Breastfeeding: A Lifeline for Health and Well-Being
In a world where we are constantly bombarded with conflicting information on health and wellness, one undeniable truth remains: breastfeeding is a lifeline for the health and survival of infants.
Despite its proven benefits, the alarming reality is that less than half of infants under 6 months of age are exclusively breastfed.
This is not just a cause for concern, but a call to action.
Join us as we explore the myriad of benefits that breastfeeding provides, ranging from protection against illnesses to improved cognitive development.
Discover why the inappropriate marketing of breastmilk substitutes is a formidable obstacle in promoting breastfeeding rates, and learn how to ensure that newborns and older babies receive the nourishment they need.
Buckle up and prepare to be enlightened about the power of breastfeeding – a journey that will redefine what you thought you knew.
breast feeding
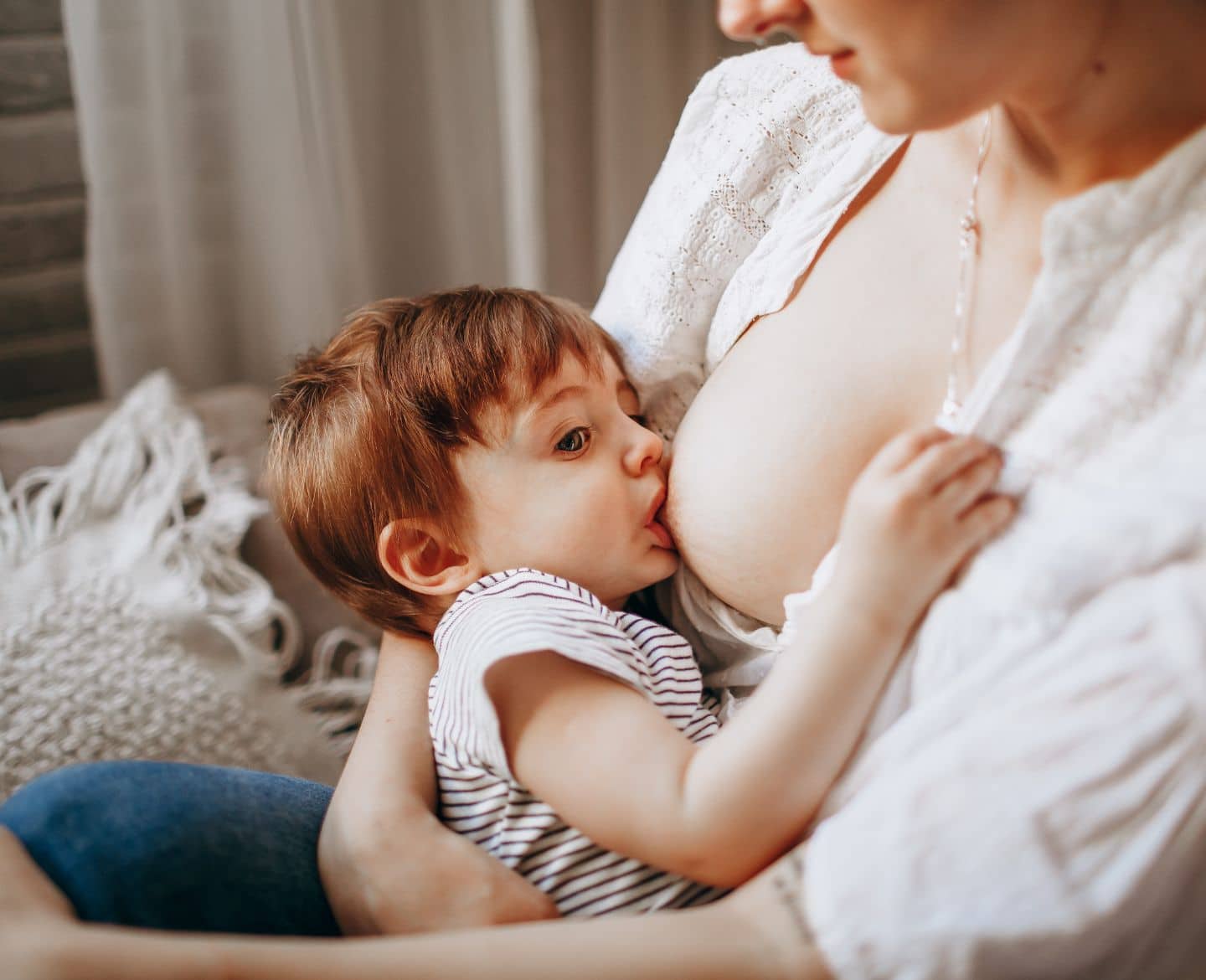
Breastfeeding is a highly effective way to ensure child health and survival.
Breastmilk is safe, clean, and contains antibodies that protect against common childhood illnesses.
It provides all the necessary energy and nutrients for the first months of life, and continues to provide a significant portion of a child’s nutritional needs during the first and second years.
Breastfed children tend to perform better on intelligence tests, have reduced risk of obesity and diabetes, and breastfeeding also reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancers for women.
To establish and maintain successful breastfeeding, newborn babies should breastfeed 8-12 times a day, and by 1-2 months old, babies will nurse 7-9 times a day.
In the first few weeks, breastfeeding should be on demand every 1.5-3 hours, with newborns not going more than 4 hours without feeding.
Key Points:
- Breastfeeding is highly effective in ensuring child health and survival.
- Breastmilk is safe, clean, and contains antibodies that protect against childhood illnesses.
- Breastmilk provides all the necessary energy and nutrients for the first months of life and continues to be a significant part of a child’s nutrition for the first and second years.
- Breastfed children tend to have better intelligence test performance and reduced risk of obesity and diabetes.
- Breastfeeding reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancers in women.
- Newborns should breastfeed 8-12 times a day, and by 1-2 months old, babies will nurse 7-9 times a day. In the first few weeks, breastfeeding should occur every 1.5-3 hours, and newborns should not go more than 4 hours without feeding.
breast feeding – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The practice of breastfeeding has been documented as far back as ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs, dating over 4,000 years ago.
2. Breastfeeding releases a hormone called oxytocin, which not only helps the uterus contract after childbirth but also promotes a sense of relaxation and bonding between mother and baby.
3. The composition of breast milk changes throughout the day to meet the nutritional needs of the baby. It tends to be higher in fat and nutrients during the evening and night, aiding in the baby’s growth and sleep patterns.
4. Breast milk can be used for more than just feeding babies. Its antibacterial and antimicrobial properties make it effective for treating various skin conditions, such as eczema, diaper rash, and even minor wounds.
5. Studies have shown that breastfeeding can have long-term health benefits for both the mother and baby. It reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancer in mothers, while also contributing to better cognitive development, reduced risk of allergies and asthma, and stronger immune systems in breastfed babies.
Importance Of Exclusive Breastfeeding For Child Health And Survival
Breastfeeding is a highly effective practice that ensures the health and survival of infants. Unfortunately, less than half of infants under 6 months of age are exclusively breastfed, missing out on the numerous benefits it provides. Exclusive breastfeeding means that infants receive only breast milk and no other liquids or solids, except for medicines when necessary.
Research has shown that breastmilk is a remarkable substance that offers unparalleled protection against common childhood illnesses. It contains antibodies that strengthen the infant’s immune system, guarding them against infections, respiratory illnesses, and gastrointestinal diseases. Breastfed children have lower rates of hospitalization and better overall health outcomes compared to those who are not breastfed exclusively.
- Breastfeeding ensures the health and survival of infants
- Less than half of infants under 6 months exclusively breastfed
- Breastmilk contains antibodies that strengthen the immune system
- Breastfed children have lower rates of hospitalization and better health outcomes compared to non-exclusively breastfed infants.
Benefits Of Breastmilk: Safety, Cleanliness, And Antibodies
One of the most compelling reasons to breastfeed is the safety and cleanliness of breastmilk. Unlike other feeding options, breastmilk is always safe and free from contaminants. It does not require sterilization, eliminating the risk of harmful bacteria entering the infant’s digestive system. Breast milk is produced by the mother’s body in response to the specific needs of her baby, making it a perfect match tailored to their individual requirements.
Furthermore, breastmilk is rich in antibodies, which are essential for strengthening the infant’s immune system. These antibodies provide passive immunity, protecting the baby from a wide range of illnesses during their vulnerable early years. Breastfed infants are less likely to suffer from respiratory tract infections, ear infections, and urinary tract infections.
- Breastmilk is always safe and free from contaminants.
- It does not require sterilization, eliminating the risk of harmful bacteria.
- Breast milk is tailored to the individual requirements of the baby.
- Breastmilk is rich in antibodies, strengthening the immune system.
- Breastfed infants are less likely to suffer from respiratory tract infections, ear infections, and urinary tract infections.
“Breastmilk is a perfect match tailored to the individual requirements of the baby.”
Breastmilk As A Primary Source Of Energy And Nutrients
Breastmilk is nature’s perfect food for infants as it not only provides crucial energy but also supplies all the necessary nutrients for their early development. During the first months of life, breastmilk is the sole source of nutrition for the baby. It contains the ideal balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, catering to the growing needs of the infant.
As the baby continues to grow, breastmilk remains an essential source of nutrition even after the introduction of solid foods. Research suggests that breastfed children have a higher intake of essential nutrients such as vitamin A, vitamin C, and iron compared to formula-fed infants. Breastmilk composition adapts to the changing nutritional requirements of the baby, ensuring optimal growth and development.
Long-Term Advantages Of Breastfeeding On Intelligence, Weight, And Diabetes Risk
Breastfeeding is not just beneficial for immediate health; it also offers long-term advantages for the child. Studies have consistently shown that breastfed children tend to have better performance on intelligence tests as they grow older. The unique composition of breastmilk, which includes essential fatty acids and other crucial nutrients, actively promotes healthy brain development, thereby enhancing cognitive functions.
Aside from its positive impact on intelligence, breastfeeding plays a vital role in preventing childhood obesity. Infants who are breastfed have a reduced risk of becoming overweight or obese in their later years. This is because breastmilk contains substances that help regulate appetite and metabolism, ultimately contributing to healthy weight management. The protective effect against obesity extends into adolescence and adulthood, which effectively minimizes the risk of chronic diseases associated with excessive weight gain.
Moreover, breastfeeding has also been found to significantly decrease the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. The bioactive molecules present in breastmilk actively regulate glucose metabolism, leading to improved insulin sensitivity and a reduced risk of diabetes in adulthood.
To summarize the benefits of breastfeeding:
- Breastfed children have shown better performance on intelligence tests.
- Breastmilk promotes healthy brain development, enhancing cognitive functions.
- Breastfeeding reduces the risk of childhood obesity.
- Breastmilk contains substances that regulate appetite and metabolism, leading to healthy weight management.
- Breastfeeding lowers the risk of chronic diseases related to excessive weight gain.
- Breastfeeding decreases the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes in adulthood.
Breastfeeding has wide-ranging and long-lasting benefits, from boosting intelligence to preventing obesity and reducing the risk of diabetes. The composition of breastmilk is thoughtfully designed to support optimal development and overall health in children.
Reduced Risk Of Breast And Ovarian Cancers For Breastfeeding Women
Breastfeeding not only benefits the infant but also provides numerous advantages for the mother’s health. Women who breastfeed have a reduced risk of developing breast and ovarian cancers. The mechanisms behind this protective effect are still being explored, but it is believed that breastfeeding helps to regulate hormone levels, reducing the exposure of breast tissues to estrogen, which may have a protective effect against breast cancer.
Furthermore, breastfeeding also aids in the involution of the breast, the process by which the breast returns to its non-pregnant state. This natural process reduces the number of cells in the breast, potentially lowering the risk of breast cancer. Similarly, breastfeeding has been associated with a decreased risk of ovarian cancer, although more research is needed to fully understand the underlying mechanisms.
- Breastfeeding reduces the risk of developing breast and ovarian cancers.
- Breastfeeding helps regulate hormone levels, reducing breast tissue’s exposure to estrogen.
- Breastfeeding aids in the natural involution of the breast, potentially lowering the risk of breast cancer.
- Further research is required to fully understand the mechanisms behind the reduced risk of ovarian cancer associated with breastfeeding.
Breastfeeding has a protective effect against breast and ovarian cancers. It plays a role in regulating hormone levels and aiding the involution of the breast, reducing the risk of cancer. More research is needed to understand the mechanisms involved.
Undermining Breastfeeding Efforts Through Improper Marketing Of Alternatives
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting the benefits of breastfeeding, efforts to improve breastfeeding rates globally are undermined by the inappropriate marketing of breastmilk substitutes. The aggressive marketing tactics employed by formula companies undermine the confidence of mothers in their ability to breastfeed and lead to a shift away from exclusive breastfeeding.
The marketing of breastmilk substitutes creates a perception that formula feeding is a convenient and acceptable alternative to breastfeeding. This not only results in decreased breastfeeding rates but also puts infants at a higher risk of various health problems. It is crucial that governments and organizations regulate and monitor the marketing practices of formula companies to protect the health and well-being of infants around the world.
- Breastfeeding offers numerous benefits for both mother and baby, including improved immune function, lower risk of infections, and better cognitive development.
- Formula companies employ aggressive marketing tactics that undermine the confidence of mothers and promote the idea that formula feeding is easier and just as good as breastfeeding.
- This marketing strategy has led to a shift away from exclusive breastfeeding, which is important for providing optimal nutrition and protection against diseases.
- Infants who are not exclusively breastfed are at a higher risk of health problems, such as gastrointestinal infections and respiratory illnesses.
- Governments and organizations should take strong measures to regulate and monitor the marketing practices of formula companies, ensuring that they do not mislead or undermine the importance of breastfeeding.
“The aggressive marketing tactics employed by formula companies undermine the confidence of mothers in their ability to breastfeed and lead to a shift away from exclusive breastfeeding.”
- Breastmilk substitutes are being marketed in a way that creates a perception of convenience and acceptability, ultimately contributing to decreased breastfeeding rates and jeopardizing the health and well-being of infants worldwide.
Frequency Of Breastfeeding For Newborns (8-12 Times A Day)
In the early days of a newborn’s life, breastfeeding should occur frequently. Newborn babies should be breastfed around 8-12 times a day, which means feeding every 2-3 hours. It is important to note that this frequency may vary depending on the baby’s hunger cues and individual needs.
During the initial weeks, babies may need to nurse more frequently, especially during growth spurts. It is essential to respond to the baby’s hunger cues promptly and allow them to nurse whenever they show signs of hunger. By meeting their needs and feeding them on demand, mothers can ensure a healthy and satisfying breastfeeding journey for both themselves and their babies.
- Breastfeeding should occur frequently, around 8-12 times a day
- Respond promptly to the baby’s hunger cues
- Allow the baby to nurse whenever they show signs of hunger
“By meeting their needs and feeding them on demand, mothers can ensure a healthy and satisfying breastfeeding journey for both themselves and their babies.”
Frequency Of Breastfeeding For 1-2 Month Old Babies (7-9 Times A Day)
As infants grow and develop, their breastfeeding needs change. Around 1-2 months of age, babies will nurse approximately 7-9 times a day. This decrease in frequency is a natural progression as the baby’s stomach capacity increases and their nutritional needs change.
The spacing between feedings will also become more consistent, with longer intervals between each feed. However, it is important to remember that every baby is unique, and some may still require frequent feedings based on their growth and development. Mothers should continue to respond to hunger cues, allowing their babies to nurse whenever needed.
- Babies nurse 7-9 times a day at 1-2 months of age
- Spacing between feedings becomes more consistent with longer intervals
- Some babies may still require frequent feedings based on growth and development
“Mothers should continue to respond to hunger cues, allowing their babies to nurse whenever needed.”
On-Demand Breastfeeding In The Initial Weeks (Every 1.5-3 Hours)
During the initial weeks of a newborn’s life, on-demand breastfeeding is crucial to establish a healthy and efficient milk supply. Babies should be breastfed every 1.5-3 hours, counting from the beginning of each nursing session. This frequent feeding pattern helps stimulate milk production and ensures that the baby receives enough nourishment to support their growth.
Newborns have tiny stomachs and need to nurse frequently to satisfy their hunger and obtain essential nutrients. By practicing on-demand breastfeeding, mothers can establish a strong breastfeeding relationship, promote milk production, and meet their baby’s nutritional needs effectively.
Importance Of Not Letting Newborns Go More Than 4 Hours Without Feeding
It is vital to avoid letting newborns go more than 4 hours without feeding. Newborns have small stomachs that empty quickly, and frequent feedings are necessary to provide optimal nourishment and maintain their health and well-being.
Extended periods without feeding can lead to dehydration, inadequate weight gain, and an unsettled baby. By feeding every 2-3 hours and avoiding long stretches between feedings, mothers can ensure their newborns receive the nutrition they need for healthy growth and development.
In conclusion, breastfeeding is a fundamental practice for infant health and survival. It provides a wide range of benefits for both the baby and the mother, promoting optimal growth, immunity, and long-term health outcomes. Breastfeeding should be prioritized and supported by healthcare systems, governments, and communities worldwide to ensure the best start in life for every child.
💡
You may need to know these questions about breast feeding
How long should I breastfeed my baby each time?
The duration of breastfeeding can vary depending on the age and skill level of your baby. During the newborn stage, it is not uncommon for breastfeeding sessions to last up to 20 minutes or longer on one or both breasts. However, as your baby grows and becomes more proficient at nursing, they may only need about 5-10 minutes on each side. It is important to listen to your baby’s cues and let them nurse for as long as they need to ensure they are getting enough milk. Trusting your baby’s instincts and allowing them to determine the duration of each feeding will help maintain a healthy and successful breastfeeding journey.
What are the basics of breastfeeding for new moms?
Breastfeeding is a natural process that requires some basic knowledge for new moms. It is recommended to start each feeding with the fuller breast, ensuring that the baby releases the nipple or falls asleep before moving to the other breast. Burping the baby after feeding is crucial, followed by offering the other breast if necessary. Some babies may require both breasts during each feeding session, while others may be satisfied with one. Additionally, it is important for new moms to nurse their baby when their breasts feel full, as this helps maintain milk supply and ensures the baby’s nutritional needs are met.
What does it feel like when your milk comes in?
When your milk comes in, it can be a mix of physical sensations and emotional fulfillment. As the tingling or pins and needles sensation spreads through your breast, you may experience a sudden rush of fullness, signaling the arrival of nourishing milk. Simultaneously, your body might surprise you as your other breast starts leaking milk while you feed your baby, creating a sense of awe at the wonders of motherhood. Amidst these physical changes, you may also notice an increased thirst, urging you to stay hydrated as you embrace this beautiful journey of nurturing your little one.
Is 20 minutes breastfeeding enough for newborn?
The duration of a breastfeeding session for a newborn can vary, typically lasting between 10 to 20 minutes. However, it is important to note that newborns may also engage in cluster feeding, which can extend the feeding time to 25-45 minutes. While it may seem like a shorter duration, 20 minutes of breastfeeding can be sufficient for a newborn as long as they are adequately latching and receiving a proper milk supply. It is important to focus on the baby’s feeding cues and monitor their overall growth and satisfaction to ensure they are getting enough nourishment.
Reference source
https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/breastfeed-often.html
https://wicbreastfeeding.fns.usda.gov/breastfeeding-basics
https://www.healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/S_T/Signs-your-breast-milk-is-flowing
https://www.verywellfamily.com/how-long-should-a-baby-nurse-at-each-feeding-431633