Every day, medical science strives to find better ways to protect us from the lurking threats of illness and disease.
Among these advancements is the annexectomy, a surgical procedure that offers hope for preventing and minimizing the risk of malignant diseases.
With its ability to remove or treat various reproductive organs and appendages, this groundbreaking procedure not only addresses health concerns but also alters the course of hormone production in the body.
Join us as we delve into the fascinating realm of medical advancements and explore the intricate world of annexectomy.
annexectomy
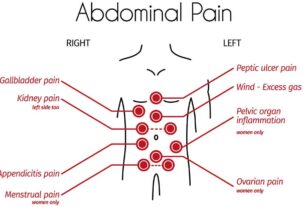
Annexectomy, also known as adnexectomy, refers to the surgical procedure that involves the removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
This can be done unilaterally, removing one side, or bilaterally, removing both sides.
Annexectomy is performed for various reasons, including the prevention of long-term malignant diseases in the ovaries, the elimination of estrogen production, and the reduction of female hormone generation.
In addition, annexectomy can be accompanied by hormone therapy after hysterectomy, and it is also a part of male hormone therapy.
Moreover, this procedure reduces the risk of malignant diseases in the uterus, cervix, and ovaries.
In some cases, laparoscopic double annexectomy may be performed.
Overall, annexectomy offers medical benefits and addresses specific health concerns.
Key Points:
- Annexectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- It can be done on one side (unilaterally) or both sides (bilaterally).
- Annexectomy is performed to prevent long-term malignant diseases in the ovaries, eliminate estrogen production, and reduce female hormone generation.
- It may be accompanied by hormone therapy after hysterectomy and is also used in male hormone therapy.
- The procedure reduces the risk of malignant diseases in the uterus, cervix, and ovaries.
- Laparoscopic double annexectomy may be performed in some cases.
annexectomy – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The term “annexectomy” refers to the surgical removal of the vermiform appendix, a small pouch-like structure attached to the large intestine.
2. The appendix, often considered a vestigial organ with no apparent function, actually plays a role in immune system function, as it contains lymphoid tissue.
3. Although an appendectomy is a common surgical procedure today, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that the appendix was recognized as a potential source of internal infections and the need for its removal became widespread.
4. The first successful appendectomy was performed in 1735 by French surgeon Claudius Amyand, who successfully removed the appendix of an 11-year-old boy suffering from appendicitis.
5. In some rare cases, an appendix can contain foreign bodies, such as seed pits or chicken bone fragments, that may cause inflammation and necessitate an appendectomy.
1. Annexectomy
An annexectomy, also known as an appendectomy, is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the appendix. The appendix is a small, finger-like organ attached to the cecum, which is part of the large intestine. While the exact function of the appendix is still uncertain, its removal is necessary in certain cases to prevent complications such as appendicitis.
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, and can be done laparoscopically or through an open incision. Laparoscopic annexectomy involves making several small incisions, through which a camera and specialized instruments are inserted to remove the appendix. This minimally invasive approach offers shorter recovery time and reduced scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
- An annexectomy, also known as an appendectomy, is a surgical procedure.
- The appendix is a small, finger-like organ attached to the cecum, which is part of the large intestine.
- The removal of the appendix is necessary in certain cases to prevent complications such as appendicitis.
- The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia.
- Annexectomy can be done laparoscopically or through an open incision.
- Laparoscopic annexectomy involves making several small incisions and using a camera and specialized instruments.
2. Excision of Appendages
The excision of bodily appendages involves the removal of organs or structures beyond the appendix. In some cases, such as the presence of tumors or severe medical conditions, an annexectomy procedure may necessitate the removal of fallopian tubes and ovaries. This additional step is often undertaken to prevent the spread of cancer or to alleviate symptoms associated with these organs.
3. Fallopian Tubes Removal
The removal of the fallopian tubes, also known as salpingectomy, may be necessary for various reasons. This procedure can be performed as part of an annexectomy or as a standalone surgery. In cases of tubal ligation, where permanent contraception is desired, the fallopian tubes are surgically closed or removed. Additionally, the removal of the fallopian tubes may be recommended to treat certain reproductive disorders or prevent the risk of future gynecological conditions.
- The removal of fallopian tubes, also known as salpingectomy, is a surgical procedure.
- It can be performed as part of an annexectomy or as a standalone surgery.
- Tubal ligation involves the closure or removal of the fallopian tubes for permanent contraception.
- It may be recommended for treating reproductive disorders or preventing future gynecological conditions.
The removal of the fallopian tubes offers various benefits, such as permanent contraception and the prevention of future gynecological conditions.
4. Ovaries Removal
The removal of the ovaries, also known as oophorectomy, is performed in conjunction with an annexectomy for various reasons. The ovaries play a crucial role in egg production and the secretion of hormones like estrogen and progesterone. Oophorectomy becomes necessary in cases of concerning factors such as ovarian cancer, tumors, or the treatment of conditions such as endometriosis. Nevertheless, this surgical intervention can result in hormonal imbalances, requiring the use of hormone replacement therapy.
- Oophorectomy is the removal of the ovaries.
- It may be performed with an annexectomy for various reasons.
- The ovaries produce eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
- Ovary removal might be necessary due to concerns like ovarian cancer, tumors, or endometriosis.
- However, oophorectomy can cause hormonal imbalances.
- Hormone replacement therapy may be needed.
5. Unilateral Annexectomy
A unilateral annexectomy refers to the removal of only one side of the appendix. This procedure is often performed when there is a clear need for appendix removal on one side, either due to appendicitis or the presence of tumors or infection. Unilateral annexectomy allows for targeted treatment while preserving the other side of the appendix and reducing the risk of complications associated with a complete removal.
- Unilateral annexectomy is the removal of only one side of the appendix.
- This procedure is performed when there is a clear need for appendix removal on one side.
- Reasons for unilateral annexectomy include appendicitis, tumors, or infection.
- It allows for targeted treatment while preserving the other side of the appendix.
- This reduces the risk of complications associated with complete removal.
“Unilateral annexectomy refers to the removal of only one side of the appendix. This procedure is often performed when there is a clear need for appendix removal on one side, either due to appendicitis or the presence of tumors or infection.”
6. Bilateral Annexectomy
A bilateral annexectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing both sides of the appendix. This procedure is usually performed when there is a necessity to completely remove the appendix, such as in cases of severe appendicitis or tumors affecting both sides. By eliminating all potential sources of infection or disease, the bilateral annexectomy significantly reduces the risk of future complications.
7. Adnexectomy
An adnexectomy is the surgical removal of the adnexa, which includes the fallopian tubes and ovaries. This procedure is commonly done for therapeutic or prophylactic reasons, such as removing ovarian tumors or to prevent the risk of future reproductive disorders. Adnexectomy can be performed alongside an annexectomy to address multiple concerns or as an independent procedure to target specific reproductive issues.
Key points:
- An adnexectomy involves the removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- It is done for therapeutic or prophylactic reasons.
- Common reasons for adnexectomy include removing ovarian tumors and preventing future reproductive disorders.
Quote: “An adnexectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the adnexa, which consists of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.”
8. Double Annexectomy
A double annexectomy refers to the removal of both the appendix and the fallopian tubes. This surgical procedure can be carried out to treat certain medical conditions or as a preventive measure. Double annexectomy is recommended in cases of hereditary disorders or known risks for specific diseases in order to reduce the risk of future complications associated with these organs.
9. Removal of Both Ovaries
The removal of both ovaries, known as bilateral oophorectomy, may be necessary in specific cases to address medical conditions or to reduce the risk of developing ovarian cancer. This surgical procedure is often performed alongside an annexectomy or independently. However, the removal of both ovaries can lead to menopause and hormonal imbalances, necessitating hormone replacement therapy to manage associated symptoms.
10. Elimination of Estrogen Production
The removal of the ovaries during an annexectomy or a standalone oophorectomy results in the elimination of estrogen production. Estrogen is a hormone primarily produced by the ovaries and plays a vital role in the female reproductive system. Its removal can have significant effects on a person’s overall health, including the onset of menopausal symptoms, changes in bone density, and an increased risk of certain conditions like heart disease.
Annexectomy procedures encompass the removal of the appendix, as well as additional organs such as the fallopian tubes and ovaries. While these surgeries may be necessary for a variety of reasons, including the prevention of malignant diseases and the management of reproductive disorders, they can have significant impacts on hormone production and overall health. It is essential for individuals considering such procedures to consult with their healthcare providers to fully understand the potential benefits and risks involved.
💡
You may need to know these questions about annexectomy
What is the meaning of Adnexectomy?
Adnexectomy refers to a surgical procedure aimed at removing the skin appendages, including sweat glands. This procedure is typically performed to address conditions like hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), bromhidrosis or osmidrosis (malodor), or hidradenitis suppurativa. Through adnexectomy, surgeons aim to alleviate the symptoms associated with these conditions by removing the specific sweat glands and reducing their activity.
1. What are the common risks and complications associated with an annexectomy procedure?
An annulectomy, also known as a discectomy, is a surgical procedure performed to remove a herniated or damaged disc in the spine. Like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with an annulectomy. Common risks include bleeding, infection, damage to nerves or blood vessels, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. These risks can be minimized by selecting a skilled and experienced surgeon and following proper pre-operative and post-operative care.
Complications that can occur after an annulectomy include recurrent herniation of the disc, formation of scar tissue, spinal fluid leak, and persistent pain or weakness. It is also possible to develop problems with adjacent discs in the spine due to altered biomechanics after the removal of a disc. While these risks and complications are relatively rare, it is important for patients to discuss them with their surgeon and carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks before proceeding with the procedure.
2. Can an annexectomy affect a woman’s fertility? If so, what are the chances of pregnancy after the procedure?
An annexectomy, which is the removal of the fallopian tube(s), can potentially affect a woman’s fertility. The fallopian tubes play a crucial role in the process of fertilization, as they are responsible for transporting the egg from the ovary to the uterus. If one or both of the tubes are removed, the chances of pregnancy may be reduced, particularly if there is no other viable tube.
The extent to which infertility may occur depends on various factors, such as the condition of the remaining fallopian tube(s), the presence of any underlying fertility issues, and the individual’s overall reproductive health. If the other tube is healthy and functioning properly, there is still a possibility of achieving pregnancy. However, the chances may be lower compared to having both tubes intact. It is essential for individuals considering an annexectomy to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized information and guidance based on their specific circumstances.
3. How does the recovery process differ for laparoscopic annexectomy versus open annexectomy?
The recovery process for laparoscopic annexectomy and open annexectomy differs mainly in terms of the incision size, surgical trauma, and healing time. In laparoscopic annexectomy, small incisions are made for the insertion of surgical instruments and a camera, resulting in less surgical trauma and pain. This minimally invasive approach allows for faster recovery, with most patients returning to normal activities within a few days and experiencing less postoperative discomfort.
On the other hand, open annexectomy involves a larger incision, which leads to more surgical trauma and potentially more pain during the recovery period. The healing time is usually longer compared to laparoscopic annexectomy, with patients needing more time to regain their energy and perform daily activities. However, open annexectomy might be necessary in certain cases, such as if there are complications or the surgeon needs better access to the appendix.
Reference source
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1894741-overview
https://cirugiagenero.com/en/double-annexectomy.php
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20340356/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15141521/