Unexplained bleeding can be a concerning and distressing experience, especially when it occurs during or after intimate moments.
Contact bleeding, the medical term for bleeding after sex, can have several potential causes that range from innocuous to more serious conditions.
From infections to hormonal imbalances, it is crucial to understand the underlying reasons and seek professional guidance to ensure your well-being.
In this article, we explore the possible causes of contact bleeding and the necessary steps to address them effectively.
contact bleeding
Contact bleeding, also known as postcoital bleeding, refers to bleeding that occurs after sexual intercourse.
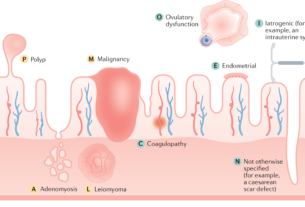
It can be caused by various factors such as infections, vaginal dryness, damage to the vagina, cervical or endometrial polyps, cervical erosion, cervical cancer, or vaginal cancer.
If experiencing contact bleeding, it is important to consult with a general practitioner or visit a sexual health clinic for a thorough assessment of symptoms.
Based on the evaluation, appropriate treatment options can be recommended, which may include pregnancy tests, pelvic examinations, cervical screening tests, and the use of lubricating gels.
In some cases, a specialist referral might be necessary.
Regular cervical screening tests are also crucial for prevention and early detection of cervical cancer.
Speculum examinations may be performed to closely examine the cervix and identify any abnormalities.
Key Points:
- Contact bleeding, or postcoital bleeding, occurs after sexual intercourse.
- It can be caused by infections, vaginal dryness, vaginal or cervical damage, polyps, erosion, or cancer.
- Consulting a general practitioner or sexual health clinic is important for assessment and treatment options.
- Assessments may include pregnancy tests, examinations, screening tests, and the use of lubricating gels.
- Specialist referrals may be necessary in some cases.
- Regular cervical screening tests are crucial for prevention and early detection of cervical cancer.
contact bleeding – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Contact bleeding:
1. The phenomenon of “contact bleeding” refers to the occurrence of bleeding from the surface of the skin or mucous membranes upon mild contact or pressure.
2. One potential cause of contact bleeding is a condition called vascular fragility, where the blood vessels are more prone to rupture.
3. Contact bleeding can commonly occur in individuals with certain skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, due to the inflammation and weakening of blood vessels in affected areas.
4. Some medications, such as blood thinners or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can increase the risk of contact bleeding by impairing the body’s ability to clot blood effectively.
5. In rare cases, contact bleeding can also be a symptom of an underlying systemic disease, such as an autoimmune disorder or a bleeding disorder. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if contact bleeding persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Contact Bleeding – Bleeding After Sex
Bleeding after sex, also known as contact bleeding, can be a distressing experience for individuals. It refers to the occurrence of vaginal bleeding that happens immediately after sexual intercourse. While it is normal to be concerned, it is important to understand that contact bleeding can have various causes, most of which are treatable or manageable.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Contact bleeding is not uncommon and can happen to women of all ages.
- The most common cause of contact bleeding is cervicitis, which refers to inflammation of the cervix.
- Other potential causes include vaginal dryness, vaginal infections, cervical polyps, or even more serious conditions such as cervical cancer (although this is rare).
- It is crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you experience contact bleeding, as they can help determine the cause and provide appropriate treatment.
- Treatment options may include antibiotics for infections, hormonal medications for hormonal imbalances, or removal of cervical polyps if present.
- In some cases, practicing good sexual hygiene, using lubricants, or exploring alternative sexual positions can help reduce the likelihood of contact bleeding.
- Remember, contact bleeding does not necessarily indicate a serious underlying condition, but it should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out any potential issues.
“It is important to understand that contact bleeding can have various causes, most of which are treatable or manageable.”
Hope this helps!
Postcoital Bleeding
Postcoital bleeding is a type of vaginal bleeding that occurs after sexual intercourse. It can range from light spotting to more significant bleeding. Some potential causes of postcoital bleeding include:
- Infections
- Vaginal dryness
- Damage to the vagina
- Cervical or endometrial polyps
- Cervical erosion
- Cervical cancer
- Vaginal cancer
It’s important to seek medical advice if you experience postcoital bleeding to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Note: It’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance.
Infections
Infections are a common cause of contact bleeding. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or herpes can lead to inflammation and irritation in the cervix or vagina, resulting in bleeding. Other infections like bacterial vaginosis or yeast infections can also cause contact bleeding. It is crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect an infection as appropriate treatment can prevent further complications.
Vaginal Dryness
Vaginal dryness can be a significant factor in contact bleeding. It is commonly caused by hormonal changes, breastfeeding, certain medications, or menopause. Insufficient lubrication during sexual activity can lead to friction and irritation, leading to small tears or trauma in the vaginal wall, which can ultimately result in bleeding. To address this issue, it is advised to use lubricating gels or consult with a healthcare professional about hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
Improvements:
Damage To The Vagina
Damage to the vagina can occur during sexual intercourse, especially if there is rough or vigorous penetration. This can cause small tears or lacerations in the vaginal tissue, leading to bleeding.
To reduce the risk of vaginal damage and subsequent bleeding, it is important to follow these recommendations:
- Use sufficient lubrication: It can help to use a water-based lubricant to reduce friction during intercourse.
- Engage in foreplay: Spending enough time on foreplay can stimulate natural lubrication, making intercourse more comfortable and reducing the likelihood of tissue damage.
- Communicate with your partner: Clear and open communication about comfort levels can help ensure a more pleasurable and safe sexual experience.
Remember, being informed and taking these precautions can minimize the chances of experiencing vaginal damage and bleeding during sexual intercourse.
“Using sufficient lubrication, engaging in foreplay to stimulate natural lubrication, and communicating with your partner about comfort levels can help prevent vaginal damage and subsequent bleeding.”
Cervical Or Endometrial Polyps
Cervical or endometrial polyps are noncancerous growths that can develop in the cervix or uterus. These growths can cause bleeding, both during and after sexual intercourse, due to their fragile nature. If you suspect the presence of polyps, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can perform necessary tests and recommend appropriate treatment, such as polyp removal.
Cervical Erosion
Cervical erosion (also known as cervical ectropion) is a condition where the cells from the inside of the cervix spread to the outside, exposing them to the vagina. This can make the cervix more sensitive and susceptible to bleeding, particularly after sexual contact. Regular cervical screening tests are essential for detecting and monitoring cervical erosion. Appropriate treatment can alleviate symptoms and reduce the occurrence of contact bleeding.
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a serious medical condition that can cause contact bleeding. It typically develops from persistent infections with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) strains. If you notice bleeding after sex, it could be an early warning sign of cervical cancer. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience contact bleeding, as well as other symptoms like pelvic pain or abnormal vaginal discharge. Contacting your GP for further evaluation and possible referral to a specialist is crucial.
- Cervical cancer is a serious medical condition that can cause contact bleeding.
- It generally develops from persistent infections with high-risk HPV strains.
- Bleeding after sex can be an early warning sign of cervical cancer.
- Look out for other symptoms such as pelvic pain or abnormal vaginal discharge.
- Contact your GP for further evaluation and potential referral to a specialist.
Vaginal Cancer
While relatively rare, vaginal cancer can also cause bleeding after sex. Vaginal cancer develops in the lining of the vagina and can lead to symptoms such as persistent vaginal bleeding or discharge. If you suspect vaginal cancer, it is important to seek medical advice promptly to receive an accurate diagnosis and discuss appropriate treatment options.
- Bleeding after sex can be a symptom of vaginal cancer.
- Vaginal cancer affects the lining of the vagina.
- Persistent vaginal bleeding or discharge may indicate vaginal cancer.
- Seeking medical advice promptly is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment options.
“If you suspect vaginal cancer, it is important to seek medical advice promptly to receive an accurate diagnosis and discuss appropriate treatment options.”
Consultation With A GP
Experiencing contact bleeding can be concerning and may warrant a consultation with a GP. Your GP will likely inquire about your medical history, sexual activity, and any other symptoms you may be experiencing. They may conduct a physical examination, including a pelvic examination, to assess the potential causes of contact bleeding. Additional tests, such as pregnancy tests or cervical screening tests, may be recommended to rule out specific conditions and guide appropriate treatment.
Symptoms Assessment
During your consultation, your GP will conduct a thorough assessment of your symptoms to determine the cause of contact bleeding. They will evaluate factors such as the frequency and severity of bleeding, associated pain or discomfort, presence of other symptoms like abnormal discharge or pelvic pain, and any relevant medical history or risk factors.
Appropriate Treatment
Once the cause of contact bleeding has been identified, your healthcare professional will recommend the appropriate treatment. This may involve addressing underlying infections through antibiotics or antifungal medications, managing hormonal imbalances with HRT, or removing cervical or endometrial polyps through minor procedures. In cases of cervical or vaginal cancer, treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Pregnancy Tests and Pelvic Examinations
During the evaluation process, pregnancy tests may be recommended by your healthcare professional to rule out pregnancy-related causes of contact bleeding. Additionally, pelvic examinations can be performed to assess the condition of your cervix and vaginal tissues, with the aim of identifying any abnormalities or potential sources of bleeding.
- Pregnancy tests help rule out pregnancy-related causes of contact bleeding
- Pelvic examinations assess cervix and vaginal tissue condition
- They help identify abnormalities or potential sources of bleeding
Cervical Screening Tests
Regular cervical screening tests, commonly known as Pap smears, are essential for detecting any precancerous or cancerous changes in the cervix. These tests can help identify early signs of cervical cancer that may contribute to contact bleeding. It is important to attend regular cervical screening appointments as recommended by your healthcare professional for the prevention and early detection of cervical abnormalities.
- Regular cervical screening tests are also referred to as Pap smears.
- These tests are crucial for detecting any precancerous or cancerous changes in the cervix.
- They help identify early signs of cervical cancer that may cause contact bleeding.
- It is highly recommended to attend regular cervical screening appointments.
- Healthcare professionals advise these appointments to ensure prevention and early detection of cervical abnormalities.
“Regular cervical screening tests are essential for the prevention and early detection of cervical abnormalities.”
Lubricating Gels
Using lubricating gels or water-based lubricants during sexual activity can help address vaginal dryness and reduce the friction and irritation that can lead to contact bleeding. These products can enhance comfort and reduce the risk of vaginal tissue damage. It is advisable to choose lubricants that are specifically designed for sexual intimacy to ensure safety and compatibility.
Specialist Referral
In some cases, a referral to a specialist may be necessary to provide further evaluation and treatment. Specialists such as gynecologists or oncologists have extensive knowledge and expertise in managing conditions related to contact bleeding. If your GP determines that a specialist consultation is required, they will guide you through the referral process and ensure continuity of care.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Regular cervical screening tests are essential in the prevention of cervical cancer. Other preventive measures include:
- Practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of HPV transmission
- Completing the HPV vaccination series
- Maintaining good overall vaginal health
- Avoiding tobacco use, as it can increase the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Remember that prevention is key in decreasing the chances of developing cervical cancer.
Speculum Examination
A speculum examination is a diagnostic procedure performed by healthcare professionals to visualize the cervix and vaginal canal. It involves the insertion of a speculum, a medical instrument that gently spreads the vaginal walls, allowing for clear visualization of the cervix. A speculum examination can help detect any abnormalities that may contribute to contact bleeding and guide appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, contact bleeding, also known as bleeding after sex, can have various causes, ranging from benign conditions such as vaginal dryness or cervical erosion to more serious conditions like cervical or vaginal cancer. Seeking medical attention is crucial to diagnose the underlying cause and determine the appropriate treatment. Regular cervical screening tests, practicing safe sex, and maintaining good vaginal health are key factors in preventing and managing contact bleeding.
To summarize:
- A speculum examination is a diagnostic procedure performed to visualize the cervix and vaginal canal.
- Contact bleeding can have various causes, ranging from benign to more serious conditions.
- Seeking medical attention is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Regular cervical screening tests, safe sex practices, and maintaining good vaginal health can help prevent and manage contact bleeding.
💡
You may need to know these questions about contact bleeding
What causes contact bleeding?
Contact bleeding can be caused by various factors, including infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia. These infections can lead to inflammation and irritation of the vaginal tissues, making them more prone to bleeding upon contact. Additionally, vaginal dryness known as atrophic vaginitis, which occurs as a result of reduced vaginal secretions after menopause, can also contribute to contact bleeding. The dryness increases the vulnerability of the vaginal tissues, making them more likely to tear or bleed during sexual activity. Similarly, damage to the vagina from childbirth or due to dryness or friction during sex can cause contact bleeding as well.
What is postcoital and contact bleeding?
Postcoital bleeding, also known as post-sex bleeding, refers to non-menstrual bleeding that occurs immediately after sexual intercourse. This type of bleeding can be concerning for individuals experiencing it and may require further evaluation. Approximately 1 in 12 women experience postcoital bleeding, which is frequently associated with heavy menstrual periods. It is essential to seek appropriate medical attention to determine the underlying cause and address any potential concerns.
Contact bleeding, on the other hand, is a term used to describe bleeding that occurs upon contact or manipulation of certain body parts or tissues. This bleeding can occur in various contexts, such as during a medical examination or sexual activity. In the case of postcoital bleeding, contact bleeding may occur due to the physical interaction involved in sexual intercourse. It is crucial to understand the specific cause and consult a healthcare professional to ensure appropriate evaluation and management.
What does it mean if your cervix is bleeding?
If your cervix is bleeding, it may be a sign of cervicitis, which is an inflammation of the cervix. This inflammation can lead to various symptoms such as bleeding between menstrual periods, pain during intercourse or pelvic exams, and abnormal vaginal discharge. The presence of bleeding suggests that there may be irritation or injury to the cervix, which could be caused by infection, sexually transmitted diseases, or other factors. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment to address the underlying cause of the bleeding and alleviate any accompanying symptoms.
Can hitting the cervix cause bleeding?
While deep penetration during sexual intercourse has the potential to cause bruising on the cervix, it is possible for it to lead to bleeding as well. The forceful impact on the cervix may cause small blood vessels to rupture, resulting in bleeding. This could manifest as spotting or more substantial bleeding, depending on the severity of the injury. It’s important to note that if you experience bleeding or discomfort during or after sex, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and advice on managing any potential injuries.
Reference source
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321032
https://www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/sexual-health/what-causes-a-woman-to-bleed-after-sex/
https://www.cheshiregynaecologist.co.uk/treatments-procedures/postcoital-bleeding/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cervicitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20370814