Discover the hidden dangers lurking beneath the sheets.
Chlamydia, the sneaky and stealthy STD, can wreak havoc on your health without warning.
Uncover its secrets, learn how to protect yourself, and explore the crucial steps you must take to avoid dire consequences.
Buckle up for this eye-opening journey!
chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) that can cause serious health problems if left untreated.
It can be spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex, even without ejaculation.
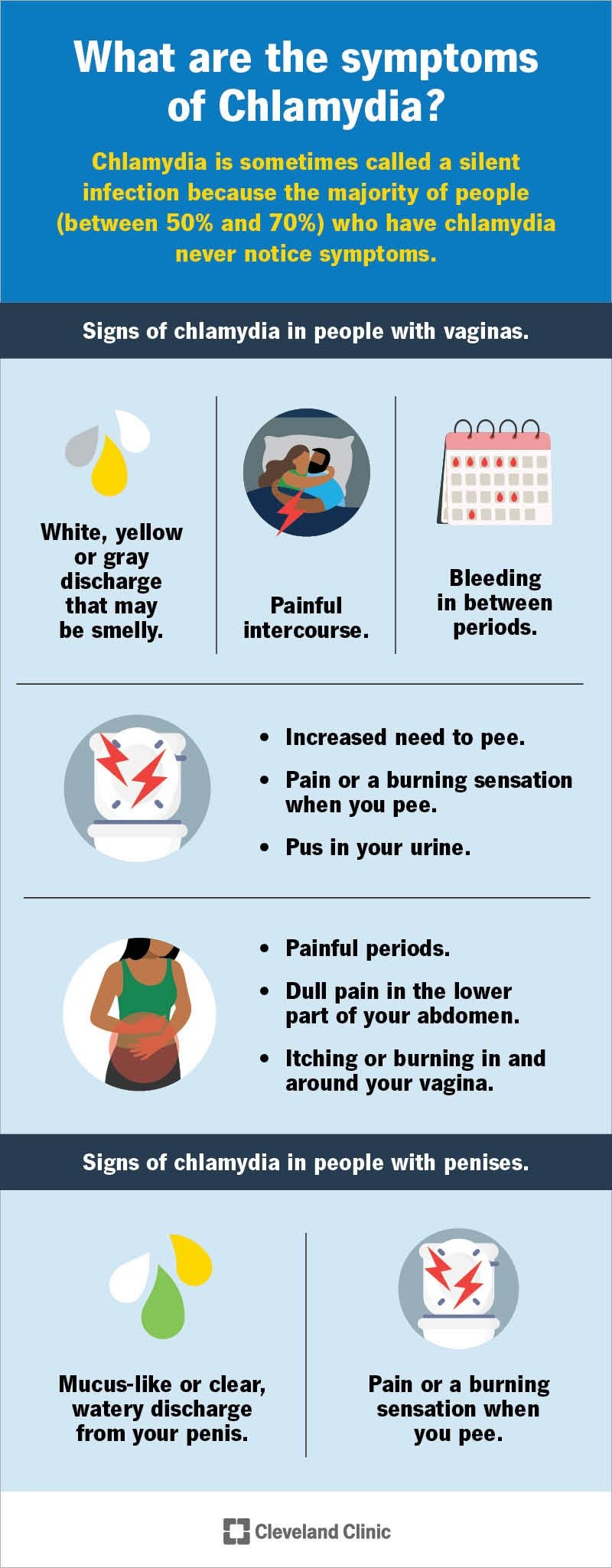
While chlamydia often has no symptoms, it can lead to abnormal vaginal discharge, burning during urination, and other complications in women.
In men, it can cause discharge from the penis and pain during urination.
Chlamydia can be diagnosed through laboratory tests using urine or vaginal samples, and it can be cured with proper treatment.
However, repeat infection is common, so testing should be done again after treatment.
It is important to wait until completion of treatment before having sex again.
Untreated chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and increased risk of HIV transmission.
Key Points:
- Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) that can cause serious health problems if left untreated.
- It can be spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex, even without ejaculation.
- Symptoms may not always be present for chlamydia, but it can lead to abnormal vaginal discharge, burning during urination, and other complications in women.
- In men, it can cause discharge from the penis and pain during urination.
- Chlamydia can be diagnosed through laboratory tests using urine or vaginal samples and can be cured with proper treatment.
- It is important to wait until completion of treatment before having sex again, as repeat infection is common and untreated chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and increased risk of HIV transmission.
chlamydia – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the world, with approximately 131 million new cases reported annually.
2. Contrary to popular belief, chlamydia can infect both men and women, but its symptoms are often more noticeable in women. However, the infection can still cause serious complications in men, such as epididymitis (inflammation of the reproductive system) and infertility.
3. While chlamydia primarily affects the genital areas, it can also infect the throat and eyes through oral or ocular sexual contact. This type of infection is called pharyngeal chlamydia or ocular chlamydia, respectively.
4. Chlamydia can be transmitted from an infected pregnant person to their baby during childbirth. If left untreated, it can lead to various health problems in the newborn, including pneumonia, conjunctivitis, and even blindness.
5. Interestingly, chlamydia is caused by a bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis, which undergoes a distinctive life cycle. It exists in two forms: the infectious elementary body that allows transmission between individuals, and the non-infectious reticulate body that reproduces inside human cells.
Introduction To Chlamydia As A Common STD
Chlamydia, caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis, is a highly prevalent sexually transmitted disease (STD) affecting both men and women globally. It is easily transmitted during sexual activities. However, the alarming aspect is that Chlamydia often goes unnoticed because it does not exhibit symptoms, leading to detrimental effects for individuals unaware of their infection.
- Chlamydia is a silent STD that affects both men and women worldwide
- Caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis
- Easily transmitted through sexual activities
- Lacks noticeable symptoms, hence often goes unnoticed
- Unaware individuals may face significant harm from the infection
Permanent Damage And Potential Fatalities
One of the most concerning aspects of Chlamydia is its ability to cause permanent damage, particularly in women. If left untreated, Chlamydia can lead to severe complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can cause scarring of the fallopian tubes, leading to infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and the potential for ectopic pregnancy, which can be life-threatening.
In addition, Chlamydia increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy and potentially fatal complications. Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tubes. This condition requires immediate medical attention as it can lead to internal bleeding and threaten the lives of both the mother and the unborn child.
Modes Of Transmission: Vaginal, Anal, And Oral Sex
Chlamydia is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Moreover, it can be contracted even without ejaculation or penetration. The bacteria can infect the cervix in women, urethra in men, rectum, and throat, making it highly transmissible and a serious concern for sexually active individuals.
It is crucial to understand that Chlamydia can easily spread through various types of sexual activities, regardless of gender or sexual orientation. This knowledge reinforces the importance of safer sex practices and regular testing to maintain sexual health and prevent the transmission and spread of Chlamydia.
- Chlamydia is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
- It can be contracted even without ejaculation or penetration.
- The bacteria can infect the cervix in women, urethra in men, rectum, and throat.
- Chlamydia is highly transmissible and a serious concern for sexually active individuals.
- Safer sex practices and regular testing are essential in maintaining sexual health and preventing the transmission and spread of Chlamydia.
“It is crucial to understand that Chlamydia can easily spread through various types of sexual activities, regardless of gender or sexual orientation.”
Prevention Methods: Abstinence, Condom Usage, And Long-Term Monogamy
While practicing abstinence is the only foolproof way to completely avoid STDs, it may not be a feasible option for everyone. For those who choose to engage in sexual activities, precautions can be taken to reduce the risk of Chlamydia and other STDs.
Using condoms consistently and correctly during every sexual encounter provides substantial protection against Chlamydia. Condoms act as a barrier, preventing the exchange of bodily fluids and significantly reducing the chances of transmission. It is essential to emphasize the correct usage of condoms, including storage, expiration dates, and proper application.
Engaging in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has tested negative for Chlamydia can also lower the risk of infection. However, it is crucial to note that regular testing is necessary to ensure ongoing sexual health, as individuals can acquire Chlamydia outside of their monogamous relationship.
Increased Risk Factors For Chlamydia
Certain populations are at a higher risk of contracting Chlamydia due to various factors. Sexually active individuals, especially young people, have a greater likelihood of acquiring the infection. This is attributed to factors such as:
- Multiple sexual partners
- Inconsistent use of protection
- A lack of awareness about sexual health
Additionally, gay and bisexual men face an increased risk of Chlamydia due to the higher prevalence of the infection in their communities. Therefore, it is crucial for these individuals to prioritize:
- Regular testing
- Safer-sex practices, including condom usage
- Regular medical check-ups
It is important to acknowledge the higher risk faced by certain populations and take proactive measures to prevent and detect Chlamydia infections.
Transmission And Impact On Newborns
Pregnant individuals with Chlamydia can pass the infection to their infants during childbirth. This is known as perinatal transmission and can have severe consequences for the newborn. Chlamydia infection in infants can lead to eye infection (conjunctivitis) or pneumonia.
It is essential for pregnant individuals to undergo testing for Chlamydia early in their pregnancy to receive appropriate treatment and reduce the risk of transmission to their babies.
- Perinatal transmission is the transmission of Chlamydia from a pregnant individual to their baby during childbirth.
- Chlamydia infection in infants can result in conjunctivitis or pneumonia.
- Early testing for Chlamydia during pregnancy is crucial for timely treatment and reducing the risk of transmission.
Symptoms And Health Problems In Women
One of the most challenging aspects of Chlamydia is its asymptomatic nature, particularly in women. The infection often goes unnoticed, allowing the bacteria to cause significant damage before it is detected. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include abnormal vaginal discharge, a burning sensation when urinating, and unusual sores.
If left untreated, Chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause long-term health issues and reproductive complications. It is crucial for women to seek regular testing and promptly report any symptoms to healthcare providers for early diagnosis and treatment.
Importance Of Testing And Treatment
Testing and treatment are paramount in preventing the health problems associated with Chlamydia. Regular testing allows for early detection of the infection, even in the absence of symptoms. Screening can be done through laboratory tests using urine or vaginal samples. It is vital for sexually active individuals, especially those at higher risk, to undergo routine testing for Chlamydia as part of their regular healthcare.
Chlamydia can be effectively treated with appropriate antibiotics. However, it is essential to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by a healthcare provider. Failure to do so may result in recurrent or persistent infections that can lead to complications and increase the chances of transmitting the infection to others.
- Testing and treatment are paramount in preventing health problems associated with Chlamydia.
- Regular testing allows for early detection of the infection, even without symptoms.
- Screening can be done through laboratory tests using urine or vaginal samples.
- It is vital for sexually active individuals, especially those at higher risk, to undergo routine testing.
- Chlamydia can be effectively treated with appropriate antibiotics.
- Completing the full course of treatment is essential.
- Failure to do so may result in recurrent or persistent infections and increase the chances of transmitting the infection to others.
“Testing and treatment are paramount in preventing the health problems associated with Chlamydia.”
Additional Symptoms And Complications In Men
While men often experience milder symptoms compared to women, Chlamydia can still cause health problems in males. Symptoms may include:
- Discharge from the penis
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Pain and swelling in the testicles
In rare cases, if Chlamydia is left untreated in men, the infection can spread to the epididymis (the tube carrying sperm) and cause epididymitis. This can result in severe pain and infertility. Therefore, it is crucial for men to seek timely medical attention if they experience any symptoms or suspect exposure to Chlamydia.
Remember:
Early detection and treatment are key to preventing complications associated with Chlamydia in men.
Long-Term Consequences And HIV Transmission Risks
Untreated Chlamydia can have long-term consequences for both men and women. In women, untreated Chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), scarring of the fallopian tubes, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility. Additionally, it can cause chronic pelvic or abdominal pain.
Furthermore, untreated Chlamydia increases the risk of HIV transmission. The presence of Chlamydia can make it easier for HIV to enter the body during sexual activity, leading to a higher likelihood of HIV infection. This highlights the importance of regular testing for both Chlamydia and HIV, especially in high-risk populations.
Chlamydia is a prevalent and easily transmissible STD that can cause significant harm to both men and women. Its silent nature and potential for long-term damage make it crucial for sexually active individuals to prioritize regular testing and safe-sex practices. Early diagnosis and proper treatment not only protect individual health but also prevent the transmission and spread of Chlamydia within communities. Awareness, education, and access to testing and treatment are vital in combating the impact of this silent yet impactful STI.
💡
You may need to know these questions about chlamydia
What is one of the first signs of chlamydia?
One of the first signs of chlamydia can be the presence of abnormal vaginal discharge, which may appear yellowish and have a strong smell. Additionally, individuals may experience swelling inside the vagina and pain during sexual intercourse. Furthermore, another early indication can be discomfort or a burning sensation while urinating.
How long does chlamydia last in me?
While antibiotic treatment for chlamydia typically takes one to three weeks to resolve the infection, it is essential to note that asymptomatic individuals may unknowingly carry the infection for years. This extended duration of infection could lead to various severe complications and increase the risk of transmitting the infection to others. Therefore, timely detection, diagnosis, and treatment are crucial to ensure the prompt resolution of the infection and mitigate potential long-term consequences.
What does chlamydia turn to?
If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health complications. In women, it can progress to pelvic inflammatory disease, causing long-term pain and infertility. In men, untreated chlamydia can result in painful testicular inflammation. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent these adverse outcomes and ensure a healthy reproductive system.
Will chlamydia go away on its own?
Chlamydia, a common sexually transmitted infection, does not typically resolve on its own. Without treatment, it can lead to severe health complications. However, the good news is that antibiotics are highly effective in curing Chlamydia. Regular testing is crucial for sexually active individuals who are not in a committed monogamous relationship to ensure early detection and timely treatment. With appropriate medical intervention, Chlamydia can be effectively treated and its potential long-term consequences can be avoided.
Reference source
https://www.cdc.gov/std/chlamydia/stdfact-chlamydia.htm
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/stds-hiv-safer-sex/chlamydia/chlamydia-symptoms
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chlamydia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355349
https://www.verywellhealth.com/how-long-does-chlamydia-last-5323749