While it is rare, pregnancy can occur in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. Ectopic pregnancies, accounting for around 1-2% of all pregnancies, often occur in the fallopian tube, with the majority happening in the ampulla. This specific case is particularly unusual, as it is a slow-leaking ampullary tubal pregnancy detected at 16 weeks of gestation, which is quite advanced for this type of ectopic pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of Ampullary ectopic pregnancy?
Ampullary ectopic pregnancy refers to the implantation of a fertilized egg within the ampulla portion of the fallopian tube. Symptoms of this condition often include abdominal pain accompanied by vaginal bleeding. Additionally, individuals may experience more general symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. Prompt diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial in managing ampullary ectopic pregnancies.
How many weeks can an ectopic pregnancy survive?
In most cases, an ectopic pregnancy cannot survive past 6 to 16 weeks. Due to the lack of adequate blood supply and support from the tissues outside the uterus, the fetus is unable to develop and grow. Eventually, the structure containing the fetus usually ruptures, resulting in the termination of the pregnancy.
Does ectopic pregnancy have a fetus?
Yes, an ectopic pregnancy can have a fetus, but it is not viable. The developing fetus implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. As the pregnancy progresses, the fetus and placenta start to grow, but since the fallopian tube is not designed to accommodate this growth, it eventually leads to rupture and internal bleeding. In order to prevent further complications, it is necessary to terminate the ectopic pregnancy through medical intervention.
Reference source
https://www.britannica.com/science/ampullar-pregnancy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8351844/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539860/
https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/complications-of-pregnancy/ectopic-pregnancy