In the intricate landscape of the human body, hidden marvels lie waiting to be explored.
While many are familiar with organs like the heart and lungs, there is a lesser-known structure that holds mysterious power – the diaphragma pelvis.
Journey with us as we delve into the intriguing depths of this enigmatic region, unveiling the secrets it holds and shedding light on its role in our overall well-being.
Brace yourself, for a captivating adventure awaits!
diaphragma pelvis
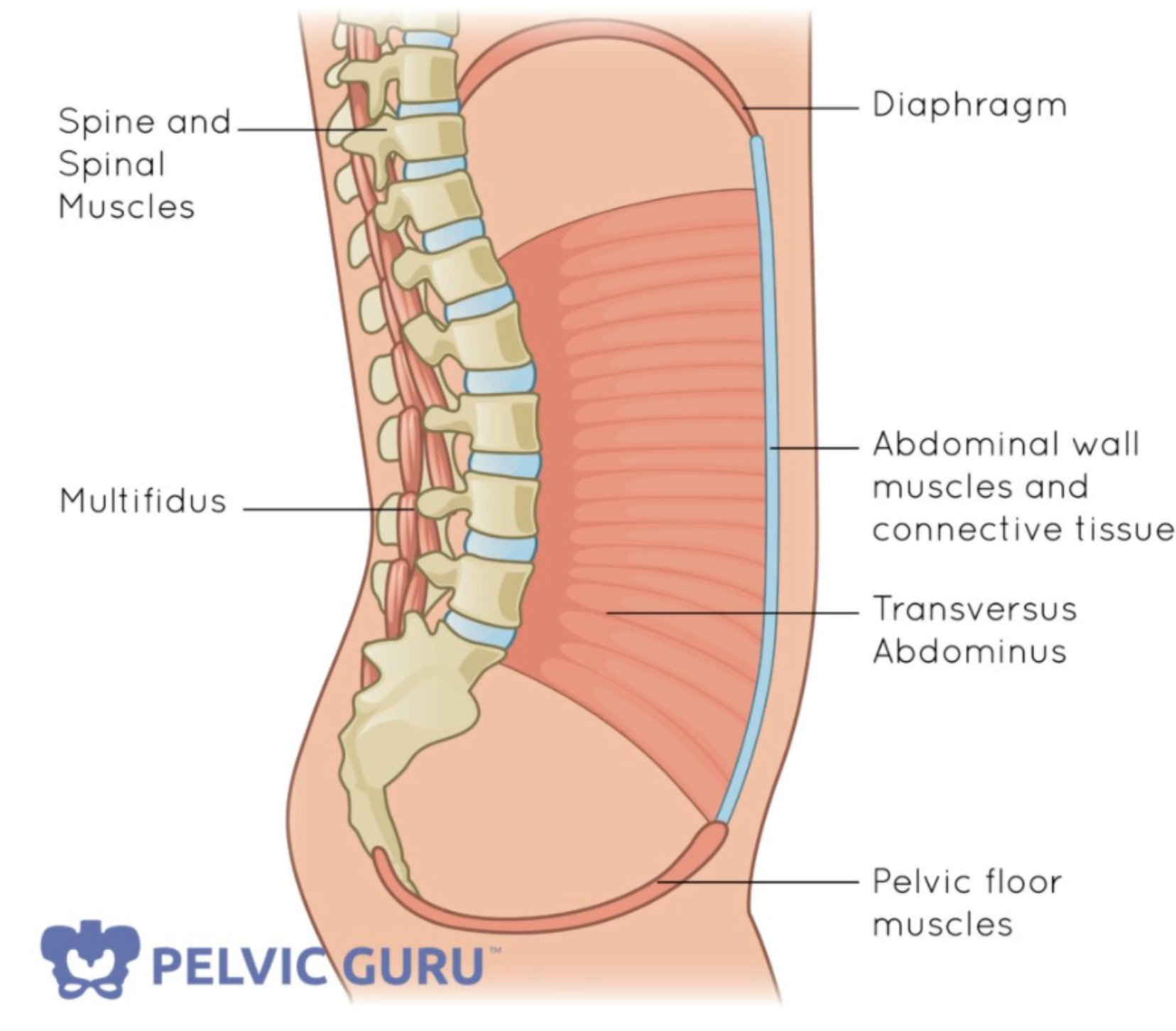
The diaphragma pelvis, also known as the pelvic diaphragm, refers to a group of muscles located at the bottom of the pelvic cavity.
It serves as a supportive structure for the organs within the pelvis, including the bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs.
The muscles of the diaphragma pelvis play a crucial role in maintaining continence, supporting the abdominal and pelvic organs, and providing stability to the pelvis.
Its proper function is important for various bodily functions, such as urination, defecation, and sexual activity.
Key Points:
- Diaphragma pelvis is a group of muscles located at the bottom of the pelvic cavity.
- It supports organs in the pelvis, such as the bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs.
- The muscles of diaphragma pelvis help maintain continence, support abdominal and pelvic organs, and stabilize the pelvis.
- Proper function is crucial for bodily functions like urination, defecation, and sexual activity.
diaphragma pelvis – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The diaphragma pelvis, also known as the pelvic diaphragm, is a group of muscles located at the bottom of the pelvis that provide support for the organs in the pelvic cavity.
2. The muscles of the diaphragma pelvis include the levator ani and the coccygeus muscles, which play a crucial role in controlling bowel movements and urination.
3. The diaphragma pelvis acts as a flexible barrier between the pelvic organs and the abdominal cavity, preventing the organs from pressing down on the pelvic floor during activities such as coughing or lifting heavy objects.
4. Pelvic organ prolapse is a condition that can occur when the muscles of the diaphragma pelvis weaken or become damaged, causing the organs to push down on or protrude through the pelvic floor.
5. Exercises such as Kegels can help strengthen the muscles of the diaphragma pelvis and improve bladder and bowel control in individuals with weakened pelvic floor muscles.
Introduction To The Diaphragma Pelvis
The diaphragma pelvis is a vital component of the human body that provides critical support and stability to the pelvic region. Also known as the pelvic diaphragm, this structure is composed of various muscles and connective tissues that work together to maintain the integrity of the pelvic floor. Despite its significance, the diaphragma pelvis is often underestimated and not given the attention it deserves.
In this article, we will explore the anatomy, function, common issues, diagnosis, treatment options, and exercises to strengthen the diaphragma pelvis. By shedding light on this frequently overlooked structure, we aim to raise awareness and underscore the importance of maintaining a healthy diaphragma pelvis for overall well-being.
- The diaphragma pelvis, or pelvic diaphragm, is a crucial part of the human body.
- It is composed of various muscles and connective tissues.
- The primary function of the diaphragma pelvis is to provide support and stability to the pelvic region.
- Despite its importance, the diaphragma pelvis is often undervalued.
- Common issues related to the diaphragma pelvis can arise.
- Proper diagnosis is essential to address any problems.
- Treatment options exist to address diaphragma pelvis issues.
- Strengthening exercises can be beneficial for a healthy diaphragma pelvis.
“The diaphragma pelvis is an often-overlooked structure that plays a significant role in supporting the pelvic region.”
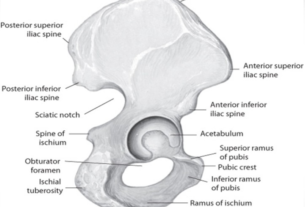
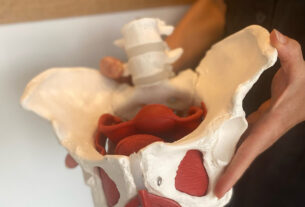
Anatomy And Structure Of The Diaphragma Pelvis
The diaphragma pelvis is a complex structure consisting of several muscles and connective tissues that form a muscular barrier at the base of the pelvis. It is located between the pelvic cavity and the perineum, separating the pelvic organs from the structures of the perineum, such as the genitals and anus. The major muscles involved in this structure include the levator ani, coccygeus, and obturator internus muscles. These muscles play a vital role in providing support to the pelvic organs, maintaining continence, and facilitating sexual function.
Furthermore, the diaphragma pelvis is reinforced by various connective tissues, such as the fascia and ligaments. The fascia provides support to the muscular components of the diaphragma pelvis, ensuring proper functioning and preventing prolapse or other issues. Additionally, ligaments such as the sacrospinous ligament and the uterosacral ligament provide stability and help anchor the pelvic organs in place.
Function And Role Of The Diaphragma Pelvis
The diaphragma pelvis plays a significant role in maintaining the structural integrity of the pelvis and supporting the pelvic organs. One of its primary functions is to provide support to the bladder, uterus, and rectum, preventing them from descending into the perineum or prolapsing. This support is crucial for maintaining continence, allowing proper bowel and bladder function, and preventing conditions like urinary incontinence or pelvic organ prolapse.
Another important function of the diaphragma pelvis is its role in sexual function. During sexual arousal, the muscles of the diaphragma pelvis contract, contributing to the intensity of orgasms. Additionally, the diaphragma pelvis and its associated muscles play a role in providing stability and support to the pelvic floor during sexual activity, enhancing pleasure and facilitating optimal sexual function.
Common Issues And Problems With The Diaphragma Pelvis
Despite its crucial role, the diaphragma pelvis is prone to various issues and dysfunctions. One common problem is a weakened or dysfunctional diaphragma pelvis. This can occur due to factors such as:
- Pregnancy
- Childbirth
- Obesity
- Aging
- Sedentary lifestyle
A weakened diaphragma pelvis can lead to pelvic floor disorders, including:
- Urinary incontinence
- Fecal incontinence
- Pelvic organ prolapse
These conditions can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, affecting their physical, emotional, and social well-being.
Furthermore, a dysfunctional diaphragma pelvis can also contribute to sexual dysfunction, such as:
- Decreased sexual satisfaction
- Pain during intercourse
The weakening or dysfunction of the diaphragma pelvis can result in reduced support and stability of the pelvic organs, leading to discomfort and a decrease in overall sexual function.
Diagnosis And Testing Of Diaphragma Pelvis Dysfunction
Diagnosing diaphragma pelvis dysfunction typically involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional specializing in pelvic floor disorders. The evaluation may include a detailed medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. The examination may involve assessing pelvic muscle strength, pelvic organ support, and evaluating any symptoms such as urinary or fecal incontinence, pelvic pain, or sexual dysfunction.
Diagnostic tests that may be used to assess diaphragma pelvis dysfunction include pelvic floor electromyography (EMG), urodynamic testing, cystoscopy, and imaging studies such as pelvic ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These tests can help provide valuable information about the function and structure of the diaphragma pelvis, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment planning.
Treatment Options For Diaphragma Pelvis Issues
The treatment for diaphragma pelvis issues focuses on:
- Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles
- Improving support
- Addressing any underlying conditions contributing to the dysfunction
Treatment options may include:
- Pelvic floor physical therapy
- Behavioral modifications
- Medications
- Surgical interventions (in some cases)
Pelvic floor physical therapy is often a first-line treatment. It may include:
- Exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles
- Biofeedback techniques to improve muscle coordination
- Specialized therapies such as electrical stimulation or vaginal weights
Behavioral modifications may involve:
- Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss
- Dietary adjustments
- Proper toileting habits
In cases where conservative measures are ineffective or in more severe cases, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical options may include:
- Procedures to repair pelvic organ prolapse
- Reinforce the diaphragma pelvis
- Addressing any contributing factors such as urethral slings for urinary incontinence
The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the diaphragma pelvis dysfunction. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Exercises And Therapies To Strengthen The Diaphragma Pelvis
Exercises and therapies to strengthen the diaphragma pelvis can play a crucial role in improving muscle tone, function, and overall pelvic floor support. Pelvic floor exercises, commonly referred to as Kegel exercises, are one of the most well-known forms of therapy for the diaphragma pelvis. These exercises involve contracting and relaxing the muscles of the pelvis to improve strength and control.
In addition to Kegel exercises, other therapies such as biofeedback, electrical stimulation, and vaginal weights may be used to enhance muscle coordination and strengthen the diaphragma pelvis. Biofeedback involves using sensors to provide visual or auditory cues about muscle activity, helping individuals learn to control and strengthen the muscles effectively. Electrical stimulation uses low-level electrical currents to stimulate the pelvic floor muscles, promoting muscle contraction and strengthening. Vaginal weights are small, cone-shaped weights that can be inserted into the vagina to add resistance during exercise, further enhancing muscle strength and control.
Importance Of Maintaining A Healthy Diaphragma Pelvis
Maintaining a healthy diaphragma pelvis is crucial for overall well-being and optimal functioning of the pelvic floor. A strong and functional diaphragma pelvis provides support to the pelvic organs, maintains continence, and contributes to sexual satisfaction. By investing in the health of the diaphragma pelvis, individuals can:
- Prevent or mitigate the risks of pelvic floor disorders
- Improve quality of life
- Enhance overall physical and emotional well-being
“A strong and functional diaphragma pelvis is essential for a healthy pelvic floor. It supports the pelvic organs, maintains continence, and contributes to sexual satisfaction.“
Remember to incorporate regular exercise, proper diet, and effective stress management into your routine to ensure the wellness of the diaphragma pelvis.
Prevention And Lifestyle Tips For Maintaining A Strong Diaphragma Pelvis
There are several measures individuals can take to promote a healthy diaphragma pelvis and minimize the risk of dysfunction. These include:
1. Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, including targeted exercises for the pelvic floor muscles, can help strengthen the diaphragma pelvis and maintain overall pelvic health.
2. Maintain a healthy weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain and pressure on the pelvic floor muscles, minimizing the risk of dysfunction.
3. Practice good toileting habits: Adopting proper toileting habits, such as avoiding straining during bowel movements and emptying the bladder fully, can help prevent undue strain on the pelvic floor muscles.
4. Avoid heavy lifting: Minimizing heavy lifting can reduce the strain placed on the diaphragma pelvis and associated pelvic floor muscles, preventing potential issues.
5. Seek treatment for chronic cough or constipation: Chronic coughing and constipation can put additional stress on the pelvic floor muscles. Seeking treatment and managing these conditions can help maintain the health of the diaphragma pelvis.
- Regular exercise
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Practice good toileting habits
- Avoid heavy lifting
- Seek treatment for chronic cough or constipation
Conclusion And Future Research On The Diaphragma Pelvis
The diaphragma pelvis is a remarkable structure that plays a vital role in supporting the pelvic organs, maintaining continence, and facilitating sexual function. Despite its essential functions, the diaphragma pelvis often goes unnoticed until problems arise. By understanding the anatomy, function, and potential issues associated with the diaphragma pelvis, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their pelvic health and seek appropriate treatment when needed. Continued research in this field will further enhance our understanding of the diaphragma pelvis and contribute to improved prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies for pelvic floor disorders. It is important for healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals alike to recognize the significance of a healthy diaphragma pelvis and its impact on overall well-being.
💡
You may need to know these questions about diaphragma pelvis
What is diaphragma pelvis?
The diaphragma pelvis, also known as the pelvic diaphragm, is a unique structure formed by the levator ani muscle and the coccygeus muscle. This flat, funnel-shaped membrane extends from the walls of the pelvis and attaches to the hiatus analis, the passage through which the anus passes. Acting as a muscular support system, the diaphragma pelvis plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the pelvic region. By providing necessary support and control, it helps facilitate various bodily functions such as defecation and urination, while also contributing to stability and balance within the pelvis.
Is diaphragm part of pelvic floor?
The diaphragm is not considered part of the pelvic floor. Although both the diaphragm and the pelvic floor are muscles involved in bodily functions, they have distinct anatomical locations and functions. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lungs that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities, aiding in respiration. On the other hand, the pelvic floor, or pelvic diaphragm, is a group of muscles forming a supportive layer at the base of the pelvis, responsible for stability, continence, and supporting pelvic organs. While they both contribute to overall bodily function, the diaphragm is not regarded as a component of the pelvic floor.
Which muscles are in the pelvic diaphragm?
The pelvic diaphragm consists of several important muscles that play a crucial role in maintaining pelvic floor strength and stability. One of the main muscle groups within the pelvic diaphragm is the levator ani, which is composed of three separate muscle components: the pubococcygeus, puborectalis, and iliococcygeus muscles. These muscles form the bulk of the pelvic floor and provide support to the neighboring organs. Additionally, the coccygeus muscle is another essential component of the pelvic diaphragm, albeit smaller in size. Together, these muscles work in harmony to maintain proper pelvic floor function and contribute to overall core stability.
Does the diaphragm connect to the pelvis?
Yes, the diaphragm muscle does connect to the pelvis. It attaches to the anterior margin of the pelvic floor, specifically the pubis, as well as the posterior margin, which is the sacrum. Through the transverse muscle and the fascia, it merges with the pelvic floor, allowing for coordination between breathing and movement of the pelvis. This connection plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and functionality of both the respiratory and pelvic systems.
Reference source
https://teachmeanatomy.info/pelvis/muscles/pelvic-floor/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22729-pelvic-floor-muscles
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482200/
https://teachmeanatomy.info/pelvis/muscles/pelvic-floor/