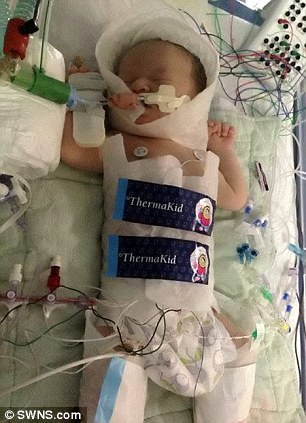
Picture a newborn baby, tiny and fragile, with skin that takes on a mysterious blue hue.
This captivating condition is known as asphyxia livida, where the heart beats strong, but oxygen deprivation threatens the infant’s well-being.
Delve into the world of this enigmatic disorder, where life hangs in the balance, and discover the innovative treatments that offer hope for a brighter future.
asphyxia livida
Asphyxia livida refers to a form of asphyxia neonatorum where the skin appears cyanotic, indicating a lack of oxygen, but the heart functions normally and reflexes are intact.
It is a condition where a baby does not receive enough oxygen before, during, or directly after birth.
This can cause serious complications and even be life-threatening.
It can occur just before, during, or after birth and is caused by various factors such as umbilical cord prolapse, compression of the umbilical cord, meconium aspiration syndrome, premature birth, and more.
Immediate treatment is crucial to reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Depending on the severity and cause of the asphyxia, treatment options include providing extra oxygen, emergency or cesarean delivery, suctioning fluid from airways, and more.
Preventing asphyxia requires effective resuscitation, monitoring, proper equipment, trained healthcare providers, and pre-treatment with certain medications.
Treatment and prevention methods aim to mitigate brain damage and prevent complications from asphyxia.
Key Points:
- Asphyxia livida is a form of asphyxia neonatorum where the skin appears cyanotic, but the heart functions normally and reflexes are intact.
- It is a condition where a baby does not receive enough oxygen before, during, or directly after birth.
- Asphyxia livida can cause serious complications and even be life-threatening.
- Causes of asphyxia livida include umbilical cord prolapse, compression of the umbilical cord, meconium aspiration syndrome, premature birth, and more.
- Immediate treatment is crucial to reduce the risk of long-term complications, which can include providing extra oxygen, emergency or cesarean delivery, suctioning fluid from airways, and more.
- Preventing asphyxia requires effective resuscitation, monitoring, proper equipment, trained healthcare providers, and pre-treatment with certain medications.
asphyxia livida – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Asphyxia Livida Trivia: In ancient Rome, a form of punishment called “Livida” was used by hanging the offender until they reached a state of asphyxia, providing the origin for the term “asphyxia livida.”
2. The term “Asphyxia Livida” is often associated with a condition known as “purple hag syndrome,” where individuals experience an episode of asphyxia during sleep, leading to their face turning a deep shade of purple.
3. Asphyxia Livida can also refer to a rare medical phenomenon called “inverted hanging,” where individuals die of asphyxia due to suspension by the feet instead of the traditional neck suspension.
4. A curious historical fact reveals that the notorious serial killer H. H. Holmes, also known as “America’s First Serial Killer,” experimented with various methods of asphyxia, including using air-tight chambers to suffocate his victims.
5. Asphyxia Livida has been used as an artistic metaphor for a sense of suffocation or strangulation in several literary works, symbolizing the suppression of one’s freedom or creativity, such as in Edgar Allan Poe’s famous poem “The Raven.”
Asphyxia Livida: Definition And Symptoms
Asphyxia livida is a specific form of asphyxia neonatorum, a condition that occurs when a baby does not receive enough oxygen before, during, or right after birth. The term “livida” refers to the appearance of cyanosis or bluish discoloration of the skin, which is indicative of oxygen deprivation. While the skin may appear cyanotic, it is important to note that the heart functions normally and reflexes are intact in cases of asphyxia livida.
Symptoms of asphyxia livida can occur at any time before, during, or after birth. Signs in newborns at birth may include:
- Unusual skin tone
- Silence
- Low heart rate
- Weak muscle tone and reflexes
- Lack of breathing
- Amniotic fluid stained with meconium
- Seizures
- Poor circulation
- Limpness or lethargy
- Low blood pressure
- Lack of urination
- Abnormal blood clotting
It is crucial for healthcare providers to be vigilant and recognize these symptoms promptly, as early diagnosis and intervention can significantly impact the outcomes for affected infants.
Early diagnosis and intervention are key in cases of asphyxia livida.
The Dangers Of Birth Asphyxia
Birth asphyxia is a serious condition that can pose life-threatening risks to newborns. Insufficient oxygen supply during the crucial moments surrounding birth can lead to low oxygen levels or excessive acid in the baby’s blood, potentially causing organ damage and impairing vital bodily functions. While mild or moderate cases of birth asphyxia may result in full recovery, severe cases can lead to permanent brain and organ damage, and in some cases, even be fatal.
The rates of birth asphyxia vary across different regions and healthcare systems. Developed countries typically experience lower rates, occurring in approximately 2 out of every 1,000 births. However, in developing countries with limited access to adequate neonatal care, the incidence of birth asphyxia can be up to 10 times higher.
To tackle this global issue effectively, it is paramount to focus on addressing and preventing birth asphyxia through improved healthcare infrastructure and education.
- Birth asphyxia is a serious condition with life-threatening consequences
- Insufficient oxygen supply during birth can cause organ damage and impair vital bodily functions
- Severe cases of birth asphyxia can result in permanent brain and organ damage or even be fatal
- Developed countries tend to have lower rates of birth asphyxia (2 out of 1,000 births)
- The incidence of birth asphyxia can be up to 10 times higher in developing countries
- Addressing and preventing birth asphyxia requires improved healthcare infrastructure and education
Causes Of Birth Asphyxia
Various factors can contribute to the occurrence of birth asphyxia. These include:
- Umbilical cord prolapse: This happens when the cord slips into the birth canal ahead of the baby, leading to compression or cutting off the oxygen supply.
- Compression of the umbilical cord during labor can result from a prolonged or difficult delivery, compromising the oxygen flow.
- Meconium aspiration syndrome occurs when a baby inhales meconium, the first stool passed after birth, which can obstruct the airways and cause asphyxia.
Other potential causes of birth asphyxia include:
- Premature birth
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Uterine rupture
- Placental separation
- Infection during labor
- High or low blood pressure during pregnancy
- Anemia in the baby
It is crucial for healthcare providers to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate precautions during prenatal care and the birthing process to minimize the risk of birth asphyxia.
- Umbilical cord prolapse: cord slips into birth canal ahead of baby, leading to compression or cutting off oxygen supply
- Compression of umbilical cord: during prolonged or difficult delivery, compromising oxygen flow
- Meconium aspiration syndrome: baby inhales first stool after birth, obstructs airways causing asphyxia
- Premature birth
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Uterine rupture
- Placental separation
- Infection during labor
- High or low blood pressure during pregnancy
- Anemia in the baby
Risk Factors For Birth Asphyxia
While birth asphyxia can occur unpredictably, certain factors increase the likelihood of its occurrence. Pregnant individuals between the ages of 20 and 25 have a slightly higher risk of experiencing birth asphyxia. Multiple births, such as twins or triplets, also carry an increased risk due to potential complications during delivery. Lack of prenatal care, low birth weight, abnormal fetal position, and conditions like preeclampsia or eclampsia, characterized by high blood pressure during pregnancy, are additional risk factors.
Furthermore, a history of birth asphyxia increases the risk of its recurrence in subsequent pregnancies. It is crucial for healthcare providers to identify these risk factors early on and provide appropriate monitoring and intervention throughout pregnancy, labor, and delivery.
Signs And Symptoms Of Birth Asphyxia
The signs and symptoms of birth asphyxia can manifest before, during, or after birth. Prompt recognition and intervention are essential to mitigate potential complications. Newborns affected by birth asphyxia may present with unusual skin tone, such as bluish discoloration or cyanosis, indicating oxygen deprivation. They may also be silent, with a low heart rate, weak muscle tone and reflexes, and a lack of breathing.
Other signs include:
- Meconium-stained amniotic fluid
- Seizures
- Poor circulation
- Limpness or lethargy
- Low blood pressure
- Lack of urination
- Abnormal blood clotting
These symptoms require immediate attention from healthcare professionals to prevent further deterioration and minimize potential long-term effects of birth asphyxia.
The Importance Of Apgar Score In Diagnosing Birth Asphyxia
The Apgar score is a vital tool used to evaluate a newborn’s physical condition and assess their need for immediate medical intervention. The score is assigned based on several factors, including heart rate, muscle tone, reflexes, skin color, and breathing efforts.
A low Apgar score (between 0 and 3) that persists for more than 5 minutes can indicate the presence of birth asphyxia.
The Apgar scoring system, developed by Dr. Virginia Apgar, helps healthcare providers quickly evaluate the newborn’s well-being and determine the urgency of required interventions. It serves as an important diagnostic tool for birth asphyxia and guides subsequent treatment decisions.
Immediate Treatment For Birth Asphyxia
Immediate treatment is crucial in reducing the risk of long-term complications associated with birth asphyxia. The specific interventions administered depend on the severity and underlying cause of the asphyxia.
-
Oxygen supplementation is often provided to ensure the newborn receives adequate oxygenation.
-
In some cases, emergency or cesarean delivery may be necessary to expedite the delivery process and prevent further harm.
Other immediate treatment options include:
-
Suctioning fluid from the airways to clear obstructions.
-
Placing the newborn on a respirator to assist with breathing.
-
Utilizing hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which involves placing the baby in a specialized chamber that delivers oxygen under increased pressure.
-
Induced hypothermia, a technique that lowers the newborn’s body temperature, may also be employed to minimize potential brain damage.
Short-Term And Long-Term Effects Of Birth Asphyxia
The effects of birth asphyxia can vary depending on the severity and duration of oxygen deprivation. Short-term effects can include:
- Abnormalities in blood acid levels (acidosis)
- Respiratory distress
- High blood pressure
- Blood clotting problems
- Kidney issues
These effects may require immediate medical intervention, such as:
- Medication to regulate blood pressure
- Dialysis to support the kidneys
- Medications to control seizures.
In the long term, infants with mild-to-moderate birth asphyxia can experience:
- Cognitive and behavioral changes
- Hyperactivity
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Attention deficits
- A low intelligence quotient score
- An increased risk of developing schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders.
Severe asphyxia can lead to:
- Intellectual disability
- Cerebral palsy
- Epilepsy
- Sight or hearing impairments.
Treatment Options For Asphyxia Livida
Treatment options for asphyxia livida aim to prevent further complications and mitigate the damage caused by oxygen deprivation. Depending on the specific situation and severity of the condition, healthcare providers may provide additional oxygen supplementation, emergency deliveries, and suctioning to clear the airways of any obstructions.
Furthermore, specialized treatments such as placing the newborn in a hyperbaric oxygen tank or inducing hypothermia may be utilized to reduce the risk of long-term brain damage. In severe cases, life support with a heart and lung pump may be necessary. Treatment plans often involve a multidisciplinary approach, with a team of healthcare professionals working together to address the specific needs of the infant.
Preventing Birth Asphyxia: Steps And Strategies
While it may be challenging to prevent birth asphyxia entirely, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk and minimize the potential consequences.
Effective resuscitation techniques, including prompt recognition of the need for interventions, can greatly impact the outcome for newborns affected by birth asphyxia.
Maintaining the newborn’s optimal body temperature and ensuring that the correct equipment is readily available are also crucial in preventing complications.
It is essential to have trained healthcare providers present for every birth as their expertise and ability to recognize and address potential complications promptly can significantly improve outcomes.
Pre-treatment with certain medications, such as magnesium sulfate for pregnant individuals at risk of premature birth, can help reduce the likelihood of birth asphyxia.
In cases of asphyxia, body cooling may be employed to prevent further damage.
By implementing these preventive measures and strategies, the medical community can work towards minimizing the occurrence and impact of birth asphyxia, ultimately improving the well-being of newborns and their families.
Bullet points:
- Effective resuscitation techniques
- Prompt recognition of the need for interventions
- Maintaining optimal body temperature
- Having correct equipment readily available
- Trained healthcare providers present for every birth
- Pre-treatment with medications, such as magnesium sulfate
- Body cooling to prevent further damage
💡
You may need to know these questions about asphyxia livida
What causes asphyxia pallida?
Asphyxia pallida occurs due to a combination of respiratory and metabolic acidosis, which leads to a decrease in heart rate and blood pressure, resulting in circulatory collapse. The low PaO2 and increased PaCO2 levels further contribute to the condition. This state of shock causes the baby’s skin to become pale grey and the baby becomes limp. It is important to address the underlying causes of asphyxia pallida promptly to stabilize the baby’s condition and restore normal blood circulation.
What is asphyxia pallida in newborn?
Asphyxia pallida in newborns refers to a severe condition characterized by a deathlike pallor in the body and face. The umbilical cord vessels are empty, and the muscles of the infant are relaxed, resulting in a completely limp state. This condition indicates a critical lack of oxygen supply to the newborn, leading to potential life-threatening consequences. Immediate medical attention and intervention are crucial to address this severe breathing difficulty and prevent further complications.
How do you treat asphyxia pallida?
To effectively address asphyxia pallida, a multi-faceted approach is adopted. Primarily, placing the baby in a hyperbaric oxygen tank is employed as it allows for the administration of 100% oxygen, aiding the body’s oxygenation needs and assisting recovery. Furthermore, induced hypothermia is utilized to lower the body temperature, mitigating the risk of potential brain damage. Additionally, medication is administered to regulate blood pressure, ensuring stable cardiovascular function and supporting the overall treatment process. This comprehensive treatment strategy aims to alleviate the effects of asphyxia pallida and foster the baby’s recovery, promoting better health outcomes.
What are the stages of asphyxia?
Asphyxia progresses through four distinct stages. The first stage is known as initial apnea, where a temporary cessation of breathing occurs. This is followed by dyspnea, where the individual experiences difficulty in breathing. The third stage is cessation of respiration or terminal apnea, characterized by a complete halt in breathing. Finally, the fourth and most critical stage is the arrest of the heart. At this stage, the heart ceases to function, leading to a life-threatening situation.
Reference source
https://ecommons.luc.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?referer=&httpsredir=1&article=4371&context=luc_theses
https://www.ajol.info/index.php/mjst/article/view/18058/17058
https://ecommons.luc.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4371&context=luc_theses
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/birth-asphyxia