Have you ever wondered how your body signals the ideal time for conception?
Look no further than the enigmatic world of cervical mucus.
This often-overlooked substance undergoes incredible transformations throughout your menstrual cycle, acting as a secret messenger that reveals your fertility.
Join us as we delve into the fascinating realm of cervical mucus examination, where deciphering its consistency holds the key to unlocking your safe and unsafe days.
Get ready for a journey of enlightenment and empowerment!
cervical mucus examination
Cervical mucus examination involves tracking changes in the consistency and appearance of cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle.
This method helps determine the fertile and non-fertile days for sexual activity to prevent pregnancy.
Cervical mucus changes as hormone levels fluctuate.
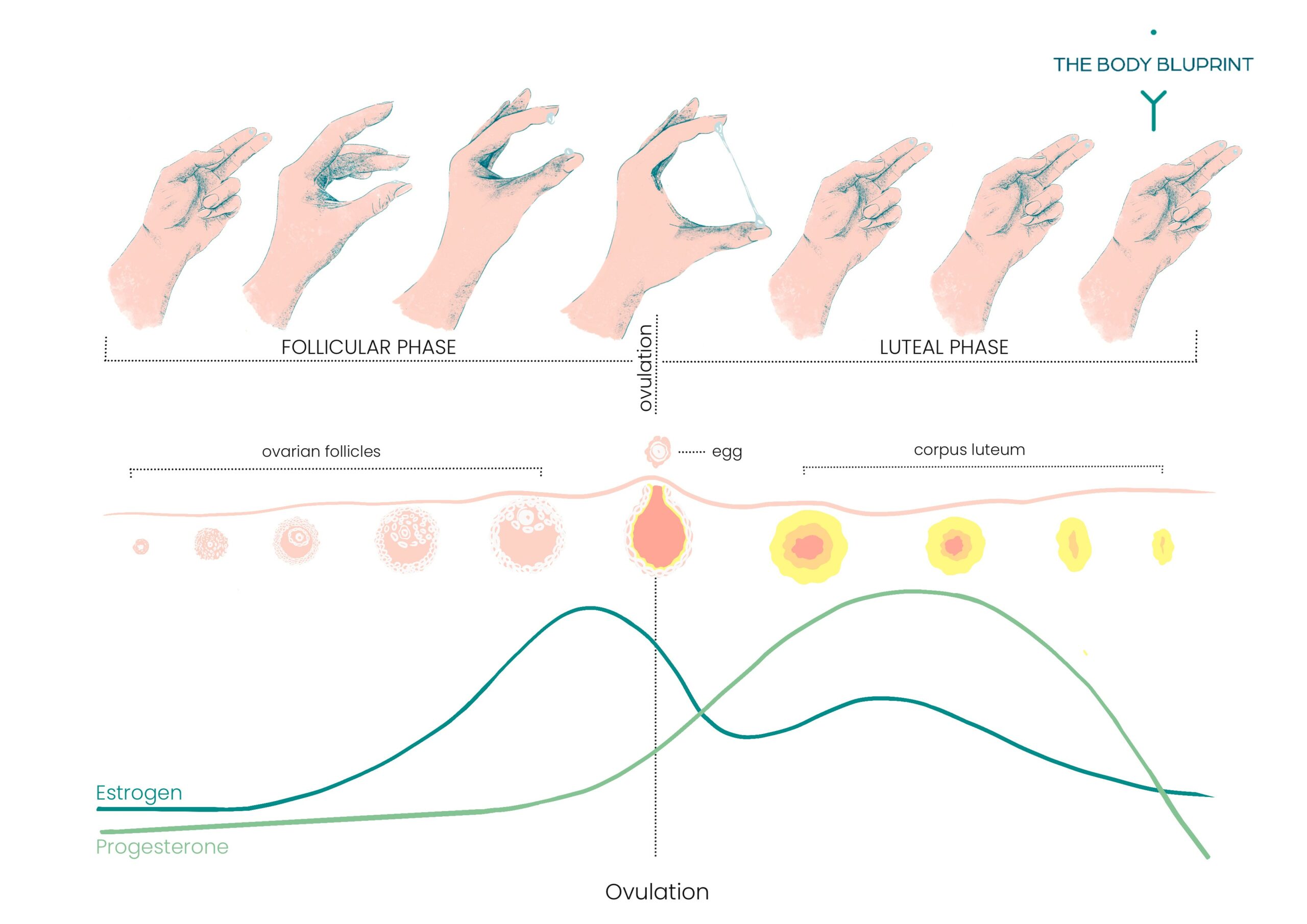
Before ovulation, estrogen increases and the mucus becomes stretchy and slippery, resembling raw egg whites.
This fertile mucus allows sperm to move through the cervix to reach the egg.
After ovulation, estrogen levels drop and progesterone levels rise, causing the mucus to dry up.
Safe days for unprotected sex occur after ovulation and before the period, typically lasting for about 11-14 days.
It is recommended to start this method with the guidance of a healthcare professional and to combine it with the temperature method for increased effectiveness.
Key Points:
- Cervical mucus examination tracks changes in consistency and appearance throughout the menstrual cycle.
- Helps determine fertile and non-fertile days for preventing pregnancy.
- Cervical mucus changes with fluctuating hormone levels.
- Before ovulation, estrogen increases, making mucus stretchy and slippery.
- Fertile mucus allows sperm to reach the egg.
- After ovulation, estrogen levels decrease and progesterone levels rise, causing mucus to dry up.
cervical mucus examination – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The practice of cervical mucus examination, also known as the Billings Ovulation Method, was developed by Drs. John and Evelyn Billings in the 1950s as a natural method of family planning.
2. Cervical mucus examination involves observing changes in the consistency and appearance of cervical mucus throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle to determine fertility. This method relies on the fact that cervical mucus changes in response to hormone levels in a woman’s body.
3. The consistency and appearance of cervical mucus can indicate whether a woman is fertile or infertile. During fertile days, the mucus becomes slippery, stretchy, and clear, resembling egg whites. This type of mucus helps sperm travel through the cervix and into the uterus.
4. By tracking changes in cervical mucus, women can identify the most fertile days in their menstrual cycle, which can be helpful for those trying to achieve or avoid pregnancy. This method is considered natural, non-invasive, and hormone-free.
5. Cervical mucus examination can provide valuable insights into women’s reproductive health. It can help detect hormonal imbalances, certain infections, and issues with cervical function. In some cases, abnormalities in the cervical mucus can serve as an early indicator of potential fertility problems.
The Two Jobs of Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus plays two crucial roles in the female reproductive system.
- Firstly, it facilitates the movement of sperm through the cervix during ovulation, increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
- Secondly, it acts as a barrier, preventing harmful substances such as bacteria and viruses from entering the cervix and potentially causing infection.
Cervical mucus is instrumental in both fertility and protection within the female reproductive system.
Types of Cervical Mucus Throughout the Menstrual Cycle
Throughout the menstrual cycle, the consistency and appearance of cervical mucus can vary, indicating different stages of fertility. The different types of cervical mucus include dry, sticky, creamy, slippery (resembling raw egg whites), and wet. These variations reflect the changes in hormone levels that regulate the menstrual cycle.
Dry and Sticky Mucus
During the post-menstruation phase, which typically occurs in the first few days of the menstrual cycle, the cervical mucus may not be easily noticeable. However, as this phase progresses, the mucus may undergo changes and become sticky or tacky in texture. It is common for the mucus to appear yellow, white, or cloudy in color during this stage. The presence of sticky mucus indicates that ovulation is still a few days away.
Creamy and Wet Mucus
As the menstrual cycle continues, estrogen levels rise, causing the cervical mucus to become creamy and wet. This type of mucus provides a more favorable environment for sperm, although it is not as fertile as the slippery mucus that occurs closer to ovulation.
Slippery and Stretchy Mucus
Right before ovulation, estrogen levels peak, leading to the production of slippery and stretchy cervical mucus. This mucus closely resembles raw egg whites and is highly fertile. It is during this time that fertilization is most likely to occur.
- The peak in estrogen levels occurs right before ovulation.
- As a result, the cervical mucus becomes slippery and stretchy.
- This mucus is similar in appearance to raw egg whites.
- This type of cervical mucus is considered highly fertile.
- The fertile cervical mucus provides an ideal environment for sperm survival and movement.
- The presence of this mucus indicates that ovulation is about to occur.
- Couples trying to conceive are advised to have intercourse during this time to increase their chances of successful fertilization.
“Right before ovulation, estrogen levels peak, leading to the production of slippery and stretchy cervical mucus. This mucus closely resembles raw egg whites and is highly fertile. It is during this time that fertilization is most likely to occur.”
Cloudy and Sticky Mucus
After ovulation, estrogen levels drop, and progesterone levels rise. As a result, the cervical mucus thickens and may become cloudy and sticky again. This change in mucus consistency indicates the closing of the fertile window and the approach of menstruation.
- Estrogen levels decrease
- Progesterone levels increase
- Cervical mucus thickens
- Mucus may become cloudy and sticky
- Indicates the closing of the fertile window and approaching menstruation
“This change in mucus consistency indicates the closing of the fertile window and the approach of menstruation.”
Hormonal Shifts and Changes in Cervical Mucus
The changes in cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle are closely tied to hormonal shifts. Estrogen and progesterone, the primary reproductive hormones, regulate the production and quality of cervical mucus.
- Cervical mucus changes throughout the menstrual cycle
- Hormonal shifts influence cervical mucus
- Estrogen and progesterone regulate production and quality of cervical mucus.
“The changes in cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle are closely tied to hormonal shifts.”
Estrogen and Cervical Mucus
As estrogen levels rise before ovulation, the cervical mucus undergoes a significant transformation. It becomes increasingly abundant, thin, and stretchy, which is crucial for improving sperm motility and providing a suitable medium for sperm transport in the female reproductive tract. Additionally, estrogen causes an increase in blood flow to the cervix, leading to an increased production of mucus.
- The rise in estrogen levels before ovulation.
- Increased abundance, thinness, and stretchiness of cervical mucus.
- Importance of these changes for sperm motility and transport.
- Estrogen’s role in increasing blood flow to the cervix.
- Increased mucus production as a result.
“Estrogen plays a vital role in preparing the female reproductive tract for fertility by transforming the cervical mucus into a favorable environment for sperm transport.”
Progesterone and Cervical Mucus
After ovulation, progesterone becomes dominant, causing the cervical mucus to thicken. This change in mucus consistency serves as a physical barrier to prevent sperm from reaching the egg. The thickening of the mucus is essential for creating an environment more hostile to sperm and minimizing the chances of fertilization.
- Progesterone dominance after ovulation
- Thicker cervical mucus acts as a barrier to sperm
- Increased hostile environment for sperm
- Reduced chances of fertilization.
Fertile Cervical Mucus and Conception
The presence of fertile cervical mucus indicates the most optimum time for conception. When cervical mucus resembles raw egg whites and is slippery and stretchy, it signifies heightened fertility. This type of mucus facilitates the movement and survival of sperm, making it easier for them to reach the egg for fertilization.
- Fertile cervical mucus indicates the best time for conception
- Raw egg whites-like consistency suggests heightened fertility
- Slippery and stretchy mucus aids the movement and survival of sperm
- Helps sperm reach the egg for fertilization
The Role of Cervical Mucus in Sperm Transport
Cervical mucus plays a crucial role in facilitating sperm movement towards the egg for fertilization. This slippery and stretchy medium helps sperm navigate the cervix and reach the fallopian tubes.
Key Point: Fertile cervical mucus provides optimal conditions for sperm motility, increasing their likelihood of successfully reaching the egg.
- Cervical mucus aids in sperm transportation.
- Fertile cervical mucus enhances sperm motility.
- Cervical mucus creates a favorable environment for sperm on their journey to the egg.
“The slippery and stretchy texture of fertile cervical mucus provides optimal conditions for sperm motility, enhancing their chances of reaching the egg.”
Estrogen and Progesterone: The Hormones Behind Cervical Mucus Changes
Estrogen and progesterone are two hormones that have crucial functions in controlling cervical mucus during the menstrual cycle. Specifically, estrogen stimulates the production of thin, stretchy, and fertile mucus, which aids in the movement of sperm towards the egg. On the other hand, progesterone causes the mucus to thicken, making it less fertile and more difficult for sperm to penetrate.
To summarize:
- Estrogen promotes the production of thin, stretchy, and fertile cervical mucus.
- Progesterone causes the mucus to thicken, reducing its fertility.
It is important to understand the effects of these hormones on cervical mucus as it greatly impacts fertility and the possibility of conception.
Note: Cervical mucus changes throughout the menstrual cycle due to the influence of estrogen and progesterone.
Cervical Mucus Examination: Menstrual Cycle and Early Pregnancy
Understanding the changes in cervical mucus is crucial for monitoring fertility and identifying potential pregnancy.
-
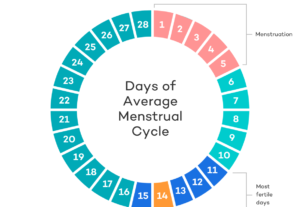
Most women with a 28-day menstrual cycle ovulate around day 14, coinciding with the presence of slippery, stretchy, and highly fertile cervical mucus.
-
Bullet points added for clarity
Cervical Mucus Changes during Early Pregnancy
If fertilization occurs at ovulation, some women may continue to produce cervical mucus, even after ovulation has taken place. The persistence of cervical mucus following ovulation can indicate a possible pregnancy, as hormonal changes associated with early pregnancy can lead to increased mucus production.
- Fertilization at ovulation can result in continued cervical mucus production.
- The presence of cervical mucus after ovulation suggests a potential pregnancy.
- Hormonal changes during early pregnancy stimulate increased mucus production.
“The persistence of cervical mucus following ovulation can indicate a possible pregnancy.”
Implantation Bleeding and Cervical Mucus
Implantation bleeding is a common occurrence when the fertilized egg implants into the uterine lining. It is characterized by light spotting or brown or pink tinged cervical mucus. This discharge is typically lighter and shorter in duration compared to menstrual bleeding. It is important to note that implantation bleeding can sometimes be mistaken for the start of menstruation.
Key points to remember:
- Implantation bleeding is characterized by light spotting or brown or pink tinged cervical mucus.
- It occurs when the fertilized egg implants into the uterine lining.
- The discharge is typically lighter and shorter in duration compared to menstrual bleeding.
- It can sometimes be mistaken for the start of menstruation.
Cervical Mucus Method: Tracking and Predicting Fertility
The cervical mucus method is a technique used to predict and track fertility patterns by monitoring the changes in cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle. This method is often used as part of a fertility awareness-based method (FAM) to help individuals determine their fertile and non-fertile days.
How to Examine and Chart Cervical Mucus
To examine cervical mucus, one can:
- Wipe the opening of the vagina with tissue
- Check the mucus on underwear
- Insert clean fingers into the vagina.
It is crucial to check the mucus consistently and record the findings on a chart to accurately track the changes.
Timing and Safe Days
The cervical mucus method is a useful technique for identifying safe and unsafe days for sexual activity. It relies on observing the presence or absence of fertile mucus.
During non-fertile days, unprotected sex can be considered safe. However, it is important to use alternative forms of birth control during fertile days to prevent unplanned pregnancy.
To summarize:
- The cervical mucus method identifies safe and unsafe days for sexual activity.
- Unprotected sex is safe during non-fertile days.
- Alternative forms of birth control should be used during fertile days.
Combining the Cervical Mucus Method with the Temperature Method
The effectiveness of the cervical mucus method can be further enhanced by combining it with the temperature method. This combination allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the woman’s fertility cycle.
- By tracking changes in basal body temperature, we can gain additional insights into the timing of ovulation.
- The temperature method involves taking daily temperature readings using a special thermometer.
- The rise in basal body temperature after ovulation can confirm the fertile window determined by cervical mucus observation.
Combining these two methods provides a more accurate and reliable way to determine the most fertile days in a woman’s cycle.
Note: The temperature method should be used in conjunction with the cervical mucus method for better results.
The 2-Day Method
The 2-day method is a simpler approach to tracking fertility through cervical mucus observation. To determine fertility, individuals only need to ask themselves if they had cervical mucus on a particular day and the previous day. If the answer is “yes” to either of those days, it is advised to use birth control or abstain from vaginal intercourse to avoid the risk of pregnancy.
Influence on Cervical Mucus and Factors Affecting Accuracy
Several factors can influence changes to cervical mucus and impact the accuracy of the cervical mucus method. These factors include:
-
Vaginal sex: Engaging in sexual activity can affect the consistency and appearance of cervical mucus. It is important to take this into consideration when using the cervical mucus method for fertility tracking.
-
Use of lubricants: Certain lubricants can alter the texture of cervical mucus, which may affect the accuracy of tracking. It is recommended to avoid using lubricants when practicing the cervical mucus method.
-
Medications: Some medications can impact cervical mucus production and quality. If you are taking any medications, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to understand how they may affect your mucus observations.
-
Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding can influence cervical mucus, leading to changes in its consistency and amount. Women who are breastfeeding should be aware of these changes when using the cervical mucus method.
-
Surgical procedures on the cervix: Any surgical procedure done on the cervix has the potential to affect cervical mucus production and characteristics. It is important to discuss this with your healthcare provider if you have recently undergone any such procedures.
-
Douching: Douching can alter the natural pH balance and flora of the vagina, which can in turn affect cervical mucus. Douching should be avoided when using the cervical mucus method for tracking fertility.
-
Early menopause: Women approaching or experiencing early menopause may notice changes in their cervical mucus patterns. These changes can make it more challenging to accurately track fertility using the cervical mucus method.
-
Recent use of hormonal birth control or emergency contraception pills: The use of hormonal birth control or emergency contraception pills can affect cervical mucus production and quality. It is important to consider the impact of these medications on the cervical mucus method and consult with a healthcare professional if necessary.
By being aware of these factors and their potential influence on cervical mucus, individuals can make more informed decisions and improve the accuracy of the cervical mucus method for fertility tracking.
Low Discharge Production
Individuals with low discharge production may find it challenging to observe and track changes in cervical mucus accurately. This can affect the effectiveness of the cervical mucus method as a fertility awareness tool.
In conclusion, understanding cervical mucus examination is essential for predicting fertility and ensuring effective contraception. Charting and observing changes in cervical mucus provide valuable insights into the menstrual cycle and the optimum time for conception. It is important to note that consulting a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and improve the accuracy of using the cervical mucus method to track and predict fertility.
- Individuals with low discharge production may struggle to accurately track changes in cervical mucus.
- Effective use of the cervical mucus method is crucial for fertility awareness.
- Charting and observing cervical mucus changes offer insights into the menstrual cycle and best time for conception.
- Consultation with a healthcare professional can enhance accuracy and provide personalized guidance.
💡
You may need to know these questions about cervical mucus examination
What are the 4 types of cervical mucus?
In addition to the categories of dry, damp, and wet/slippery cervical mucus, there is a fourth type known as creamy cervical mucus. This type typically appears after the fertile window and signifies the end of ovulation. Creamy cervical mucus has a thicker consistency and may provide a protective environment for the sperm to survive in the reproductive tract for longer periods.
Type 1 and Type 2 cervical mucus are usually associated with the early stages of the menstrual cycle and have lower fertility potential. Type 3 cervical mucus indicates a transition and suggests that you are entering the fertile window. This transitional mucus is often characterized by a more stretchy and slippery texture, making it easier for sperm to swim through the cervix towards the egg. Understanding the different types of cervical mucus can help individuals track their fertility and plan accordingly for conception.
What does unhealthy cervical mucus look like?
Unhealthy cervical mucus can exhibit distinct characteristics that deviate from the normal texture and appearance. It may appear clumpy, lumpy, or have an irregular consistency. An unhealthy mucus may also emit an unpleasant odor, which is not typical for healthy cervical mucus that is generally odorless. It is important to pay attention to any changes in texture, consistency, or odor, as these variations could indicate an underlying issue that requires further medical evaluation.
How effective is cervical mucus examination?
Cervical mucus examination can be an effective method for birth control when used correctly and with proper training. However, its effectiveness may vary depending on individual circumstances. It is estimated that about 23 out of 100 women using the cervical mucus method for birth control may get pregnant in the first year of typical use. With perfect use and comprehensive understanding of the method, the pregnancy rate can be as low as 3 out of 100 women a year. Therefore, it is clear that formal training is essential to master the cervical mucus method and optimize its effectiveness in preventing pregnancy.
How do you check cervical mucus internally?
To check cervical mucus internally, you may gently insert two fingers into your vagina until you reach your cervix. Once you find the cervix, place one finger on each side and lightly press to collect the mucus. Slowly move your fingers towards the opening of the cervix to gather the mucus for observation. It is important to ensure cleanliness and proper hygiene during this process to avoid any potential infections or discomfort.
Reference source
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/birth-control/fertility-awareness/whats-cervical-mucus-method-fams
https://www.med.unc.edu/timetoconceive/study-participant-resources/cervical-mucus-testing-information/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21957-cervical-mucus
https://middlesexhealth.org/learning-center/tests-and-procedures/cervical-mucus-method-for-natural-family-planning