In a world where preventing pregnancy and managing hormonal imbalances are crucial concerns, a group of secret agents silently work to maintain the delicate balance of reproductive health.
Known as “contraceptive agents,” these powerful progestins and estrogens are not just ordinary hormones.
Join us on a thrilling journey as we uncover the hidden world of these extraordinary substances and explore the countless ways they impact our lives.
contraceptive agents
Contraceptive agents are medications or substances that prevent pregnancy by inhibiting or altering the natural reproductive processes of the body.
They can be taken orally, inserted, or applied topically.
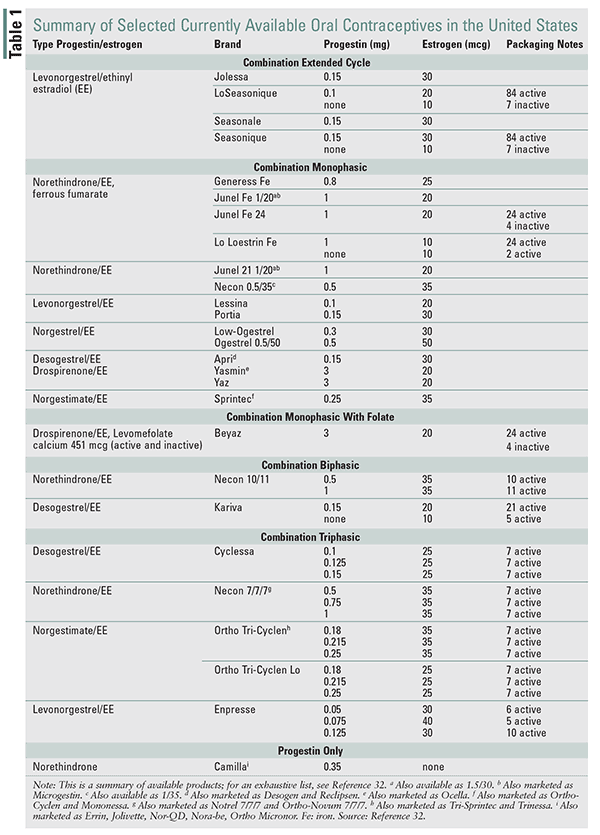
Some commonly used contraceptive agents include Etonogestrel, Desogestrel, Megestrol acetate, Levonorgestrel, Medroxyprogesterone acetate, Norethisterone, Ethynodiol diacetate, Mifepristone, Norgestimate, Dienogest, Estradiol cypionate, Ormeloxifene, Diethylstilbestrol, Cyproterone acetate, Drospirenone, Hydroxyprogesterone caproate, Nomegestrol acetate, Quingestanol, Ethinylestradiol, Ulipristal, Estradiol valerate, Mestranol, Demegestone, Segesterone acetate, Norethindrone enanthate, Algestone acetophenide, and Chlormadinone acetate.
Each of these contraceptive agents has specific mechanisms of action and is used for various purposes, such as contraception, hormone replacement therapy, treatment of gynecological disorders, and prevention of pregnancy-related complications.
Key Points:
- Contraceptive agents prevent pregnancy by inhibiting or altering natural reproductive processes in the body
- They can be taken orally, inserted, or applied topically
- Examples include Etonogestrel, Levonorgestrel, Mifepristone, and Ethinylestradiol
- These agents have specific mechanisms of action
- They are used for contraception, hormone replacement therapy, treating gynecological disorders, and preventing complications during pregnancy
- There are various types of contraceptive agents available including progestins, estrogens, and combination formulations.
contraceptive agents – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. While many people associate contraceptive agents with preventing pregnancy, they were initially developed to treat other medical conditions. In the early 20th century, birth control pills were primarily used to regulate menstrual cycles and relieve symptoms of conditions like endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome.
2. Did you know that the contraceptive sponge, a popular form of birth control in the 1980s and 1990s, went out of production in 1994? The sponge was introduced as a non-hormonal contraceptive option and offered protection against pregnancy for up to 24 hours. However, due to manufacturing issues and rising competition from other contraceptive methods, it eventually disappeared from the market.
3. Although widely known as a symbol of peace, the herb known as “Queen Anne’s Lace” has historical ties to contraception. During ancient times, women used its seeds as a primitive form of contraception. The seeds were believed to have contraceptive properties due to their ability to prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus.
4. Long before the invention of modern contraception, various natural substances were used as spermicides. For instance, ancient Egyptian women sometimes used a mixture of crocodile dung, honey, and sodium carbonate as a contraceptive agent. While this method may seem unorthodox (and unappealing), it nonetheless demonstrates the creativity and resourcefulness of early contraceptive practices.
5. The idea of using a diaphragm as a form of contraception dates back to ancient Greece, where women would use pomegranate rinds to create makeshift diaphragms. These rinds were believed to function as physical barriers, preventing sperm from reaching the cervix. Although the materials and methods have certainly evolved, it’s intriguing to consider the historical roots of this commonly used contraceptive device.
Etonogestrel: A Long-Acting Synthetic Progestin Contraceptive
Etonogestrel is a synthetic progestin with long-acting contraceptive properties. It is often administered through rings and implants to provide effective contraception for an extended period.
This convenient and reliable form of contraception is favored by many individuals. Etonogestrel works by inhibiting ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and altering the uterine lining to prevent implantation.
Thanks to its high efficacy, etonogestrel is widely considered a highly reliable method of contraception.
Desogestrel: Synthetic Progestin in Contraception with Ethinyl Estradiol
Desogestrel is a synthetic progestin commonly used in combination with ethinyl estradiol for contraception. This combination medication is available in various forms, such as oral contraceptive pills.
Desogestrel, along with ethinyl estradiol, works by suppressing ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and altering the endometrium to prevent implantation.
This combination contraceptive method is highly effective when used correctly and consistently.
Megestrol Acetate: Progestin for Anorexia, Weight Loss, and Anticancer Treatment
Megestrol acetate is an oral progestin that is primarily used for the treatment of anorexia, weight loss, and as an anticancer agent. It has been found to effectively increase appetite and promote weight gain in individuals experiencing significant weight loss due to conditions such as cancer or AIDS. Furthermore, megestrol acetate is utilized in hormonal therapy for certain types of cancer. Its ability to regulate hormonal imbalances makes it a valuable tool in cancer treatment strategies.
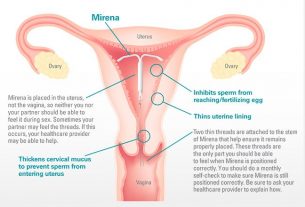
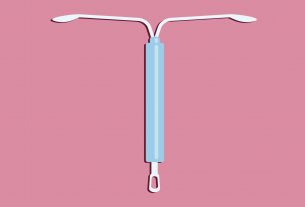
Levonorgestrel: Progestin in Oral and IUD Contraceptives, Emergency Contraceptives
Levonorgestrel is a progestin commonly used in oral contraceptives, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and emergency contraceptive pills. It is a highly effective method of contraception, working by inhibiting ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and altering the endometrium.
Levonorgestrel emergency contraceptive pills, often known as “morning-after” pills, can be taken up to 72 hours after unprotected intercourse to prevent pregnancy. Thanks to its accessibility and reliability, levonorgestrel is a popular choice for many individuals seeking contraception.
-
Levonorgestrel is a progestin found in:
- Oral contraceptives
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
- Emergency contraceptive pills
-
It works by:
- Inhibiting ovulation
- Thickening cervical mucus
- Altering the endometrium
Levonorgestrel emergency contraceptive pills, also known as “morning-after” pills, can be taken up to 72 hours after unprotected intercourse to prevent pregnancy. Its accessibility and reliability make it a popular choice for many individuals seeking contraception.
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate: Progestin for Contraception, Amenorrhea, and Cancer Treatment
Medroxyprogesterone acetate is a progestin commonly used for contraception, amenorrhea (absence of menstruation), and as part of cancer treatment regimens. It can be administered orally or by injection, providing a flexible and reliable method of birth control.
Medroxyprogesterone acetate works by:
- Suppressing ovulation
- Altering cervical mucus
- Thinning the endometrium to prevent implantation
Its effectiveness and versatility make it a popular choice for individuals seeking contraception and managing hormonal imbalances.
Norethisterone: Synthetic Progestin for Contraception and Endometriosis
Norethisterone is a synthetic progestin that is widely used for contraception, hormone replacement therapy, and the treatment of endometriosis. It is available in various forms, including oral contraceptive pills and implants.
Norethisterone works by inhibiting ovulation, altering cervical mucus consistency, and thinning the endometrial lining. This makes it effective in preventing pregnancy and managing endometriosis symptoms.
In terms of endometriosis management, norethisterone helps reduce symptoms and control abnormal tissue growth. It is an effective choice for treating this condition.
To summarize:
- Norethisterone is a synthetic progestin used for contraception, hormone replacement therapy, and endometriosis treatment.
- It works by inhibiting ovulation, altering cervical mucus consistency, and thinning the endometrial lining.
- Norethisterone is available as oral contraceptive pills and implants.
- It is an effective choice for various reproductive health needs, including managing endometriosis.
“The versatility of norethisterone makes it an effective choice for various reproductive health needs.”
Ethynodiol Diacetate: Oral Contraceptive to Prevent Pregnancy
Ethynodiol diacetate is an oral contraceptive that is widely used to prevent pregnancy. It is classified as a synthetic progestin and, when combined with an estrogen, it offers reliable contraception by performing multiple functions such as inhibiting ovulation, altering cervical mucus consistency, and thinning the endometrial lining.
The medication is conveniently available in the form of oral contraceptive pills and is taken daily to ensure effective contraception. Its user-friendly nature and remarkable efficacy have contributed to its widespread popularity among individuals who desire a reliable method of birth control.
To summarize:
- Ethynodiol diacetate is a synthetic progestin used in oral contraceptive pills.
- It works by inhibiting ovulation, altering cervical mucus, and thinning the endometrial lining.
- The medication is taken daily for effective contraception.
- Ethynodiol diacetate is favored by many due to its ease of use and high efficacy.
Mifepristone: Cortisol Receptor Blocker for Cushing’s Syndrome and Pregnancy Termination
Mifepristone is a cortisol receptor blocker with multiple medical applications. It is commonly used to treat Cushing’s syndrome and for pregnancy termination. In the case of Cushing’s syndrome, mifepristone aids in blocking the harmful effects of excess cortisol in the body, thereby alleviating symptoms. Another noteworthy use of mifepristone is when it is combined with misoprostol to safely and effectively terminate early pregnancies. Given its ability to block cortisol receptors, mifepristone plays a crucial role in managing hormonal imbalances and facilitating pregnancy termination.
Norgestimate: Progesterone for Contraception and Acne Treatment
Norgestimate is a progesterone commonly used in combination with an estrogen for contraception and acne treatment. It is available in various oral contraceptive pills and works by inhibiting ovulation, altering cervical mucus consistency, and thinning the endometrial lining.
In addition to its contraceptive effects, the use of norgestimate has been found to help improve acne by reducing excessive oil production and decreasing inflammation. This dual action makes norgestimate a popular choice for individuals seeking contraception and acne management.
- Norgestimate is a progesterone used for contraception and acne treatment
- Available in oral contraceptive pills
- Works by inhibiting ovulation, altering cervical mucus consistency, and thinning the endometrial lining
- Helps improve acne by reducing excessive oil production and decreasing inflammation
“Norgestimate is an effective option for those looking to manage contraception and acne.”
Dienogest: Oral Progestin for Endometriosis Treatment and Contraception
Dienogest is an oral progestin specifically used for the treatment of endometriosis and contraception. It helps reduce the growth and proliferation of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, effectively managing the symptoms associated with endometriosis.
Additionally, dienogest is available as a combination oral contraceptive pill, providing reliable contraception by inhibiting ovulation, altering cervical mucus consistency, and thinning the endometrium.
The dual benefits of dienogest make it a preferred choice for individuals managing endometriosis and seeking contraception.
- Dienogest is an oral progestin used for the treatment of endometriosis and contraception.
- It helps reduce the growth and proliferation of endometrial tissue.
- Dienogest is available as a combination oral contraceptive pill.
- It provides reliable contraception by inhibiting ovulation, altering cervical mucus consistency, and thinning the endometrium.
“The dual benefits of dienogest make it a preferred choice for individuals managing endometriosis and seeking contraception.”
💡
You may need to know these questions about contraceptive agents
What are the examples of contraceptive agents?
In addition to the birth control pill, there are various examples of contraceptive agents available today. One example is the contraceptive patch, which is a small, adhesive patch applied to the skin that releases hormones to prevent pregnancy. Another example is the vaginal ring, which is a flexible ring inserted into the vagina that releases hormones over a period of time. Additionally, contraceptive coils, also known as intrauterine devices (IUDs), are another type of hormone-based contraception that are inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. These diverse contraceptive agents offer individuals different options to choose from based on their personal preferences and needs.
What are the top 5 contraceptives?
The top five contraceptives include the contraceptive patch, which is a thin, adhesive patch worn on the skin that releases hormones to prevent pregnancy. It is easy to use and does not require daily upkeep. Another effective method is the contraceptive pill, which is a daily hormonal medication that prevents ovulation. The pill is convenient and offers a high success rate when taken correctly.
Additionally, the contraceptive injection is a popular choice that provides protection against pregnancy for up to three months with a single injection. It is a convenient option for those who prefer a longer-acting method. Furthermore, the contraceptive ring is a flexible plastic ring inserted into the vagina that releases hormones to prevent pregnancy. It is inserted once a month and offers heightened ease of use. Lastly, the barrier method known as the male and female condom provides both contraception and protection against sexually transmitted infections. Condoms are widely accessible, affordable, and offer the added benefit of dual protection.
What are the 3 most effective types of contraceptives?
Based on the provided background information, the three most effective types of contraceptives are the birth control implant, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and sterilization. The birth control implant is a convenient and low-maintenance option as it is a small rod placed under the skin that releases hormones to prevent pregnancy for up to three years. Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are also highly effective as they can prevent pregnancy for several years, with some types lasting up to 10 years. Sterilization, which is a permanent form of contraception, is extremely effective as it involves permanent blocking or cutting of the fallopian tubes or vas deferens to prevent the egg and sperm from meeting.
These three methods stand out for their high effectiveness rates and minimal need for ongoing maintenance, providing long-term contraceptive options and ensuring reliable pregnancy prevention. Other methods, such as fertility awareness or withdrawal, have lower effectiveness rates and may require more monitoring or self-control, reducing their overall effectiveness compared to the aforementioned methods.
What are the 5 examples of hormonal contraceptives?
There are various types of hormonal contraceptives available for individuals seeking birth control. Five examples include the implant, which is a small rod placed under the skin to release hormones and prevent pregnancy for up to three years. Another example is the intrauterine device (IUD), a T-shaped device inserted into the uterus to provide long-term contraception. Injections, such as Depo-Provera, offer a reliable method of birth control by administering hormones every few months. Additionally, oral contraceptives, commonly known as birth control pills, are a widely used method that involves taking a daily pill to prevent pregnancy. Lastly, vaginal rings and skin patches also fall under the category of hormonal contraceptives, providing convenience and effectiveness in preventing pregnancy.
Reference source
https://go.drugbank.com/categories/DBCAT000688
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441576/
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/which-method-suits-me/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/11427-birth-control-options