Every month, the remarkable phenomenon of decidua vera takes place within a woman’s body, silently preparing for the possibility of new life.
As the mucosal lining of the uterus, it plays a crucial role in sustaining pregnancy, yet its intricate functions remain a mystery.
Join us on a journey to uncover the secrets hidden within the decidua vera, as we explore its captivating journey through conception, gestation, and beyond.
Discover how this enigmatic tissue is intricately linked to both the miracle of life and the challenging circumstances of pre-term labor.
decidua vera
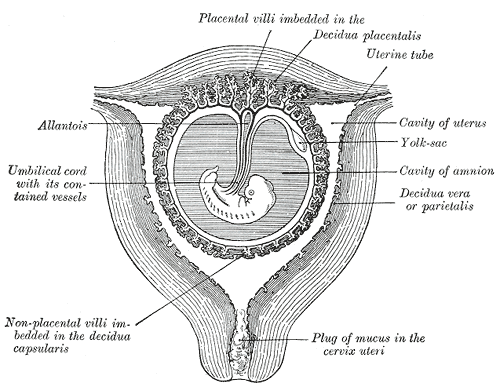
Decidua vera, also known as parietal decidua or true decidua, refers to the mucosal lining of the uterus that does not include the area occupied by the implanted ovum and chorion.
It is shed after childbirth, except for the deepest layer.
The decidua plays a crucial role in pregnancy by forming the maternal part of the placenta, facilitating nutrient exchange, and secreting hormones, growth factors, and cytokines.
Additionally, chronic deciduitis, an infection of the decidua, is associated with pre-term labor.
However, the exact role and interplay of these factors are not well understood.
In invasive placental disorders like placenta accreta, the decidua is found to be deficient.
Key Points:
- Decidua vera refers to the mucosal lining of the uterus excluding the area occupied by the implanted ovum and chorion.
- It is shed after childbirth, except for the deepest layer.
- The decidua forms the maternal part of the placenta, facilitating nutrient exchange and secreting hormones, growth factors, and cytokines.
- Chronic deciduitis, an infection of the decidua, is associated with pre-term labor.
- The exact role and interplay of these factors are not well understood.
- In invasive placental disorders like placenta accreta, the decidua is deficient.
decidua vera – Watch Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FupW_7D6EJ4
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The decidua vera is a specialized tissue that forms in the uterus during pregnancy, helping to nourish and support the developing fetus.
2. The decidua vera is made up of a combination of maternal and fetal cells, creating a unique blend of genetic material within this tissue.
3. The decidua vera secretes hormones such as progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which are crucial for maintaining pregnancy and supporting fetal development.
4. Studies have shown that abnormalities in the decidua vera can contribute to certain pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia and recurrent miscarriages.
5. Some researchers believe that studying the decidua vera could provide valuable insights into the mechanisms behind infertility and pregnancy-related disorders, potentially leading to new treatments and interventions.
1. Introduction To Decidua Vera
The decidua vera, also known as parietal decidua or true decidua, is a vital component of the uterus during pregnancy. It is a specialized mucosal lining that forms every month in preparation for pregnancy. During pregnancy, the decidua vera provides important support and protection for the developing embryo.
The term “decidua vera” specifically refers to the decidua that does not include the area occupied by the implanted ovum and chorion. In other words, it is the lining of the uterus that does not directly surround the embryo.
After childbirth, the decidua vera is shed, except for the deepest layer. This shedding process is a natural part of the postpartum recovery.
Some key points about the decidua vera include:
- It is a specialized mucosal lining in the uterus
- It forms every month in preparation for pregnancy
- It provides support and protection for the developing embryo during pregnancy
- “Decidua vera” refers to the lining that does not surround the embryo
- It is shed after childbirth, except for the deepest layer
2. Definition And Synonyms Of Decidua Vera
Decidua vera, also known as parietal decidua or true decidua, refers to the decidua that is not occupied by the implanted ovum and chorion. It is important to note that “decidua vera” is interchangeable with the terms “parietal decidua” or “true decidua.” These synonyms highlight the fact that decidua vera solely represents the genuine decidua, excluding any tissues occupied by the developing embryo and the placenta.
3. Function And Formation Of Decidua
The decidua is an essential component in the process of pregnancy, as it serves as the innermost layer of the uterine wall. This layer plays a critical role in creating an optimal environment for the developing embryo by promoting implantation and growth. Moreover, the decidua acts as the maternal portion of the placenta, facilitating essential functions such as nutrient exchange, gas exchange, and waste removal, all of which are necessary to support the developing fetus.
- The decidua acts as the innermost layer of the uterine wall.
- It promotes implantation and growth of the fertilized egg.
- The decidua plays a maternal role in nutrient exchange, gas exchange, and waste removal.
- Its main function is to support the development of the fetus.
4. Postpartum Shedding Of Decidua Vera
After childbirth, the decidua vera is shed, with the exception of the deepest layer. This shedding occurs as the uterus contracts to expel the placenta and any remaining tissues from pregnancy. The detachment and removal of the decidua vera are important steps in the natural postpartum process, allowing the uterus to return to its pre-pregnancy state.
- Postpartum shedding of the decidua vera is a normal process after childbirth.
- The deepest layer of the decidua vera remains intact.
- The uterus contracts to expel the placenta and any remaining tissues.
- Removal of the decidua vera helps the uterus return to its pre-pregnancy state.
“The detachment and removal of the decidua vera are part of the natural postpartum process.”
5. Decidua’s Role In Placenta Formation
During pregnancy, the decidua transforms into the maternal part of the placenta, facilitating the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between the mother and the fetus. The decidua also anchors the placenta to the uterine wall and supports the development of vital structures necessary for fetal growth and development.
- The decidua transforms into the maternal part of the placenta.
- Facilitates exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products.
- Anchors the placenta to the uterine wall.
- Supports development of vital structures for fetal growth and development.
6. Histological Features Of Decidua
Histologically, the decidua exhibits distinct features that differentiate it from other uterine tissues. One notable characteristic is the presence of large decidual cells. These cells undergo significant changes during pregnancy and are responsible for secreting various substances necessary for implantation, placentation, and fetal development.
- The decidua is histologically different from other uterine tissues.
- Large decidual cells are a prominent feature of the decidua.
- During pregnancy, these cells undergo significant changes.
- The decidual cells secrete crucial substances for implantation, placentation, and fetal development.
It is important to note the specialized role of the decidua in supporting and nurturing the developing embryo and fetus.
7. Functions Of Decidua During Pregnancy
The decidua plays a crucial role during pregnancy by serving multiple functions. It provides a nurturing environment for the developing embryo. Additionally, it secretes hormones, growth factors, and cytokines. These secretions play a vital role in regulating various biological processes that are essential for a successful pregnancy. However, the exact interplay of these substances is still not fully understood.
8. Decidua Deficiency In Placental Disorders
In placenta accreta, a placental disorder, the decidua is deficient or lacking. This condition arises when the placenta attaches too deeply into the uterine wall, which may result in serious childbirth complications. The absence or inadequate development of the decidua plays a role in these abnormal implantation conditions.
- Placenta accreta is a placental disorder
- Decidua is deficient or lacking in this condition
- Placenta attaches too deeply into the uterine wall
- Serious childbirth complications can occur
- Absence or inadequate development of decidua contributes to abnormal implantation conditions.
9. Secretions From Decidua
Apart from providing structural support, the decidua plays a crucial role in pregnancy by secreting various substances that have important functions. These substances include hormones, growth factors, and cytokines, which play key roles in regulating immune response, tissue remodeling, and fetal development.
Ongoing research and exploration are focused on uncovering the specific functions and interactions of these secretions.
- The decidua secretes hormones, growth factors, and cytokines.
- These substances regulate immune response, tissue remodeling, and fetal development.
“The specific functions and interactions of these secretions are subjects of ongoing research and exploration.”
10. Understanding The Role Of Decidua In Hormones And Factors
Research efforts are currently focused on unraveling the complexities of the substances secreted by the decidua in pregnancy. These substances include hormones, growth factors, and cytokines. Their precise role and interplay in pregnancy are not yet fully understood.
It is believed that these substances play a crucial role in various aspects of pregnancy, including implantation, placental development, and overall maternal-fetal health. However, further research is needed to fully comprehend their significance and how they influence these processes.
Understanding the role of these substances in pregnancy may have significant implications for advancements in reproductive medicine and the improved management of pregnancy-related conditions.
- The decidua secretes hormones, growth factors, and cytokines
- Precise role and interplay of these substances in pregnancy not fully understood
- Research efforts focused on unraveling their complexities and impact on pregnancy
- Importance of these substances in implantation, placental development, and maternal-fetal health
- Further understanding may lead to advancements in reproductive medicine and improved management of pregnancy-related conditions.
11. Association Of Deciduitis With Pre-Term Labor
Chronic deciduitis is a long-lasting infection of the decidua, and it has been found to increase the risk of pre-term labor. This infection disrupts the normal functioning of the decidua and leads to inflammation, which can have a negative impact on a healthy pregnancy.
Understanding and addressing the role of deciduitis in pre-term labor is crucial for effectively managing and improving outcomes for pregnancies affected by this condition.
To summarize:
- Chronic deciduitis is a long-lasting infection of the decidua that increases the risk of pre-term labor.
- This infection disrupts the normal functioning of the decidua and causes inflammation.
- Understanding the role of deciduitis in pre-term labor is essential for better managing affected pregnancies.
“The decidua vera, or parietal decidua, is an integral component of the uterus during pregnancy. It forms the maternal part of the placenta, supports the developing embryo, and plays a vital role in nutrient exchange, gas exchange, and waste removal.”
💡
You may need to know these questions about decidua vera
1. What is decidua vera and how does it play a role in pregnancy?
The decidua vera, also known as the maternal decidua, refers to the lining of the uterus during pregnancy. It is formed by the transformation of the uterine mucosa in response to hormonal changes, particularly the rise in progesterone levels. The decidua vera plays a crucial role in supporting and nourishing the developing embryo.
During pregnancy, the decidua vera interacts with the gestational sac, which contains the developing fetus. It helps to anchor and protect the embryo, providing a nurturing environment for its growth. The decidua vera also contributes to the formation of the placenta, which is responsible for the exchange of nutrients and waste between the mother and the fetus. Additionally, it plays a role in immune tolerance, preventing the mother’s immune system from rejecting the fetus as a foreign entity. In summary, the decidua vera is essential for successful implantation and the maintenance of a healthy pregnancy.
2. What are the differences between decidua vera and decidua basalis?
Decidua vera and decidua basalis are two different layers of the endometrium, or uterine lining, that develop during pregnancy. Decidua vera refers to the part of the endometrium that lines the entire uterine cavity, separate from the placenta. It undergoes changes to support implantation and nourishment of the developing embryo. It sheds during menstruation if pregnancy does not occur.
On the other hand, decidua basalis is the portion of the endometrium that lies in direct contact with the developing placenta. It forms at the site where the embryo implants into the uterine wall. The decidua basalis is responsible for facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the maternal and fetal bloodstreams. It remains intact throughout pregnancy and is expelled during childbirth as a part of the placenta.
3. How does decidua vera prevent immune rejection during pregnancy?
The decidua vera, also known as the maternal part of the placenta, plays a crucial role in preventing immune rejection during pregnancy. It acts as a barrier between the developing fetus and the maternal immune system.
The decidua vera contains specialized immune cells called uterine natural killer (uNK) cells. These cells help regulate the immune response by promoting tolerance towards the fetus. They release certain molecules and cytokines that suppress the maternal immune response, preventing it from recognizing the fetus as a foreign entity and rejecting it. Additionally, the decidua vera also produces factors that promote the growth of blood vessels and support the development of the placenta, further ensuring a stable environment for the fetus.
4. Are there any medical conditions associated with abnormalities in the decidua vera?
Yes, there are medical conditions associated with abnormalities in the decidua vera. The decidua vera is the lining of the uterus during pregnancy and any abnormalities in this tissue can lead to complications. Conditions such as placenta accreta, which is the abnormal adherence of the placenta to the uterine wall, can occur when there are abnormalities in the decidua vera. This can result in a higher risk of bleeding during pregnancy and difficulty in separating the placenta during childbirth. Another condition associated with abnormalities in the decidua vera is ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube. These abnormalities can have serious implications on the health of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5065593/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7312091/
https://www.bionity.com/en/encyclopedia/Decidua.html
https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/decidua+vera