In the mysterious realm of pregnancy, hidden dangers lurk beneath the surface, waiting to be discovered.
One such enigma is concealed abruption, a condition that silently threatens both mother and baby.
With its invisible symptoms and potential for calamity, this stealthy complication demands our attention.
Join us as we unearth the secrets of placental abruption, unravel its intricacies, and explore the magnitude of its impact on childbirth.
Brace yourself for an exploration into the clandestine world of concealed abruption, where knowledge is power and ignorance can be fatal.
concealed abruption
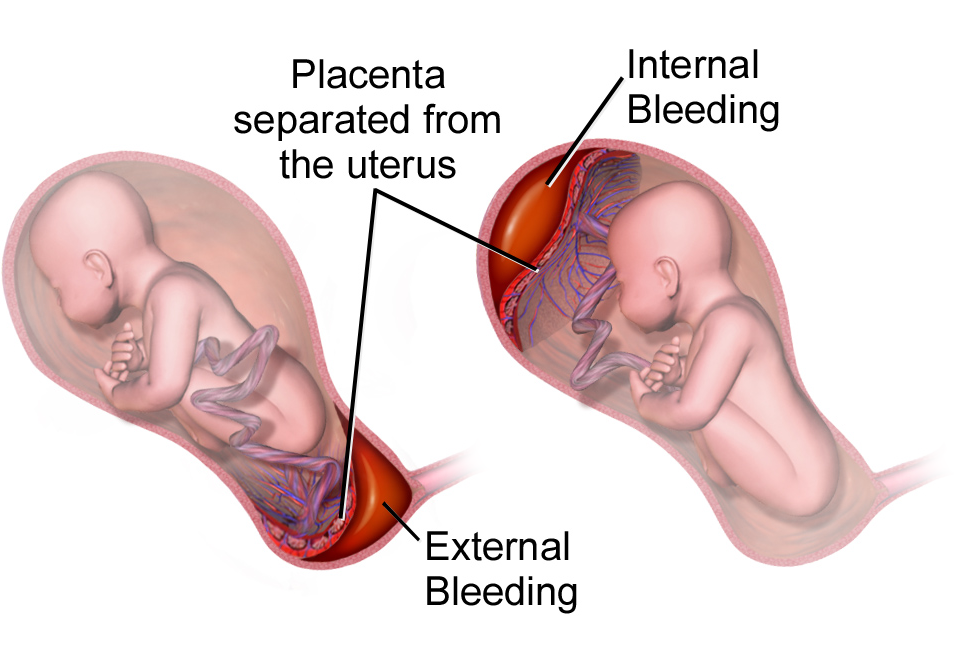
Concealed abruption refers to a complication of pregnancy where the placenta separates from the uterus without visible bleeding.
This condition can occur in about 1 out of 100 pregnancies and is usually seen in the third trimester but can occur after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, pain, contractions, discomfort, and tenderness.
While mild cases may cause few problems, placental abruption needs to be closely monitored as it can lead to complications such as growth problems for the baby, preterm birth, stillbirth, and anemia for the pregnant person.
Risk factors for placental abruption include high blood pressure, smoking, cocaine use, abdominal trauma, advanced maternal age, uterine infection, preterm labor, and issues with the uterus or umbilical cord.
In cases of placental abruption, delivery by cesarean birth may be required.
Key Points:
- Concealed abruption is a pregnancy complication where the placenta separates from the uterus without visible bleeding.
- It occurs in about 1 out of 100 pregnancies, usually in the third trimester but can happen after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Symptoms include vaginal bleeding, pain, contractions, discomfort, and tenderness.
- Placental abruption can lead to complications such as growth problems for the baby, preterm birth, stillbirth, and anemia for the pregnant person.
- Risk factors include:
- high blood pressure
- smoking
- cocaine use
- abdominal trauma
- advanced maternal age
- uterine infection
- preterm labor
- issues with the uterus or umbilical cord.
- Delivery by cesarean birth may be required in cases of placental abruption.
concealed abruption – Watch Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0yUORSHifKM
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The term “concealed abruption” refers to a rare and hidden medical condition where the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery, leading to potential complications and jeopardizing fetal health.
2. In geology, a concealed abruption refers to a fracture in the Earth’s crust that is hidden beneath layers of sediment or other formations, often causing unexpected shifts in the landscape and making it difficult to predict seismic activities.
3. Did you know that in the world of magic tricks, concealed abruption is a technique used by illusionists to abruptly hide or secretly switch objects under the audience’s noses, leaving them astounded and confused?
4. In architecture, concealed abruption describes a design concept where structural elements or features are purposely hidden, such as concealed doors, secret compartments, or hidden passages, adding mystery and intrigue to the building’s overall design.
5. The concept of concealed abruption is also found in literature, often used metaphorically to describe sudden plot twists, unexpected revelations, or hidden motives of characters that completely alter the course of the story, leaving readers stunned and engrossed in the narrative.
1. Definition Of Concealed Placental Abruption
Concealed placental abruption is a serious complication that can occur during pregnancy. It refers to the separation of the placenta from the uterus without any visible bleeding. This condition is different from typical placental abruptions, which are characterized by noticeable vaginal bleeding. The absence of visible bleeding in concealed abruption makes it difficult to detect and potentially more dangerous.
-
Key points:
-
Concealed placental abruption is a serious complication during pregnancy.
- It involves the separation of the placenta from the uterus without visible bleeding.
- Unlike typical placental abruptions, there is no noticeable vaginal bleeding.
- The absence of visible bleeding makes concealed abruption difficult to detect.
- Concealed abruption can be more dangerous due to the lack of visible symptoms.
“Concealed placental abruption is a condition where the placenta separates from the uterus without any visible bleeding. This silent occurrence makes it difficult to detect and potentially more dangerous.”
2. Types And Severity Of Placental Abruption
Placental abruption can be either partial or complete. Partial abruptions involve a partial separation of the placenta from the uterus, while complete abruptions involve a complete detachment. Naturally, complete abruptions result in more severe symptoms, including significant vaginal bleeding. However, concealed abruption, which occurs without visible bleeding, can be just as dangerous despite its silent nature as the separation can go unnoticed, leading to delayed diagnosis and potentially serious consequences.
Some key points about placental abruption include:
- Placental abruption can be partial or complete
- Complete abruptions result in more severe symptoms, including significant vaginal bleeding
- Concealed abruption can be just as dangerous as visible abruption, as it can go unnoticed
- Delayed diagnosis of placental abruption can lead to serious consequences
3. Incidence Of Placental Abruption In Pregnancies
Placental abruption is a relatively rare complication, occurring in approximately 1 out of 100 pregnancies. However, the incidence may vary depending on various factors such as maternal age, pre-existing medical conditions, and lifestyle choices. It is crucial to recognize the signs and risk factors of placental abruption to ensure early detection and prompt medical intervention.
- Placental abruption occurs in approximately 1 out of 100 pregnancies.
- The incidence may vary depending on factors such as maternal age, pre-existing medical conditions, and lifestyle choices.
- Early detection and prompt medical intervention are crucial in managing placental abruption.
- Recognizing the signs and risk factors can help in identifying and treating the condition effectively.
“It is crucial to recognize the signs and risk factors of placental abruption to ensure early detection and prompt medical intervention.”
4. Symptoms And Signs Of Placental Abruption
Symptoms of placental abruption can vary, but they commonly include:
- Vaginal bleeding
- Pain
- Contractions
- Discomfort
- Tenderness
The severity of these symptoms depends on the extent of separation and whether it is concealed or visible. It is important to note that concealed abruption may not present with any external signs of bleeding, making it challenging to identify and diagnose.
Therefore, pregnant individuals should always report any new or concerning symptoms to their healthcare providers for appropriate evaluation.
5. Timing Of Placental Abruption During Pregnancy
Placental abruption typically occurs in the third trimester of pregnancy, but it can happen after 20 weeks of gestation. The risk increases as pregnancy progresses, so vigilance is essential, especially during the later stages. However, placental abruption can occur at any point during pregnancy, underscoring the need for continuous monitoring and prompt medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise.
6. Monitoring And Management Of Mild Cases Of Placental Abruption
Mild cases of placental abruption may not immediately pose significant problems, but they still require close monitoring and management. Regular check-ups, ultrasounds, and fetal monitoring are important to assess the well-being of the baby and identify any potential complications. In some cases, bed rest or reduced physical activity may be recommended to minimize the risk of aggravated placental separation.
7. Potential Complications Of Placental Abruption
Placental abruption can lead to several complications for both the baby and the expectant person. These complications include growth problems for the baby, preterm birth, stillbirth, and anemia for the pregnant individual. Furthermore, placental abruption is associated with an increased risk of hemorrhage and blood clotting complications, which can pose serious threats to both the mother and the baby. Therefore, timely intervention and comprehensive medical care are crucial to mitigate these potential complications.
8. Association Between Placental Abruption And Premature Birth
Placental abruption is strongly linked to premature birth, with about 1 in 10 premature births being caused by this condition. Premature babies, who are born before completing the full term of pregnancy, are at a higher risk of encountering health issues, long-term disabilities, and even mortality. Thus, it is crucial to identify and address placental abruption promptly in order to reduce the chances of premature birth and its related complications.
9. Long-Term Consequences For Premature Babies
Premature babies are confronted with distinct challenges and are at risk of experiencing long-term consequences. These consequences encompass developmental delays, cognitive impairments, chronic health conditions, and heightened mortality rates. The profound impact of prematurity underscores the significance of preventing and effectively managing placental abruption. This approach is crucial in enhancing outcomes for both the baby and the family.
10. Risk Factors For Placental Abruption And Recurrence In Future Pregnancies
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of placental abruption. These include:
- History of previous abruption
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Cocaine use
- Abdominal trauma
- Advanced maternal age (35 or older)
- Uterine infection
- Preterm labor
- Early rupture of membranes
- Uterine or umbilical cord abnormalities
- Excess amniotic fluid
- Multiple pregnancies
- Asthma
- Family history of abruption
- Previous cesarean birth
- Exposure to air pollution
It is important for healthcare providers to identify these risk factors during prenatal care to closely monitor and implement preventive measures. Additionally, individuals who have experienced placental abruption in a previous pregnancy have a 10% chance of recurrence in subsequent pregnancies, underscoring the need for vigilant monitoring and specialized care.
In conclusion, concealed placental abruption is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of pregnancy. Despite its lack of visible bleeding, it can have profound consequences for both the baby and the expecting person. Recognizing the signs, risk factors, and potential complications associated with placental abruption is vital for early detection and effective management. Healthcare providers play a critical role in monitoring pregnancies, implementing appropriate interventions, and educating individuals to ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and child. Ultimately, by shedding light on this silent killer of pregnancy, we can strive for improved care and reduced morbidity and mortality rates associated with placental abruption.
💡
You may need to know these questions about concealed abruption
What are the symptoms of concealed abruption?
Concealed placental abruption, while lacking visible vaginal bleeding, still presents several symptoms. Pain, contractions, and discomfort are commonly experienced by those affected. Additionally, sudden and persistent belly or back pain may be indicative of this condition. It is worth noting that in some cases, these symptoms can occur without visible bleeding as the blood becomes confined behind the placenta.
What is concealed hemorrhage and abruptio Placentae?
Concealed hemorrhage refers to blood that accumulates behind the placenta during a placental abruption. In this condition, the symptoms and signs may not immediately indicate the severity of the bleeding. The presence of blood behind the placenta can make it challenging to assess the extent of blood loss and can lead to delayed recognition of the condition. As separation persists, the uterus may become painful, tender, and sensitive to touch, indicating increasing severity.
Abruptio placentae, also known as placental abruption, occurs when the placenta detaches from the inner uterine wall before delivery. The severity of symptoms and signs observed in this condition depends on the extent of separation and subsequent blood loss. Manifestations can include uterine bleeding, along with the characteristic pain, tenderness, and irritability of the uterus upon palpation. Prompt recognition and proper management are crucial to mitigate potential complications for both the mother and the fetus.
Can a baby survive placental abruption?
The survival of a baby in the case of placental abruption greatly depends on various factors. Placental abruption can lead to severe complications such as prematurity, hypoxia, and congenital anomalies, which significantly increase the risk of mortality. However, if prompt medical intervention and appropriate treatment are provided, the possibility of a baby surviving placental abruption may exist. Timely medical attention can help mitigate potential risks and improve the chances of the baby’s survival, although the outcome remains uncertain and varies from case to case.
Can a concealed placental abruption be seen on ultrasound?
While ultrasound is a commonly used imaging technique to detect various conditions during pregnancy, a concealed placental abruption may not always be visible. The high-frequency sound waves used in ultrasound create an image of the uterus on a monitor, allowing healthcare providers to identify potential sources of vaginal bleeding. However, due to the nature of a concealed placental abruption, where the placenta separates from the uterus but remains hidden behind intact membranes, it may not always be visible on ultrasound. Further tests and evaluations may be necessary to properly diagnose this condition.
Reference source
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9435-placental-abruption
https://www.marchofdimes.org/find-support/topics/pregnancy/placental-abruption
https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/p/placental-abruption.html
https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/abnormalities-of-pregnancy/placental-abruption-abruptio-placentae