In the fast-paced world we live in, the delivery mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring efficient and secure transactions.
From smart cards to mobile money transfers and even cash in envelopes, these innovative methods have revolutionized the way we handle cash and voucher transfers.
Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of delivery mechanisms and explore how they shape our modern economy.
delivery mechanism
A delivery mechanism refers to the method used to deliver cash or voucher transfers.
It encompasses various means such as smart cards, mobile money transfers, and cash in envelopes.
These delivery mechanisms offer convenience and flexibility in distributing financial assistance, allowing recipients to access funds in a manner that suits their preferences and circumstances.
Key Points:
- Delivery mechanisms are methods used to distribute cash or voucher transfers.
- They include smart cards, mobile money transfers, and cash in envelopes.
- Delivery mechanisms offer convenience and flexibility in distributing financial assistance.
- They allow recipients to access funds in a way that suits their preferences and circumstances.
- The goal is to make the distribution process more efficient and user-friendly.
- Different delivery mechanisms cater to different needs and technological capabilities.
delivery mechanism – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The first known delivery mechanism for sending messages and letters across long distances was the pigeon post. Dating back to ancient times, this method involved attaching messages to homing pigeons who would then fly back to their home, transporting the messages to their intended recipients.
2. The very first successful recorded drone delivery was made in 1849. Airmail pioneer John Wise utilized a hot air balloon to deliver mail between two towns in Pennsylvania. The mail pouch was dropped by parachute, marking the birth of aerial delivery mechanisms.
3. In 1929, German engineer Fritz von Opel designed and successfully tested a rocket-powered mail delivery system. The rocket, named Opel RAK.2, launched from a car and traveled at a speed of 238 mph, delivering a package of letters to a predetermined location.
4. The world’s first self-propelled torpedo was developed by engineer Robert Whitehead in 1866. Initially designed as a naval weapon, it soon became clear that this torpedo could also be used as a delivery mechanism for explosives. This invention revolutionized underwater warfare and laid the foundation for future delivery systems, such as modern-day submarines.
5. During the 1800s, the Lamson Cash Carrier System became a popular form of delivery mechanism in large department stores and buildings. The system consisted of a network of overhead cables through which containers, holding money or small items, were transported using a pneumatic tube system. This allowed for rapid and efficient delivery within the premises, eliminating the need for manual transport.
1. Introduction To Delivery Mechanism
The delivery mechanism is essential for distributing goods and services, such as cash or voucher transfers. Its significance has increased in recent years, especially in terms of resource distribution efficiency. This article examines the development of delivery mechanisms, with a specific focus on their role in vaccine distribution. With the current global health crisis and the need to vaccinate large populations, delivery mechanisms play a critical role in ensuring the timely and efficient distribution of vaccines globally.
2. Definition Of Delivery Mechanism
A delivery mechanism, as defined by the European Commission, refers to the method employed to deliver cash or voucher transfers. It encompasses the various means through which these transfers are made accessible to the intended recipients.
In the context of vaccines, the delivery mechanism involves the systems and tools used to ensure the vaccines reach their designated destinations, such as healthcare centers or distribution points. This includes both the physical means of transportation as well as the digital platforms used to track and manage the distribution process.
3. Types Of Delivery Mechanisms
There are three commonly utilized types of delivery mechanisms for cash or voucher transfers:
- Smart cards
- Mobile money transfers
- Cash in envelopes
These mechanisms provide efficient ways to transfer funds and provide individuals with access to money. Each method has its own advantages and considerations.
-
Smart cards offer a convenient and secure way to store and access funds. They are portable and can be used at various locations that accept electronic payments. Smart cards also provide an extra layer of security through features like PIN codes or biometric authentication.
-
Mobile money transfers utilize mobile phones to send and receive funds. This method is particularly advantageous in areas with limited banking infrastructure, as it allows individuals to access and transfer funds using their mobile phones. Mobile money transfers are fast, convenient, and can be easily scalable.
-
Cash in envelopes involves physically delivering cash to recipients. Although this method may seem traditional, it is still widely used, especially in areas with limited access to electronic payment systems. Cash in envelopes provides a tangible form of funds, which could be useful in certain situations.
It is important to consider factors such as cost, security, infrastructure, and the needs of the recipients when choosing a delivery mechanism for cash or voucher transfers.
Smart Cards:
Smart cards have revolutionized the delivery of cash or voucher transfers by providing a secure and convenient method. These cards, equipped with embedded microchips, allow for electronic transactions, eliminating the need for physical cash. Users can access their funds through designated terminals or ATMs, making it easier to distribute and manage resources effectively.
- Smart cards have embedded microchips for secure transactions
- No need for physical cash
- Access funds through designated terminals or ATMs
“Smart cards have revolutionized the delivery of cash or voucher transfers by providing a secure and convenient method.”
Mobile Money Transfers:
Mobile money transfers have witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, especially in regions with limited access to traditional banking services. This innovative payment method uses mobile phone networks to efficiently transfer funds. Recipients can conveniently and securely access their money through their mobile devices, making it a reliable and user-friendly distribution channel.
Cash In Envelopes:
Cash in envelopes is a traditional method of distributing cash or voucher transfers. While not as technologically advanced as smart cards or mobile money transfers, it still serves as a viable option for areas with limited access to digital infrastructure.
Cash in envelopes guarantees that recipients, especially those in remote regions, have direct access to the transfer without the need for additional infrastructure or technology.
4. Smart Cards As A Delivery Mechanism
Smart cards have emerged as a reliable and efficient delivery mechanism in the distribution of cash or voucher transfers. These cards offer enhanced security features, reducing the risks associated with physical cash transactions. Additionally, smart cards provide a digital record of transactions, allowing for easier tracking and auditing. Their versatility and compatibility with existing payment infrastructure make them a desirable option for governments and organizations seeking to improve the efficiency of their delivery mechanisms.
5. Mobile Money Transfers As A Delivery Mechanism
Mobile money transfers have revolutionized the distribution of cash or voucher transfers. The widespread availability of mobile devices, especially in developing nations, has made this delivery method incredibly convenient and accessible. Recipients can now conveniently receive funds directly on their mobile phones, eliminating the need for physical travel or the involvement of intermediaries. Moreover, mobile money transfers foster financial inclusion, allowing individuals who lack access to traditional banking services to participate in the flourishing digital economy.
6. Cash In Envelopes As A Delivery Mechanism
Despite the advancements in digital technologies, cash in envelopes still holds relevance in certain situations. It remains an important delivery mechanism, especially in areas where technological infrastructure is limited or unreliable. Cash in envelopes ensures that recipients who may not have access to banking services or digital platforms can still receive their cash or vouchers reliably. This method requires careful planning to ensure the security and integrity of the distribution process.
7. Importance Of Delivery Mechanisms
Delivery mechanisms play a crucial role in the distribution of vaccines, particularly during global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. The prompt and efficient delivery of vaccines is essential to ensure they reach their intended recipients. The success of vaccination campaigns heavily relies on the effectiveness of the delivery mechanism. A well-designed and efficient delivery system is vital as it can save lives, prevent disease spread, and mitigate the socio-economic consequences of pandemics.
8. Factors To Consider In Choosing A Delivery Mechanism
When selecting a delivery mechanism, several factors must be taken into consideration:
- Infrastructure available in the target regions: The delivery mechanism should be compatible with the existing infrastructure to ensure smooth operation and accessibility.
- Digital literacy among recipients: The level of digital skills among the recipients should be considered. If there is low digital literacy, the delivery mechanism should be user-friendly and easy to navigate.
- Security of the delivery method: Ensuring the security of the delivery method is crucial to protect sensitive information and maintain data integrity.
- Scalability: The selected delivery mechanism should have the capability to handle increasing demands and accommodate future growth.
- Cost-effectiveness: Evaluating the cost of implementing and maintaining the delivery mechanism is essential to ensure efficient use of resources.
- Ease of integration with existing systems: The delivery mechanism should be easily integrated with any existing systems to optimize workflow and minimize disruptions.
By considering these factors, the distributing entity can select a delivery mechanism that aligns with their objectives and resources, ultimately leading to successful implementation.
9. Challenges And Opportunities In Delivery Mechanisms
While delivery mechanisms are crucial for efficient resource distribution, they encounter various challenges that need to be addressed. Some of these challenges include:
-
Technological barriers: In remote areas, unreliable connectivity can hinder the effectiveness of delivery mechanisms. This can affect the timely and accurate distribution of resources.
-
Security concerns: Digital platforms used for resource distribution may face security threats. Safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring secure transactions is of utmost importance.
-
Logistical obstacles: The transportation and storage requirements for vaccines, for example, can pose significant challenges in the distribution process. Maintaining the cold chain and ensuring the quality and efficacy of vaccines during transportation and storage is essential.
However, these challenges also pave the way for innovation and improvement. Opportunities for advancement in delivery mechanisms can arise through:
-
New technologies: The integration of emerging technologies, such as Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain, can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of delivery mechanisms. These technologies can improve tracking and monitoring capabilities, ensuring resources reach their intended recipients.
-
Partnerships and collaborations: Collaboration between different stakeholders, including governments, non-profit organizations, and private sector entities, can lead to the development of more robust delivery mechanisms. By leveraging their collective expertise and resources, innovative solutions can be devised.
In conclusion, while delivery mechanisms face challenges related to technology, security, and logistics, these obstacles also present opportunities for improvement. Embracing new technologies and fostering collaborations can help overcome these challenges and contribute to more efficient and effective resource distribution.
10. Conclusion And Future Of Delivery Mechanisms
The evolution of delivery mechanisms continues to shape the way resources, including vaccines, are distributed globally. Smart cards, mobile money transfers, and traditional cash in envelopes provide varied options to accommodate the diverse needs of different populations. As technology advances and connectivity improves, digital delivery mechanisms are expected to gain prominence. However, it is essential to acknowledge and address the existing gaps in technological infrastructure to ensure equitable access to resources for all. The future of delivery mechanisms lies in their ability to adapt, innovate, and overcome challenges to ensure efficient distribution and promote global health and well-being.
Bullet points:
- Smart cards
- Mobile money transfers
- Traditional cash in envelopes
💡
You may need to know these questions about delivery mechanism
What is the mode of delivery of the virus?
One of the most common modes of delivery for computer viruses is through infected email attachments. Cybercriminals often disguise the virus in seemingly innocent files attached to emails, tricking unsuspecting users into opening them and activating the virus. These infected attachments can then quickly spread the virus to other computers within the same network or through forwarded emails.
Additionally, malicious online downloads pose a significant risk for virus transmission. Cyber attackers may disguise viruses within seemingly harmless files or software available for download from untrustworthy websites. Once downloaded and executed, the virus can infiltrate the system and potentially infect other files or compromise the entire network. Therefore, users must exercise caution when downloading files from the internet and ensure they are from reputable sources to mitigate the risk of virus infection.
What are the principle considerations when selecting a transfer delivery mechanism?
When considering the selection of a transfer delivery mechanism, several key factors should be taken into account. Firstly, it is important to assess the cost effectiveness and efficiency of the different options available, as this will determine the overall impact and value for money of the transfers. Additionally, the potential secondary market impacts should be carefully considered, including how the transfers may affect local economies and market prices. Furthermore, the flexibility of the transfer is crucial, as it should be adaptable to the specific needs and circumstances of the beneficiaries. Lastly, local availability of goods and services should also be taken into account, as this will affect the feasibility and impact of the chosen transfer delivery mechanism. By considering these principle considerations, a well-informed decision can be made to ensure the successful implementation of the transfer program.
How are viral vectors delivered?
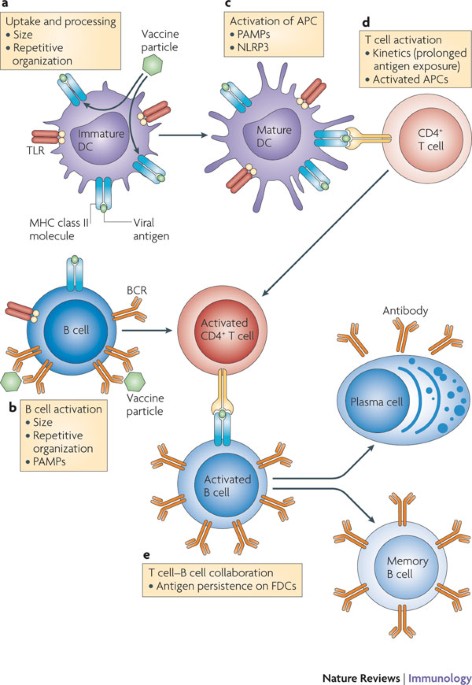
Viral vectors, such as Adeno-Associated Viral (AAV) vectors, are commonly used for delivering gene therapies in vivo. These vectors are injected into specific parts of the body, allowing them to deliver new genetic instructions directly to the targeted cells. By harnessing the natural ability of viruses to infect cells, AAV vectors can efficiently and safely transport therapeutic genes to the desired tissues, where they can exert their therapeutic effect. The precise delivery of viral vectors enables the potential treatment of various genetic disorders and diseases at a cellular level, offering promising prospects for gene therapy advancements.
What are the four methods of virus?
The four methods of virus are as follows:
1. Attach: In this method, the virus code attaches itself to a program that is not affected by the virus. By doing so, the virus can spread its malicious code when the unaffected program is executed.
2. Substitute: In this method, the virus code replaces the original executable program entirely or partially. By doing so, the virus gains control over the execution of the program and can carry out its malicious activities.
3. Embed: In this method, the viral code is embedded within the body of an executable code. This allows the virus to execute its actions while the host program is running, often resulting in unexpected and humorous outcomes.
4. Transfer: In this method, the virus code transfers itself from one host to another, often through various means such as networks, removable storage devices, or email attachments. This allows the virus to rapidly spread and infect multiple systems.
Reference source
https://socialprotection.org/learn/glossary/delivery-mechanism
https://www.avast.com/c-computer-virus
https://ec.europa.eu/echo/files/policies/sectoral/concept_paper_common_top_line_principles_en.pdf
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/delivery-mechanism