Cystoma ovarii, a term that may leave many curious and intrigued, holds secrets yet to be unravelled.
As we delve into the depths of this enigmatic medical condition, we embark on an immersive journey into the fascinating world of ovarian cysts.
Brace yourself as we uncover the mysteries of cystoma ovarii, stirring a desire to discover more.
cystoma ovarii
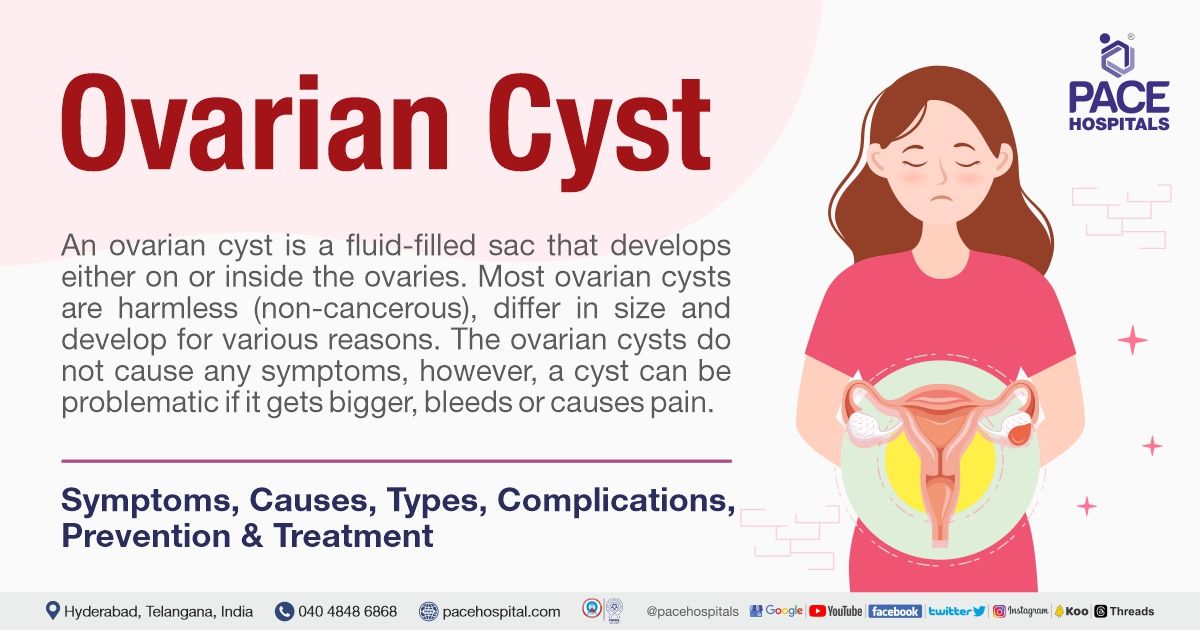
Cystoma ovarii is a type of ovarian cyst, specifically a benign cystic tumor that forms in the ovaries.
These cysts are typically filled with fluid and may vary in size, often growing very large.
They can cause abdominal discomfort, pain, and other symptoms.
Surgical removal is usually recommended for treatment, especially if they cause significant symptoms or pose a risk of rupture.
Key Points:
- Cystoma ovarii is a benign cystic tumor that develops in the ovaries.
- Commonly filled with fluid, these cysts come in various sizes and can grow to be quite large.
- Symptoms of cystoma ovarii include abdominal discomfort, pain, and others.
- Surgical removal is often the recommended course of treatment for cystoma ovarii.
- Treatment is particularly necessary if the cysts cause significant symptoms or carry a risk of rupture.
cystoma ovarii – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Cystoma ovarii refers to an ovarian tumor that develops from the lining of the ovary and consists of fluid-filled cysts.
2. One interesting fact about cystoma ovarii is that it is often asymptomatic, meaning it may not cause any noticeable signs or symptoms until it reaches a large size or causes complications.
3. While mostly benign, cystoma ovarii can occasionally turn into a malignant tumor called ovarian carcinoma, which is a more aggressive and potentially life-threatening condition.
4. Most cases of cystoma ovarii occur in women of reproductive age, typically between the ages of 30 and 60. However, these tumors can also affect postmenopausal women or, less frequently, young girls or adolescents.
5. An intriguing aspect of cystoma ovarii is that these tumors can occasionally contain unusual structures such as teeth, hair, bone, or even miniature body parts. These structures, known as dermoid cysts, form due to the embryonic development of the ovarian tissue.
Understanding Cystoma Ovarii: Causes And Symptoms
Cystoma Ovarii, also known as ovarian cystoma, is a type of cyst that forms in the ovaries. It occurs when fluid-filled sacs develop on or inside the ovaries. The exact cause of cystoma ovarii is unknown, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition. These factors include hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, and endocrine disorders.
The symptoms of cystoma ovarii can vary greatly and may depend on the size, location, and type of the cyst. Some common symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, irregular periods, pain during sexual intercourse, and frequent urination. In some cases, cystoma ovarii may also cause infertility or complications during pregnancy. It is important to note that some cysts may be asymptomatic and can only be detected through medical testing.
Symptoms of Cystoma Ovarii:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Irregular periods
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Frequent urination
Complications:
- Infertility
- Pregnancy complications
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms or suspect the presence of ovarian cysts.
Types Of Cystoma Ovarii And Their Characteristics
There are different types of cystoma ovarii, each with its own characteristics and features. The most common types include serous cystadenoma, mucinous cystadenoma, dermoid cysts, endometriomas, and cystadenofibromas.
- Serous cystadenomas are generally benign and filled with a clear, watery fluid.
- Mucinous cystadenomas, on the other hand, contain thick, sticky fluid.
- Dermoid cysts, also known as mature cystic teratomas, are usually benign and can contain different types of tissue, such as hair, skin, and teeth.
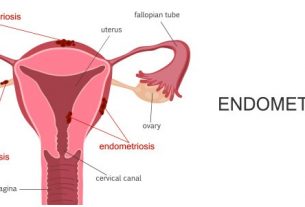
- Endometriomas are cysts that form due to endometriosis, a condition where the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
- Cystadenofibromas are a mix of cystic and solid components and are usually benign.
Examining Diagnostic Methods For Cystoma Ovarii
Diagnosing cystoma ovarii typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. A pelvic exam may help detect any abnormalities in the ovaries, while imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can provide detailed pictures of the cysts.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend additional tests such as blood tests or a biopsy to rule out the possibility of ovarian cancer or to determine the type of cyst. The diagnostic process is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment plan for cystoma ovarii.
- Medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests are used to diagnose cystoma ovarii.
- Pelvic exam detects abnormalities.
- Imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI provide detailed pictures of the cysts.
- Additional tests like blood tests or biopsy may be recommended.
- They help rule out ovarian cancer or determine the type of cyst.
- The diagnostic process is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment plan.
The diagnostic process plays a vital role in determining the treatment plan for cystoma ovarii.
Common Treatments For Cystoma Ovarii
The treatment for cystoma ovarii may vary depending on various factors, including the size of the cyst, the presence of symptoms, and the patient’s overall health.
In many cases, small cysts that are asymptomatic may not require immediate treatment and can be monitored through regular check-ups.
If the cyst is causing discomfort or if it is larger in size, the doctor may recommend surgical removal. Laparoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive procedure, is often used to remove the cyst or the affected ovary.
In more severe cases, where the cyst is suspected to be cancerous or there are complications, a more extensive surgery called laparotomy may be performed.
Surgical Options For Cystoma Ovarii Removal
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as keyhole surgery, is a common approach for removing cystoma ovarii. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using specialized tools to remove the cyst or the affected ovary.
This procedure has several advantages, including:
- Shorter recovery time
- Minimal scarring
- Reduced postoperative pain
In some cases, if the cyst is larger or if there are concerns about the potential spread of cancer, a laparotomy may be recommended. This is a more invasive procedure that involves a larger incision in the abdomen, allowing the surgeon to have better access to the ovaries.
The choice of surgical option depends on various factors and should be carefully discussed between the patient and the medical team.
Bullet Points:
- Laparoscopic surgery, also known as keyhole surgery
- Involves small incisions in the abdomen
- Specialized tools used to remove cyst or affected ovary
- Advantages include shorter recovery time, minimal scarring, and reduced postoperative pain
- Laparotomy may be recommended for larger cysts or concerns about cancer spread
- Laparotomy is a more invasive procedure with a larger incision
- Choice of surgical option depends on various factors and should be discussed with the medical team.
Managing Fertility Concerns With Cystoma Ovarii
Cystoma ovarii can have implications for a woman’s fertility. If only one ovary is affected, the remaining ovary may be able to compensate for hormone production and overall fertility. However, removal of both ovaries during surgery can lead to infertility and early menopause.
For women wishing to preserve their fertility, freezing eggs or embryos before surgery may be an option. This allows for the possibility of having children through assisted reproductive technologies in the future. It is crucial for women to discuss their fertility concerns with their healthcare providers to explore all available options.
Complications And Risks Associated With Cystoma Ovarii
While most cystoma ovarii are benign, there is a risk of complications, especially if they are not detected or treated promptly. If the cyst enlarges or ruptures, it can lead to severe pain, bleeding, and infection. In some cases, cysts can also twist or cause the ovary to twist, a condition known as ovarian torsion, which is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
Additionally, there is a small chance that a cystoma ovarii may be cancerous. If the cyst is suspected to be cancerous, further tests may be performed, such as a biopsy, to confirm the diagnosis. Early detection and timely treatment play a crucial role in managing the potential complications and risks associated with cystoma ovarii.
Lifestyle Changes For Preventing Cystoma Ovarii
Preventing Cystoma Ovarii through Lifestyle Modifications
To minimize the risk of cystoma ovarii, there are several lifestyle adjustments that can be made. These changes focus on maintaining overall reproductive health and early detection of any abnormalities.
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight: It is crucial to maintain a healthy weight as obesity has been linked to an increased risk of cystoma ovarii. By following a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise, the chances of developing this condition can be minimized.
2. Follow a Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is beneficial for reproductive health. A well-balanced diet provides essential nutrients and reduces the risk of cyst formation in the ovaries.
3. Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been associated with an increased risk of ovarian cysts. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can help reduce the likelihood of developing cystoma ovarii.
4. Undergo Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups, including pelvic exams and ultrasounds, play a crucial role in the early detection of ovarian cysts. It is recommended to schedule these check-ups with a healthcare professional to identify any abnormalities at an early stage.
5. Seek Professional Evaluation and Guidance: If you encounter any symptoms or have concerns related to cystoma ovarii, it is vital to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide appropriate evaluation, diagnosis, and guidance specific to your individual circumstances.
By implementing these lifestyle modifications and seeking proper medical attention, the risk of cystoma ovarii can be reduced. Stay proactive and prioritize your reproductive health.
Spotlight On Research And Advancements In Cystoma Ovarii Treatment
There is ongoing research and advancements in the field of cystoma ovarii treatment. Scientists and medical researchers are exploring new diagnostic methods, such as blood tests and genetic markers, to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosing cysts.
In terms of treatment, there is a focus on developing less invasive surgical techniques, such as robotic-assisted surgery, to further minimize the risks and improve patient outcomes. Additionally, targeted drug therapies and hormonal treatments are being studied as potential options for preventing cyst recurrence or managing symptoms.
Clinical trials are also being conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of new treatments and therapies. These trials provide opportunities for patients to access cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge in this field. It is important to stay informed about the latest research and discuss any potential options with a healthcare provider.
- New diagnostic methods being explored: blood tests and genetic markers
- Focus on developing less invasive surgical techniques, such as robotic-assisted surgery
- Targeted drug therapies and hormonal treatments being studied for preventing cyst recurrence and managing symptoms
- Clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of new treatments and therapies
- Stay informed about the latest research and discuss potential options with a healthcare provider.
Real-Life Stories: Surviving Cystoma Ovarii
Real-life stories of individuals who have survived cystoma ovarii can provide inspiration and support for those going through a similar journey. These stories often highlight the resilience, strength, and determination of individuals facing the challenges of cystoma ovarii.
Through sharing their experiences, survivors can raise awareness about the condition, promote early detection, and provide hope to others. Hearing about successful treatment outcomes and the ability to overcome fertility concerns can offer solace and encouragement to those starting their own battle against cystoma ovarii.
“It is through the stories of survivors that we find strength and hope.”
- Increased understanding of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options of cystoma ovarii helps individuals actively participate in their healthcare decisions.
- Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for improved outcomes.
- The stories of other survivors serve as a source of support and inspiration.
Stay strong and know that you are not alone in this journey.
💡
You may need to know these questions about cystoma ovarii
What is cystoma of ovaries?
Cystoma of the ovaries, also known as ovarian cystoma, refers to the presence of solid or fluid-filled pockets on the ovary. These cysts are frequently observed in women who are pregnant or premenopausal. Although typically painless and benign, they can occur regularly as part of the menstrual cycle without being noticed. These cysts are common and do not usually pose a significant health concern unless they grow exceptionally large or become cancerous.
How serious is a cyst on your ovaries?
While most ovarian cysts are generally benign and resolve on their own, the seriousness of a cyst on the ovaries largely depends on its size, type, and symptoms. In the majority of cases, these cysts are not a cause for concern, with less than 1% being cancerous. However, if a cyst grows larger or causes persistent pain, it may require medical attention as it could lead to complications. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare professional is crucial to ensure appropriate management and intervention if necessary.
It is essential to note that each individual’s situation is unique, and a proper diagnosis and assessment by a healthcare provider are important in determining the severity of an ovarian cyst. While the majority of cases are non-threatening, it is always advisable to keep track of symptoms, seek medical advice if concerned, and adhere to recommended follow-up appointments.
What is a cystadenoma on the ovaries?
A cystadenoma on the ovaries is a benign epithelial neoplasm that commonly occurs and has a favorable prognosis. Typically, there are two main types of cystadenomas: serous and mucinous. Serous cystadenomas are fluid-filled cysts that develop from the surface cells of the ovary, while mucinous cystadenomas are filled with a thick, gelatinous substance. However, rare types such as endometrioid and clear cell cystadenomas may also occur. Although less common, these cystadenomas can still be benign and have a positive outlook.
What is the main cause of ovarian cyst?
The main cause of ovarian cysts is hormonal problems. Sometimes these cysts occur as a result of hormonal imbalances in the body, leading to the formation of functional cysts. These types of cysts are usually self-resolving and do not require treatment. In some cases, the use of medications to induce ovulation can also contribute to the development of ovarian cysts.
Reference source
https://www.webmd.com/women/ovarian-cysts
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9133-ovarian-cysts
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536950/
https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/ovarian-cysts