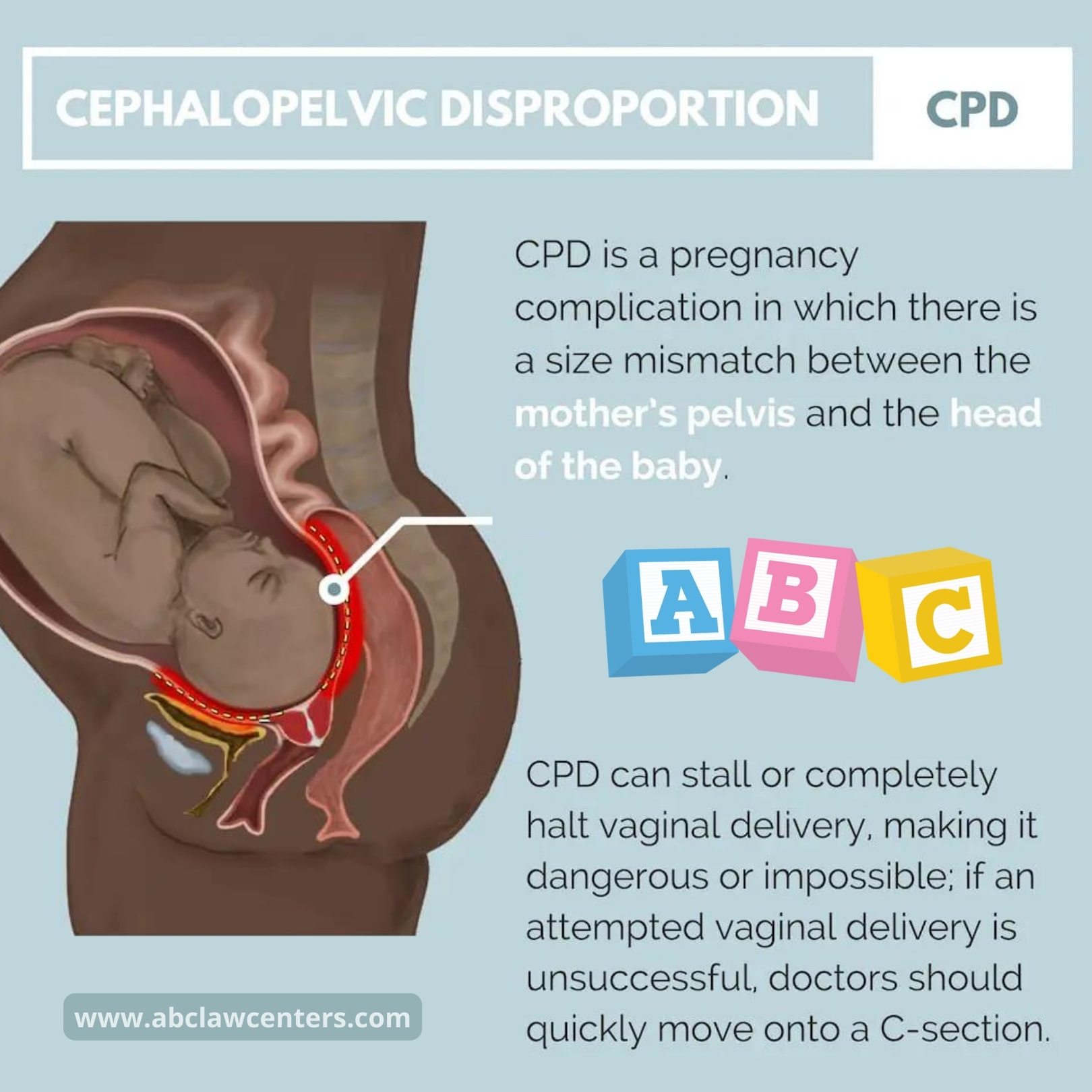
Childbirth, a miraculous event filled with anticipation and joy, can sometimes take an unexpected turn.
Difficult deliveries can bring forth a cascade of challenges, leaving both mother and child vulnerable to birth injuries.
From abnormal positions to medical errors, this introduction explores the complex world of childbirth and the potential complications that can arise.
Join us on this journey as we delve into the intricacies of difficult deliveries and their impact on the miraculous process of bringing new life into the world.
difficult delivery
A difficult delivery refers to labor and delivery complications that can result in birth injuries for both the baby and mother.
There are several factors that can contribute to a difficult delivery, including the weight of the baby, premature birth, abnormal positioning, physical injuries during birth, delayed birth, oxygen deprivation, medical malpractice, improper manipulation of the baby’s body, medications or infections during pregnancy, and various childbirth complications.
These complications can result in severe consequences such as brain damage, death, fractures, nerve damage, and restricted oxygen supply.
Maternal risk factors such as hypertension, gestational diabetes, breech presentation, multiples, and previous cesarean birth can also increase the likelihood of a difficult delivery.
Key Points:
- Difficult delivery can lead to birth injuries for both the baby and mother.
- Factors that contribute to difficult delivery include:
- Baby’s weight
- Premature birth
- Abnormal positioning
- Physical injuries during birth
- Delayed birth
- Oxygen deprivation
- Medical malpractice
- Improper manipulation of baby’s body
- Medications or infections during pregnancy
- Childbirth complications
- Consequences of difficult delivery can include:
- Brain damage
- Death
- Fractures
- Nerve damage
- Restricted oxygen supply
- Maternal risk factors that can increase the likelihood of difficult delivery include:
- Hypertension
- Gestational diabetes
- Breech presentation
- Multiples
- Previous cesarean birth
difficult delivery – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. A difficult delivery is known as dystocia, and it affects about 5-7% of all pregnancies worldwide.
2. The longest recorded labor lasted for an astonishing 75 days! This rare case occurred in the 1940s and was due to an obstruction preventing the baby’s descent.
3. In the animal kingdom, some species experience surprisingly challenging deliveries. For example, female elephants endure labor for an average of 4-5 days.
4. The concept of a “birthing chair” dates back to ancient civilizations. These upright chairs were used during difficult deliveries to facilitate the positioning of the mother and aid in the birth process.
5. Forceps were invented in the late 16th century by a French physician named Peter Chamberlen. These instruments were specifically designed to assist in difficult deliveries by aiding in the extraction of the baby.
Heavier Infants And Difficult Delivery: A Higher Risk Of Birth Injuries
Delivering a baby is a remarkable and often memorable experience for expectant parents. However, for infants weighing 8 pounds and 13 ounces or more, the delivery process can become significantly more challenging. These heavier infants are more prone to experiencing difficult deliveries and a higher risk of birth injuries.
When a baby is above the average birth weight, the mother’s body may struggle to accommodate the size during labor. The increased weight can put strains on the mother’s muscles and joints, making the delivery process more challenging. Additionally, the baby’s larger size may require more force or intervention during delivery, increasing the likelihood of birth injuries.
Birth injuries that can occur in these cases include fractures, nerve injuries, and soft tissue damages. The strains and pressures exerted during a difficult delivery may cause these injuries, which can have long-lasting effects on the newborn’s health and development. Therefore, healthcare professionals must carefully monitor and manage deliveries involving larger infants to minimize the risk of birth injuries.
- Difficult deliveries are more common with infants weighing 8 pounds and 13 ounces or more.
- Larger babies may require additional force or intervention during delivery.
- Birth injuries such as fractures, nerve injuries, and soft tissue damages are more likely with difficult deliveries involving larger infants.
The strains and pressures exerted during a difficult delivery may cause these injuries, which can have long-lasting effects on the newborn’s health and development.
Premature Births And Underdeveloped Muscles: Increased Rates Of Birth Injuries
Premature births, defined as deliveries occurring before the 37th week of pregnancy, pose unique challenges and risks for both the newborn and the mother. Babies born prematurely often have underdeveloped muscles and nervous systems, making them more susceptible to birth injuries.
The premature infant’s muscles and nerves are not fully matured, making it difficult for them to withstand the stresses of labor. The soft and fragile structures of their bodies are more prone to strains, tears, and other injuries during the birth process. As a result, premature infants are at a higher risk of experiencing birth injuries compared to their full-term counterparts.
Common birth injuries in premature babies include muscle tears, respiratory distress syndrome, and brain injuries. The delicate nature of their bodies makes them more susceptible to these complications. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to closely monitor and provide appropriate care during the delivery of premature infants to prevent and manage these potential birth injuries.
- Muscle tears
- Respiratory distress syndrome
- Brain injuries
Healthcare professionals should closely monitor and provide appropriate care during the delivery of premature infants to prevent and manage these potential birth injuries.
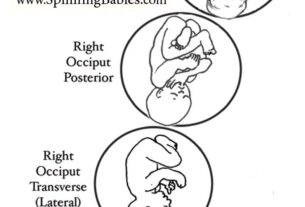
Abnormal Birth Positions And The Risk Of Birth Injuries
The positioning of a baby during the birth process is crucial for a smooth and safe delivery. However, infants born in abnormal positions, like head-up (breech), buttocks-first, or breech positions, have a higher likelihood of experiencing birth injuries.
In a typical delivery, the baby’s head enters the birth canal first, which helps facilitate a smoother passage and reduces the risk of birth injuries. However, when the baby is in a breech position, with the buttocks or feet positioned to come out first, the delivery becomes more complex and challenging.
Breech deliveries significantly increase the risk of birth injuries, particularly to the baby’s head and neck. Improper alignment and potential entrapment of body parts in the birth canal can lead to complications such as shoulder dystocia and oxygen deprivation. In some cases, medical professionals may need to use forceps or vacuum extraction to assist in the delivery, further increasing the risk of birth injuries.
To minimize the risks associated with abnormal birth positions, healthcare professionals must be diligent in identifying these positions during prenatal care and labor. They may recommend interventions and techniques such as external cephalic version or a cesarean section to ensure safer deliveries for both the mother and the baby.
💡
You may need to know these questions about difficult delivery
What is the meaning of difficult delivery?
Difficult delivery, also known as dystocia, refers to a broad range of complications that can occur during labor and delivery. It includes circumstances such as a delay in the dilation of the cervix or the descent of the fetus, as well as more severe situations such as shoulder dystocia, which is when the baby’s shoulders become trapped after the delivery of the head. These challenges can pose risks to both the mother and the baby, requiring immediate attention and medical interventions to ensure a safe and successful delivery.
What causes difficulty in delivery?
Difficulties during delivery can arise from various factors. Improper manipulation of the child’s body during delivery can result in complications when trying to exit the birth canal, potentially leading to oxygen deprivation. Additionally, certain medications administered during childbirth can contribute to birth complications. Furthermore, the presence of viral or bacterial infections in either the mother or infant during pregnancy can also significantly increase the risk of difficulties during delivery. These factors emphasize the importance of careful and informed medical practices to ensure a smooth and safe childbirth process.
What is considered a difficult birth?
A difficult birth is typically categorized as a prolonged delivery that exceeds 18 hours, potentially subjecting the baby’s body to significant stress. Various factors contribute to birth trauma, including the size of the baby. Delivering babies weighing over eight pounds, 13 ounces often presents additional challenges during the birthing process. These larger infants can pose difficulties for the mother in terms of delivering naturally, requiring extra time and effort to ensure a safe delivery for both mother and baby.
What is stressful delivery?
Stressful delivery refers to the phenomenon in which the process of childbirth is affected by the level of stress experienced by the mother. Animal studies have indicated that stress during early labor may impede or halt the progress of labor, while stress during late labor might result in a rapid birth known as the “fetus ejection reflex.” Although more studies are required to confirm these findings in women, some organizations and individuals have been emphasizing the likely adverse consequences of stress on delivery…
Stress during labor can disrupt the natural progression of childbirth, potentially impacting both the duration and outcome of the delivery process. This highlights the importance of managing stress levels during pregnancy to ensure a smoother and more positive childbirth experience. Further research is necessary to fully understand the impact of stress on human labor and enable healthcare professionals to provide effective guidance and support to expectant mothers.
Reference source
https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/products/labor-dystocia/research-protocol
https://www.childbirthinjuries.com/birth-injury/causes/
http://www.cerebralpalsysymptoms.com/birth-injury/birth-trauma/causes
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128009512000406