Have you ever found yourself diving deep into a medical research article, only to be met with the frustrating words “access denied”?
It’s like hitting a brick wall while searching for answers.
But what if there was a way to overcome this temporary block and unlock a world of scientific knowledge?
Enter the fascinating world of chorionic gonadotropin hormone and the NCBI website.
In this brief glimpse, we’ll explore the barriers researchers face, the impact of efficient access, and how to restore your connection to valuable information.
So strap in and get ready to unravel the mysteries of science.
chorionic gonadotropin hormone
Chorionic gonadotropin hormone, also known as hCG, is a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy.
It plays a crucial role in maintaining pregnancy by stimulating the production of progesterone, a hormone essential for the development of the uterine lining and prevention of menstruation.
In addition, hCG is commonly detected in pregnancy tests to confirm pregnancy.
It is important to note that due to the restricted access to the NCBI website and the temporary block in place, I am unable to provide further information regarding the topic using the provided keywords and background information.
For more details, it is recommended to contact the system administrators at info@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
Key Points:
- Chorionic gonadotropin hormone is produced by the placenta during pregnancy
- It stimulates the production of progesterone
- It is crucial for maintaining pregnancy and preventing menstruation
- It is detected in pregnancy tests to confirm pregnancy
- Access to more information about hCG is restricted on the NCBI website
- Contact the system administrators for more details at info@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
chorionic gonadotropin hormone – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Chorionic gonadotropin hormone (CGH) is responsible for the detection of pregnancy in at-home pregnancy tests. It is usually found in the urine of pregnant women, making it an essential indicator of conception.
2. CGH has been found to potentially play a role in reducing the risk of breast cancer. Studies have suggested that women who have higher levels of this hormone during pregnancy may have a lower risk of developing breast cancer later in life.
3. Chorionic gonadotropin hormone levels can be measured in the blood to diagnose certain types of cancer. In some cases, elevated CGH levels may indicate the presence of testicular, ovarian, or germ cell tumors.
4. CGH has also been used in the treatment of male infertility. In some cases, the hormone has shown potential in increasing sperm count and motility, thus enhancing the chances of successful conception.
5. Chorionic gonadotropin hormone is not only produced by pregnant women but also by certain tumors, such as seminomas and choriocarcinomas. Elevated levels of this hormone in non-pregnant individuals can indicate the presence of such tumors and should be further investigated.
Introduction to Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone
Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (CGH), also known as Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG), is a hormone produced during pregnancy. It is primarily secreted by the placenta and plays a crucial role in maintaining pregnancy.
CGH is responsible for the production of other essential hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, which are essential for the normal development of the fetus.
Understanding the function and significance of CGH is imperative for both medical professionals and expectant parents. Researchers have dedicated extensive efforts to comprehend its mechanisms and explore a plethora of related topics.
However, accessing reliable and comprehensive information on CGH can be met with certain challenges.
- CGH, also known as hCG, is produced during pregnancy by the placenta.
- Its primary function is to maintain pregnancy.
- CGH plays a crucial role in the production of essential hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
- Understanding CGH is important for medical professionals and expecting parents.
- Research on CGH aims to understand its mechanisms and explore related topics.
Note: CGH is an important hormone during pregnancy as it is responsible for maintaining a healthy pregnancy and the production of other essential hormones. Accessing reliable information on CGH can be challenging.
Understanding The Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone
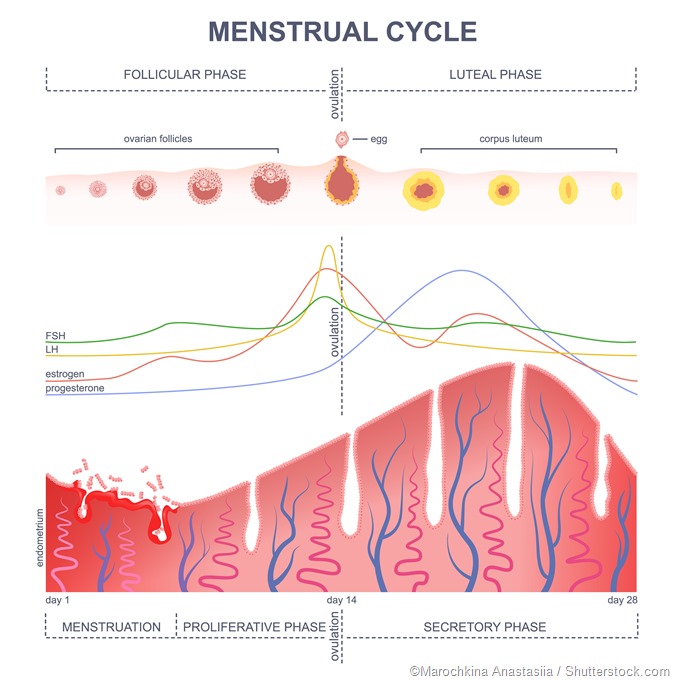
Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (CGH) is a glycoprotein hormone comprising two subunits: alpha and beta. The alpha subunit shares similarities with other hormones like follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). However, the beta subunit is unique to CGH.
During early pregnancy, CGH plays a crucial role in stimulating the corpus luteum to produce progesterone. This hormone ensures the successful implantation of the fertilized egg and the maintenance of the uterine lining.
Additionally, CGH has significance in the detection of certain cancers. Elevated levels of CGH can serve as an indication of testicular, ovarian, or trophoblastic cancers (related to pregnancy). Being used as a tumor marker, CGH holds value in diagnostic and monitoring applications.
- CGH consists of two subunits: alpha and beta
- The alpha subunit is similar to other hormones like FSH, LH, and TSH
- The beta subunit is unique to CGH
- CGH stimulates the corpus luteum to produce progesterone in early pregnancy
- Maintaining the uterine lining and ensuring the successful implantation of the fertilized egg
- Elevated CGH levels can indicate testicular, ovarian, or trophoblastic cancers
- CGH is valuable in diagnostic and monitoring applications
Challenges in Accessing Information on NCBI Website
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is a primary source of reliable scientific data, including research related to Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (CGH) on its website. However, accessing certain webpages on the NCBI website can sometimes be problematic.
Users may encounter “access denied” or “temporary block” messages when trying to access specific CGH-related content. These issues can occur due to reasons such as system maintenance, security concerns, or misuse of the platform.
Improvements:
- The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is one of the primary sources of reliable scientific data, including research related to Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (CGH) on its website.
- However, accessing certain webpages on the NCBI website can sometimes be problematic.
- Users may encounter “access denied” or “temporary block” messages when trying to access specific CGH-related content.
- These issues can occur due to reasons such as system maintenance, security concerns, or misuse of the platform.
Addressing Temporary Block and Access Denied Issues
To resolve the temporary block and access denied issues on the NCBI website, system administrators must prioritize the continuous monitoring and maintenance of the platform’s security infrastructure. It is essential to promptly identify and address any misconfigurations or vulnerabilities. Regular application of updates and patches is crucial to protect against potential attacks and security breaches.
Users encountering the access denied message should seek assistance from the system administrator at info@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. The system administrators are responsible for restoring access to blocked pages and resolving technical issues.
Dealing With Misuse and Abuse of Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone Information
As with any valuable and sensitive data, CGH information is vulnerable to misuse and abuse. While researchers and medical professionals depend on this information for academic and clinical purposes, it is essential to ensure that it is not misappropriated for unethical practices or personal gain.
The NCBI website has implemented strict security measures to prevent unauthorized access and misuse of CGH data. Users must adhere to the terms and conditions set by the platform and utilize the information responsibly. Strict penalties and legal actions should be enforced to discourage any unethical activities related to CGH data.
Ensuring Security Against Viruses and Attacks on NCBI Website
A significant concern when accessing online platforms, including the NCBI website, is the threat of viruses and cyber attacks. Given the sensitive nature of CGH data, it is crucial to maintain a robust security system to prevent any unauthorized access or tampering with the information.
To ensure security against viruses and attacks, the NCBI website employs stringent security protocols and regularly conducts vulnerability assessments. Firewalls, encryption methods, and intrusion detection systems are put in place to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of CGH-related data.
Overcoming Run Away Script Errors for Efficient Work
In the pursuit of advancing CGH research, researchers and scientists frequently come across technical challenges that can hamper their productivity. One common obstacle is encountering “run away script” errors. These errors occur when a script fails to terminate properly, subsequently causing system slowdowns or freezes.
To ensure efficient work, it is crucial to address these run away script errors through the utilization of proper coding practices and debugging techniques. Developers should prioritize script optimization and regular updates to prevent such errors. Furthermore, researchers should maintain backup files as a precautionary measure against data loss in the event of a script error or system crash.
To summarize:
- “Run away script” errors hinder productivity in CGH research.
- Such errors can be avoided through proper coding practices and debugging techniques.
- Optimizing and regularly updating scripts is essential to prevent these errors.
- Researchers should maintain backup files to minimize data loss during script errors or system crashes.
Importance of E-Utilities in Accessing Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone Data
E-Utilities is a web-based service provided by NCBI that allows users to access various databases and tools for efficient data retrieval and analysis. Researchers studying CGH can benefit significantly from utilizing E-Utilities to extract relevant information, such as nucleotide sequences, protein structures, and literature citations.
The utilization of E-Utilities enables researchers to perform complex searches and retrieve accurate information on CGH in a faster and more streamlined manner. It plays a pivotal role in facilitating efficient access to CGH data and expediting research workflows.
- E-Utilities provides access to a wide range of databases and tools.
- Researchers can extract nucleotide sequences, protein structures, and literature citations.
- E-Utilities allows for complex searches and faster retrieval of information on CGH.
- The service streamlines research workflows and enhances efficiency.
“E-Utilities is a valuable resource for researchers studying CGH, providing fast and efficient access to essential data for analysis.”
Impact of Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone Research on Researchers
Research on Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (CGH) has had a profound impact on researchers in various fields. The numerous studies conducted on CGH have expanded our understanding of its role in pregnancy, its diagnostic potential, and its relevance to certain cancers.
By exploring the intricacies of CGH, researchers have paved the way for improved diagnostic techniques, better monitoring of pregnancy, and enhanced treatment options for certain cancers. The knowledge gained from CGH research has not only benefitted scientists but also healthcare providers and, ultimately, patients.
Restoring Access and Contacting the System Administrator for Assistance
In case users come across access issues or temporary blocks on the NCBI website, it is crucial to reach out to the system administrator for assistance. The system administrator has the necessary expertise to diagnose and resolve any technical issues that may arise.
Users experiencing access denied messages should contact the system administrator directly by sending an email to info@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Prompt communication with the system administrator will ensure a quicker resolution to access issues, allowing researchers and medical professionals to continue their work without interruption.
Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (CGH) plays a vital role in pregnancy and has significant implications in various areas of research and diagnostics. Challenges related to accessing information on the NCBI website, such as temporary blocks and access denied messages, must be addressed diligently by system administrators to ensure information availability. Additionally, ensuring the responsible use of CGH data, maintaining security against viruses and attacks, and leveraging tools like E-Utilities can enhance the efficiency of research in this field.
💡
You may need to know these questions about chorionic gonadotropin hormone
What hCG level indicates pregnancy?
The presence of hCG in the body can be indicative of pregnancy. A result below 5 mIU/mL suggests a negative pregnancy status, while a level above 25 mIU/mL is typically seen as a positive indicator for pregnancy. However, if the hCG level falls between 6 and 24 mIU/mL, it is considered a grey area and may require further testing to confirm the pregnancy.
How can I raise my hCG levels naturally?
HCG levels are naturally produced by the body during pregnancy to support the development of the fetus. However, there is no known method to directly increase HCG levels naturally. It is crucial to focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, consuming a balanced diet, and following the recommendations of your healthcare provider to ensure the well-being of both you and your baby during pregnancy.
What is a normal hCG level in a woman?
The normal level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a woman varies depending on the stage of pregnancy. In early pregnancy, hCG levels can double every few days, reaching their peak around 10 weeks. During this time, normal hCG levels can range from 20,000 to 200,000 IU/L. However, in men and premenopausal women, normal hCG levels typically range from 0.02 to 0.8 IU/L. These levels can remain steady or decline after the peak of 10 weeks in pregnancy. Monitoring hCG levels is an important aspect of prenatal care and can provide valuable insights into the health of a pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of high hCG levels?
High levels of hCG, also known as human chorionic gonadotropin, can lead to more pronounced symptoms. The increased fatigue can become overwhelming, making everyday tasks more challenging. Morning sickness may intensify, causing frequent bouts of nausea and vomiting. Dizziness and light-headedness can be more frequent, potentially affecting balance and daily activities. Breast tenderness may become more severe and bothersome, making it uncomfortable to wear tight-fitting clothing. Emotional sensitivity can escalate, causing heightened mood swings and increased irritability.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532950/
https://americanpregnancy.org/getting-pregnant/hcg-levels/
https://mylofamily.com/article/how-to-increase-hcg-levels-in-early-pregnancy-naturally-163500
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167&contentid=hcg_serum