Are you familiar with the term “cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia”?
It might sound complicated, but fear not, because we’re about to embark on an intriguing journey through the world of cervical health.
Join us as we explore how Pap smears can reveal hidden secrets within our bodies, leading to life-changing treatment decisions at Moffitt Cancer Center.
Stay tuned for a mind-opening adventure!
cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia
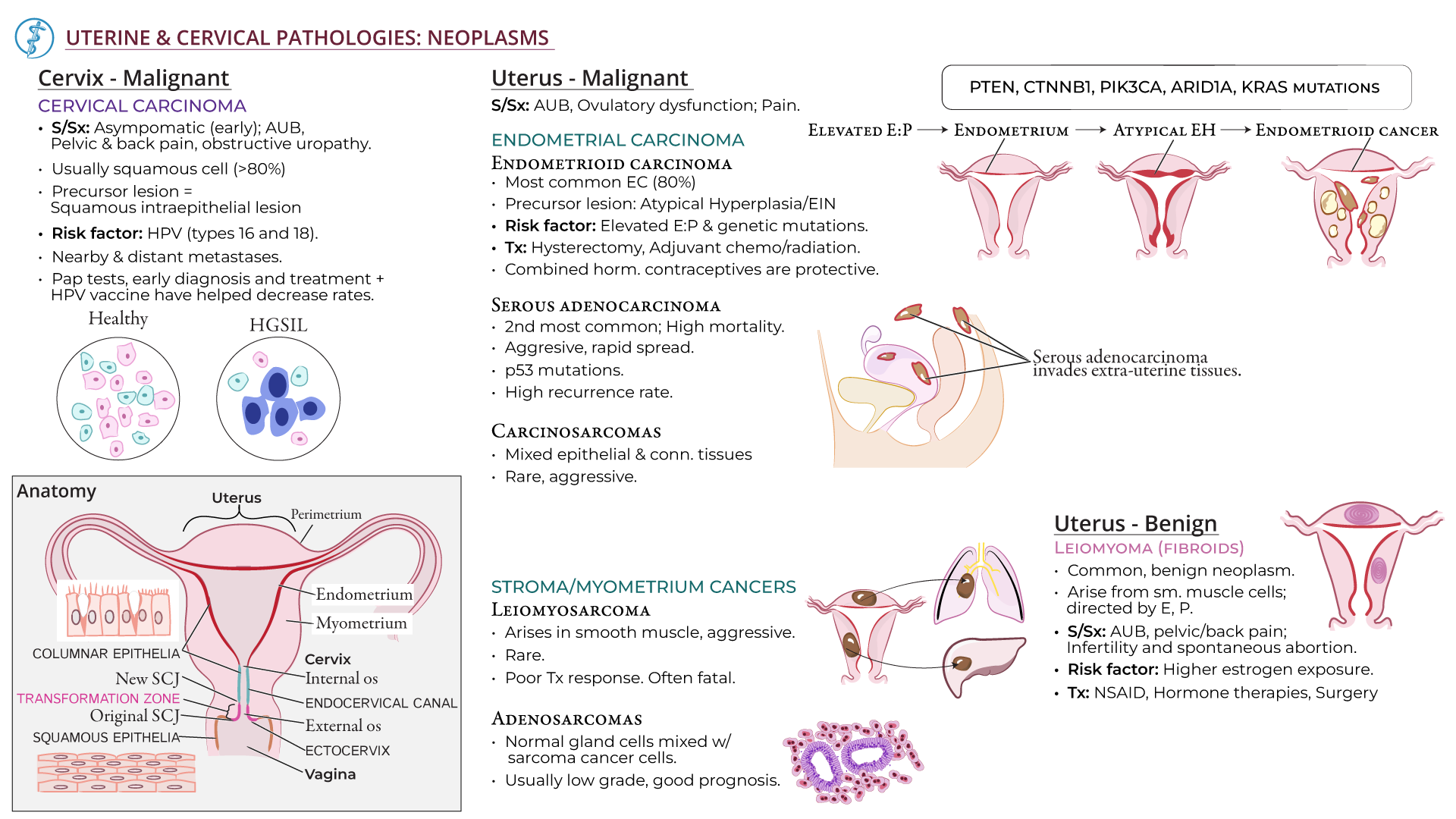
Cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia refers to the detection of atypical squamous cells in the cervix during a Pap smear.
It is important to note that the presence of these abnormal cells does not necessarily indicate cervical cancer.
Other possible causes include HPV infection, benign cellular changes, cervical cysts or polyps, and low hormone levels in menopausal or post-menopausal patients.
Further testing, such as HPV analysis or additional exams like cervical biopsies, may be recommended after an atypical Pap smear result.
It is crucial to promptly treat any detection of cancerous squamous cells.
Early detection allows for a wider range of treatment options.
Moffitt Cancer Center provides comprehensive diagnostic tests and treatments for cervical cancer, supported by the latest research and clinical trials.
Individuals with abnormal Pap smear results can contact Moffitt Cancer Center to request an appointment with a gynecologic oncologist.
While virtual visits may be available, in-person examination and evaluation are typically necessary for treatment decisions.
Key Points:
- Cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia is the detection of atypical squamous cells in the cervix during a Pap smear.
- Presence of these cells does not always indicate cervical cancer.
- Other possible causes include HPV infection, benign cellular changes, cervical cysts or polyps, and low hormone levels.
- Further testing, such as HPV analysis or cervical biopsies, may be recommended.
- Prompt treatment is crucial for cancerous squamous cell detection.
- Early detection allows for more treatment options.
cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia refers to an abnormal growth of squamous cells in the cervix, which can be a precursor to cervical cancer if left untreated.
2. Research indicates that cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia is commonly associated with infection by the high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), emphasizing the importance of HPV vaccination and regular cervical screening.
3. Although cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia is a concerning condition, it can often be effectively managed through various treatment options, such as cryotherapy, cone biopsy, or excisional procedures.
4. In some cases, hormonal factors like estrogen imbalances or prolonged use of hormonal contraceptives can contribute to the development of cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia.
5. Regular follow-up examinations are crucial for individuals diagnosed with cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia, as it is essential to monitor for any changes or progression of the condition over time.
Pap Smears And The Detection Of Atypical Squamous Cells
Pap smears are commonly used screening tests to detect abnormalities in the cervix, such as atypical squamous cells. During a Pap smear, a sample of cells from the cervix is collected and examined under a microscope. This procedure enables early detection of various cervical conditions, including atypical squamous cells.
It is important to note that atypical squamous cells are not always indicative of cervical cancer. In fact, most cases do not progress to cancer. However, they should be viewed as a warning sign that further testing and evaluation are necessary. It is crucial to understand that the presence of atypical squamous cells in a Pap smear does not automatically mean a cancer diagnosis. Additional testing is generally recommended to determine the underlying cause.
To summarize:
- Pap smears are screening tests for detecting cervical abnormalities.
- Atypical squamous cells can be identified through Pap smears.
- Atypical squamous cells do not always indicate cervical cancer.
- Further testing is usually recommended to identify the underlying cause.
Understanding The Link Between Atypical Squamous Cells And Cervical Cancer
The presence of atypical squamous cells does not always indicate cervical cancer, but it is important to investigate further to rule out the possibility. One significant cause of atypical squamous cells is infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection that can lead to abnormal cell growth and potentially develop into cervical cancer if left untreated.
It is essential to note that while HPV infection is a known risk factor for cervical cancer, not all women with atypical squamous cells have HPV or will develop cancer. Other potential causes of atypical squamous cells include benign cellular changes, cervical cysts or polyps, and hormonal imbalances in menopausal or post-menopausal individuals.
- Atypical squamous cells may not indicate cervical cancer
- HPV infection can lead to abnormal cell growth and cervical cancer
- Not all women with atypical squamous cells have HPV or will develop cancer
- Other causes: benign cellular changes, cervical cysts or polyps, hormonal imbalances in menopausal or post-menopausal individuals.
Other Causes Of Atypical Squamous Cells
In addition to HPV infection, several other factors can contribute to the presence of atypical squamous cells in a Pap smear. Benign cellular changes, such as inflammation or irritation of the cervix, can lead to the appearance of atypical cells. Cervical cysts or polyps, which are abnormal growths in the cervix, can also cause the presence of atypical squamous cells.
Furthermore, low hormone levels in menopausal or post-menopausal patients can lead to changes in the cervical cells, including the appearance of atypical squamous cells. It is important to consider these other potential causes before jumping to conclusions about the presence of cancerous cells.
Additional Testing Options Following An Atypical Pap Smear Result
When receiving an atypical Pap smear result, healthcare providers often recommend further testing to determine the underlying cause of the abnormal cells. This can include re-analyzing the cell sample for HPV presence or performing additional exams, such as cervical biopsies, endocervical sampling exams, and colposcopies.
Re-analyzing the sample for HPV can help identify if the atypical cells are caused by an HPV infection, which may require specific treatment or close monitoring. Cervical biopsies, endocervical sampling exams, and colposcopies allow for a more detailed examination of the cervix, providing valuable information for diagnosis and treatment planning.
The Importance Of Prompt Treatment For Cancerous Squamous Cells
If cancerous squamous cells are detected during a Pap smear, prompt treatment becomes crucial to prevent further progression and potential spread of the disease. Early detection allows for a higher likelihood of successful treatment outcomes and provides more options for treatment.
Cervical cancer that is caught early is highly treatable, with various treatment options available, including:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Prompt treatment can help minimize the impact of cancer on an individual’s life and increase the chances of a full recovery.
Early Detection And Treatment Options For Cervical Cancer
Early detection of cervical cancer is possible through routine Pap smears, which can detect abnormal cells that may indicate the presence of cancer. Regular screenings play a crucial role in identifying early-stage cervical cancer when treatment options are most effective and less invasive.
Moffitt Cancer Center offers comprehensive diagnostic tests and treatments for cervical cancer. With a multidisciplinary approach and access to the latest research and clinical trials, Moffitt provides patients with the best possible care. Their team of experts is dedicated to ensuring timely and accurate diagnoses, tailoring treatment plans to each individual’s unique needs.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Tests And Treatments At Moffitt Cancer Center
At Moffitt Cancer Center, patients can expect to receive comprehensive diagnostic tests and state-of-the-art treatments for cervical cancer. The center’s team of specialists utilizes advanced imaging technologies, such as MRI and PET scans, to assess the extent and stage of the disease accurately.
Treatment options at Moffitt Cancer Center are tailored to the individual needs of each patient. These options may include:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Combination of these treatments
With a focus on individualized care and the latest advancements in cancer treatment, Moffitt Cancer Center strives to provide the best possible outcomes for patients with cervical cancer.
“Moffitt Cancer Center: where expertise meets innovative care.”
Requesting An Appointment With A Gynecologic Oncologist
If an individual has recently received abnormal Pap smear results with atypical squamous cells, it is crucial to seek further evaluation from a healthcare professional. Moffitt Cancer Center offers a team of skilled gynecologic oncologists who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer.
Requesting an appointment with a gynecologic oncologist at Moffitt Cancer Center is a simple process. Interested individuals can call or submit an online form to request an appointment. The center’s staff will guide patients through the necessary steps and provide the support needed to begin the evaluation process promptly.
- Seek further evaluation from a healthcare professional for abnormal Pap smear results with atypical squamous cells.
- Moffitt Cancer Center specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer.
- Request an appointment by calling or submitting an online form.
- The center’s staff will guide patients through the necessary steps and provide support.
Availability Of Virtual Visits For Consultation
Virtual visits have become an option for consultation with a gynecologic oncologist at Moffitt Cancer Center. Through these virtual visits, patients can connect with their healthcare providers remotely, which eliminates the need for in-person visits for initial evaluations or treatment option discussions.
It is essential to recognize that while virtual visits are available for some consultations, in-person examination and evaluation are usually required to make informed decisions about treatment. This ensures that healthcare providers have a comprehensive understanding of each individual’s condition, enabling the creation of the most accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
In-Person Examination And Evaluation For Treatment Decisions
While virtual visits can provide some level of initial evaluation and consultation, an in-person examination and evaluation are usually essential for treatment decisions regarding cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia. This allows healthcare providers to:
- Conduct a thorough physical examination
- Discuss treatment options in detail
- Answer any questions or concerns that the patient may have
In-person examinations provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to assess the extent of the condition and fully understand each individual’s unique circumstances before making treatment recommendations.
Moffitt Cancer Center recognizes the importance of personalized care and offers comprehensive in-person evaluations to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients with cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia.
💡
You may need to know these questions about cervical squamous atypical hyperplasia
Should I worry about atypical squamous cells?
Finding atypical squamous cells in a Pap test does not necessarily indicate a cause for alarm. While it is important to take any abnormal Pap results seriously, it is crucial to remember that most cases of atypical squamous cells are not indicative of cervical cancer. Nonetheless, discussing the results with a healthcare professional is crucial in order to create a personalized plan and determine the appropriate course of action. They can provide guidance and recommendations based on your specific situation, further ensuring your peace of mind.
What does atypical squamous cells on cervix mean?
When the term “atypical squamous cells” is used to describe cells on the cervix, it indicates that there are some abnormalities present. However, the specific cause of these changes is not determined, whether it is linked to HPV infection or not. This finding, known as atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US), is the most frequent abnormal result found in Pap tests. Further diagnostic tests may be necessary to determine the cause and severity of these cell changes.
Is cervical hyperplasia cancerous?
Cervical hyperplasia, while not inherently cancerous, does have the potential to progress into cervical cancer if left untreated. It refers to abnormal cell changes in the surface of the cervix, which can be detected through cervical screening tests. Detecting and treating cervical hyperplasia at an early stage is crucial in preventing the development of cervical cancer. Regular screenings and appropriate medical interventions are essential in managing cervical dysplasia and reducing the risk of cervical cancer.
What causes cervical hyperplasia?
Cervical hyperplasia is primarily caused by infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a widespread sexually transmitted disease and is responsible for most cases of cervical dysplasia. Although there are over 200 types of HPV, only certain strains have the potential to lead to the formation of abnormal cervical cells.
Reference source
https://www.moffitt.org/cancers/cervical-cancer/diagnosis/screening/atypical-squamous-cells/
https://www.cancer.gov/types/cervical/screening/abnormal-hpv-pap-test-results
https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/cervical-dysplasia
https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/cervical-dysplasia