Imagine a world where the most mysterious conditions lurk in the shadows, waiting to be unraveled.
One such enigma has perplexed experts for years – diabetic vulvitis.
With no concrete information or decipherable clues, this intriguing ailment captivates the mind, awakens curiosity, and demands our attention.
Delve into the unknown as we explore the depths of this peculiar affliction, weaving a tale that only the brave dare to uncover.
Welcome to the realm of diabetic vulvitis.
diabetic vulvitis
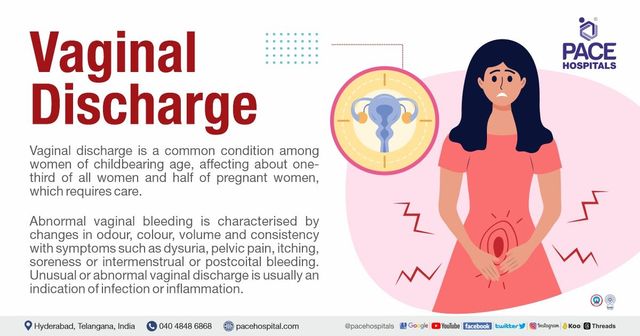
Diabetic vulvitis refers to inflammation or infection of the vulva in women with diabetes.
It is typically caused by elevated blood sugar levels, which can lead to changes in the vaginal environment and make it more susceptible to infections.
Common symptoms include itching, redness, swelling, and an increased risk of yeast or bacterial infections.
Proper management of blood sugar levels and good hygiene are important in preventing and treating diabetic vulvitis.
Topical creams or medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and clear the infection.
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are recommended for women with diabetes to monitor and address any issues related to vulvitis.
Key Points:
- Diabetic vulvitis is inflammation or infection of the vulva in women with diabetes caused by elevated blood sugar levels.
- Symptoms include itching, redness, swelling, and increased risk of yeast or bacterial infections.
- Proper management of blood sugar levels and good hygiene are important in prevention and treatment.
- Topical creams or medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and clear the infection.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are recommended for women with diabetes to monitor and address vulvitis.
- Diabetic vulvitis is more common in women with diabetes due to changes in the vaginal environment caused by elevated blood sugar levels.
diabetic vulvitis – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Diabetic Vulvitis Trivia: Did you know that the condition is more common in postmenopausal women? Although diabetic vulvitis can affect females of all ages, it tends to be more prevalent in women after menopause.
2. Did you know that proper blood sugar control is crucial in managing diabetic vulvitis? High blood sugar levels can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, leading to inflammation and infection. Maintaining stable glucose levels can help prevent or alleviate symptoms.
3. Contrary to popular belief, men can also experience symptoms similar to diabetic vulvitis. Although it is less common, males with diabetes may develop balanitis, which is the inflammation of the head of the penis, often accompanied by redness, itching, and soreness.
4. One possible complication of untreated diabetic vulvitis is increased susceptibility to urinary tract infections (UTIs). The inflamed vulvar tissues can increase the risk of bacteria entering the urinary tract, resulting in recurring UTIs.
5. Diabetic vulvitis can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions, such as yeast infections or sexually transmitted infections. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis, as different treatments may be necessary for each condition.
What Is Diabetic Vulvitis?
Diabetic Vulvitis: A Condition Affecting Women with Diabetes
Diabetic Vulvitis is a condition that specifically affects women with diabetes, causing inflammation of the vulva, which is the external genitalia. It is characterized by several uncomfortable symptoms, including itching, burning, redness, and soreness in the vulvar region. Despite its potentially misleading rarity, it is essential to shed light on this topic, as it significantly impacts the quality of life for those affected. Therefore, understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for diabetic vulvitis is crucial in managing and providing support for individuals living with this condition.
Key Facts:
- Diabetic Vulvitis is a condition that solely affects women with diabetes.
- It causes inflammation of the vulva, resulting in symptoms such as itching, burning, redness, and soreness in the vulvar region.
- The condition is not as uncommon as it may sound and requires attention due to its significant impact on the affected individuals’ quality of life.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Diabetic Vulvitis is diagnosed by a healthcare professional, typically a gynecologist, through a thorough physical examination and evaluating the patient’s medical history.
- Treatment options for diabetic vulvitis often focus on managing the symptoms and controlling diabetes effectively. The treatment plan may involve:
- Maintaining good blood sugar control through diet, exercise, and proper medication.
- Keeping the vulvar area clean and dry to minimize irritation.
- Avoiding harsh soaps, scented products, and tight-fitting clothing that can worsen symptoms.
- Using prescribed medications, such as topical corticosteroids or antifungal creams, to alleviate inflammation and discomfort.
Support and Management:
“Diabetic vulvitis not only affects physical health but also significantly impacts an individual’s emotional well-being and overall quality of life. It is important for healthcare professionals to provide empathetic support and education to those living with this condition.” –Diabetes Specialist
- Individuals living with diabetic vulvitis require comprehensive support from healthcare professionals to manage the condition effectively.
- Educational resources and awareness campaigns should be promoted to ensure accurate information reaches both patients and healthcare providers.
- Mental health support, such as counseling and therapy, can play a vital role in addressing the emotional impact of living with diabetic vulvitis.
In conclusion, Diabetic Vulvitis is a condition exclusive to women with diabetes, causing inflammation of the vulva and resulting in uncomfortable symptoms. Despite potentially being overlooked, it significantly affects the quality of life of those affected. Therefore, understanding the condition, seeking appropriate diagnosis and treatment, and providing empathetic support are crucial steps in managing and supporting individuals living with diabetic vulvitis.
- Causes: Unknown, but likely related to high blood sugar levels and weakened immune system in individuals with diabetes.
- Symptoms: Itching, burning, redness, and soreness in the vulvar region.
- Diagnosis: Through a thorough physical examination and evaluation of medical history by a healthcare professional, typically a gynecologist.
- Treatment: Managing diabetes effectively, maintaining good blood sugar control, practicing proper hygiene, and using prescribed medications.
- Support: Comprehensive support, awareness campaigns, educational resources, and mental health support are important for individuals with diabetic vulvitis.
Symptoms Of Diabetic Vulvitis
The symptoms of diabetic vulvitis can vary from person to person, but commonly reported signs include itching, burning, and soreness in the vulvar area. The affected skin may also appear red, swollen, or irritated. Some women may experience pain during sexual intercourse or notice an increase in vaginal discharge. It is important to note that these symptoms can be similar to other vaginal infections, so a proper diagnosis is essential.
Causes Of Diabetic Vulvitis
Diabetic vulvitis is primarily caused by elevated blood sugar levels that occur in diabetes. The excess glucose in the bloodstream can lead to yeast infections, as the yeast Candida thrives in a high-sugar environment. Additionally, the compromised immune system in individuals with diabetes can make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections. Poor blood sugar control, excessive sweating, and hormonal imbalances can also contribute to the development of diabetic vulvitis.
Diagnosis Of Diabetic Vulvitis
Diagnosing diabetic vulvitis involves a thorough examination of the symptoms and medical history. A healthcare professional may perform a pelvic examination and collect a sample of vaginal discharge for laboratory analysis. This analysis can help determine if there is an overgrowth of yeast or bacteria. In some cases, a biopsy of the vulvar tissue may be necessary to rule out other potential causes or complications.
Treatment Options For Diabetic Vulvitis
Treatment for diabetic vulvitis focuses on addressing the underlying causes, managing symptoms, and preventing future occurrences.
- Antifungal creams or ointments may be prescribed to combat yeast infections.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial infections.
Proper diabetes management is essential to maintain good blood sugar control and significantly reduce the risk of recurrent infections.
Other measures to manage and prevent diabetic vulvitis include:
- Practicing good hygiene.
- Avoiding irritants.
- Wearing breathable cotton underwear.
“It is essential to maintain good blood sugar control through proper diabetes management, as this can significantly reduce the risk of developing recurrent infections.”
Prevention And Management Of Diabetic Vulvitis
Prevention and Management of Diabetic Vulvitis
Diabetic vulvitis, a common complication of diabetes, can be effectively prevented and managed by implementing a combination of lifestyle changes and proper diabetes management. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
-
Blood sugar control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is essential in preventing recurrent infections. Proper diabetes management, including medication adherence and healthy eating habits, plays a pivotal role in achieving good blood sugar control.
-
Hygiene practices: Practicing good hygiene is paramount in preventing diabetic vulvitis. This includes keeping the vulvar area clean and dry. It is advisable to avoid using scented products or harsh soaps, as they can disturb the natural balance of the vaginal flora. Additionally, opting for breathable, loose-fitting cotton underwear can help maintain the vaginal area’s dryness and prevent excessive moisture buildup.
-
Regular check-ups: Scheduling regular check-ups with healthcare professionals is crucial in monitoring for any signs of infection. These professionals can provide guidance on how to manage and prevent diabetic vulvitis effectively. Seeking medical advice promptly when symptoms arise is essential to ensure timely intervention and prevent complications.
Remember, prioritizing self-care, maintaining good blood sugar control, adopting proper hygiene practices, and seeking professional guidance are key components in preventing and managing diabetic vulvitis effectively.
Bullet points:
- Maintain good blood sugar control through proper diabetes management
- Practice good hygiene by keeping the vulvar area clean and dry
- Avoid scented products or harsh soaps
- Opt for loose-fitting cotton underwear
- Schedule regular check-ups with healthcare professionals to monitor for signs of infection and receive guidance on management and prevention.
Complications Associated With Diabetic Vulvitis
If left untreated or poorly managed, diabetic vulvitis can lead to complications such as:
- Chronic vulvar pain
- Recurrent infections
- Development of ulcers or skin breakdown
These complications can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life and may require more intensive treatment options. It is essential to seek medical attention and adhere to proper management protocols to minimize the risk of complications associated with diabetic vulvitis.
Lifestyle Changes For Managing Diabetic Vulvitis
Alongside medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can contribute to the effective management of diabetic vulvitis. Here are some important tips to consider:
- Avoid excessive moisture in the vulvar region.
- Maintain proper blood sugar control through diet and exercise.
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Adopt stress-reducing activities such as yoga or meditation to manage symptoms and minimize flare-ups.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals can enhance the effectiveness of medical treatments and improve their overall management of diabetic vulvitis.
Support And Resources For Those With Diabetic Vulvitis
Living with diabetic vulvitis can be challenging, but it is important to remember that support is available. Many healthcare professionals specialized in women’s health can provide guidance and treatment options. Additionally, support groups and online communities offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, seek advice, and find emotional support from others who understand their journey. These resources can be invaluable in coping with the physical and emotional aspects of diabetic vulvitis.
Future Research And Advancements In Diabetic Vulvitis Treatment
As research in the field of diabetes and women’s health continues to evolve, there is hope for advancements in the treatment and management of diabetic vulvitis. Ongoing studies aim to better understand the underlying mechanisms of the condition and develop targeted therapies.
These advancements may lead to:
- more effective treatment options
- personalized approaches
- improved quality of life for those living with diabetic vulvitis
It is important to stay informed and advocate for further research in order to support those affected by this often overlooked condition.
💡
You may need to know these questions about diabetic vulvitis
Does diabetes cause vulvitis?
Yes, diabetes can lead to vulvitis in women. The excess sugar present in the cells of women with diabetes can create an environment that promotes the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to vulvitis. Therefore, it becomes crucial for women with diabetes to refrain from using any products that may further irritate the vulva, as this is the first step towards effective treatment. By eliminating any potential irritants, it allows the vulva to heal and reduces the risk of complications associated with vulvitis in women with diabetes.
How do diabetics treat vulvovaginitis?
Diabetic individuals effectively manage vulvovaginitis through various approaches. In addition to traditional treatments such as prescription oral antifungal medication or over-the-counter antifungal cream, it is crucial for diabetics to maintain proper blood sugar levels to prevent frequent and severe vaginal yeast infections. By prioritizing blood sugar control, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the likelihood and intensity of symptoms like itching, burning, and the presence of a thick, white discharge from the vagina.
Why vulvovaginitis with diabetes?
Vulvovaginitis in women with diabetes can be attributed to various factors, including hyperglycemia, allergy, and atopy. Hyperglycemia, a hallmark of diabetes, creates an environment conducive for the growth of Candida albicans, one of the primary pathogens associated with this condition. High blood sugar levels not only weaken the immune response but also provide a favorable setting for Candida overgrowth. Additionally, women with diabetes tend to have compromised immune systems, making them more susceptible to infections like vulvovaginitis. Allergy and atopy further exacerbate the condition, contributing to the development and persistence of resistant vulvovaginitis in diabetic women.
What is the best treatment for vulvitis?
The best treatment for vulvitis depends on the underlying cause. Your healthcare provider may recommend using provider-recommended creams such as over-the-counter hydrocortisone ointment to reduce irritation and itching. Additionally, they may prescribe topical estrogen cream to alleviate itching and other symptoms associated with vulvitis. It is essential to consult with your healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
Reference source
https://www.visualdx.com/visualdx/diagnosis/diabetic+vulvitis?diagnosisId=52791&moduleId=9
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318834
https://www.verywellhealth.com/diabetes-and-yeast-infections-5213587
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18182346/