In the mystical world of animal behavior, there exists a phenomenon known as early suckling.
While its intricacies elude us due to scarce information, allow me to take you on a journey through the elusive realms of this intriguing mystery.
Prepare to be captivated by the wonders that lie hidden within the realm of early suckling.
early suckling
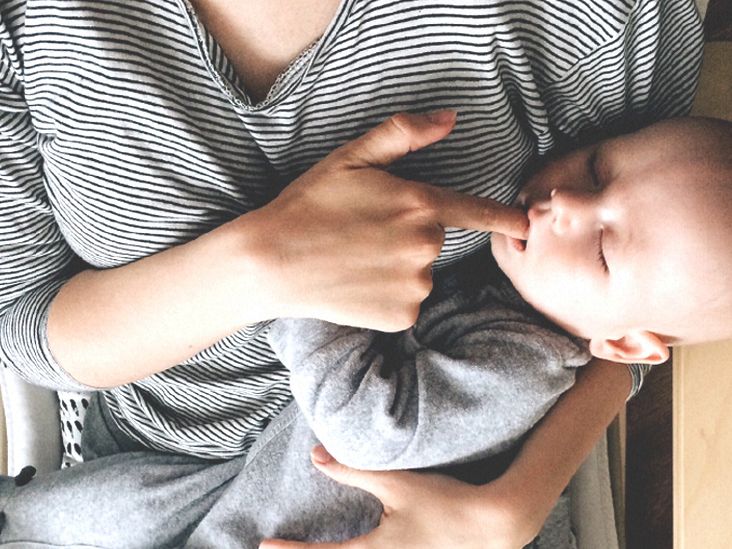
Early suckling refers to the act of an infant or animal nursing soon after birth.
This crucial stage plays a vital role in establishing the bond between the mother and offspring, as well as providing essential nutrition and immune protection.
It allows the newborn to receive colostrum, the first milk produced by the mother, which is rich in antibodies, vitamins, and minerals that enhance the newborn’s immune system and promote healthy development.
Additionally, early suckling stimulates the release of oxytocin in the mother, facilitating contraction of the uterus and preventing postpartum hemorrhage.
Overall, early suckling is a critical process that supports the well-being and survival of young mammals.
Key Points:
- Early suckling is the act of nursing soon after birth.
- It establishes the bond between mother and offspring and provides essential nutrition and immune protection.
- It allows the newborn to receive colostrum, which enhances the immune system and promotes healthy development.
- Early suckling stimulates the release of oxytocin in the mother, preventing postpartum hemorrhage.
- It is a critical process for the well-being and survival of young mammals.
early suckling – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Early suckling: In ancient Roman culture, it was common for newborn babies to be breastfed by a wet nurse rather than their own mothers. This practice allowed women to quickly resume their normal lives and attend social events without the inconvenience of breastfeeding.
2. Did you know that early suckling helps provide a layer of protection to infants from potential food allergies? Studies show that babies who are breastfed during the first few months of life are less likely to develop allergies to common foods like dairy, wheat, and nuts later in life.
3. In many traditional societies, early suckling by babies was believed to have a positive impact on their cognitive development. It was thought that the act of breastfeeding created a strong bond between mother and child, enhancing the child’s intelligence and emotional well-being.
4. Early suckling in animals is often crucial for their survival. For example, newborn mice and rats must receive milk from their mothers within the first few hours of birth, as they are born hairless, blind, and unable to regulate their body temperature. The nutrients in the mother’s milk are essential for their growth and development during this critical period.
5. The practice of wet nursing, where women breastfeed other people’s infants, dates back to ancient civilizations like Egypt, Greece, and Persia. In some cases, women who were skilled wet nurses were highly sought after and could even earn a good income for their services.
Importance Of Early Suckling
Early suckling, which refers to a newborn baby latching onto its mother’s breast within the first hour after birth, is a crucial step in establishing successful breastfeeding and promoting the well-being of both the baby and the mother. This immediate connection plays a significant role in initiating milk production and enabling the mother to breastfeed effectively. The first secretion from the mother’s breasts, known as colostrum, is particularly important as it contains essential nutrients and antibodies that provide vital immune protection for the baby. Studies have shown that infants who breastfeed within the first hour of birth are more likely to continue exclusive breastfeeding for the recommended duration. Therefore, it is essential to encourage early suckling to ensure optimal growth and development for infants.
Benefits For Newborns
Early suckling offers a plethora of benefits for newborns. Firstly, breast milk is perfectly designed to meet the nutritional needs of infants, providing the ideal balance of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. This natural goodness is easily digestible, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal issues such as colic and constipation. Breastfeeding also decreases the likelihood of respiratory infections, ear infections, and gastrointestinal infections due to the presence of antibodies passed from the mother to the baby through breast milk.
Moreover, studies suggest that breastfed infants have a decreased risk of developing chronic diseases later in life, such as obesity, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Breast milk contains essential enzymes and hormones that aid in the development of the baby’s immune system, gastrointestinal tract, and brain. This early nutrition and immune protection lay the foundation for a healthy and robust future.
Bonding Through Early Suckling
Beyond the nutritional benefits, early suckling is invaluable for the emotional bond between mother and baby. The act of breastfeeding releases oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone,” in both the mother and the baby. This hormone promotes feelings of love, attachment, and relaxation. It creates a sense of security and closeness, enhancing the emotional bond between the two.
Furthermore, early suckling establishes a rhythm and routine between the mother and the baby. Through the skin-to-skin contact and eye contact during breastfeeding, the baby feels loved, nurtured, and secure. This bonding experience builds trust, fostering a secure attachment that positively impacts the baby’s emotional and psychological development.
Health Benefits For Mothers
While early suckling is crucial for newborns, it also provides significant health benefits for mothers. Breastfeeding triggers the release of oxytocin, which helps the uterus contract, reducing the risk of postpartum hemorrhage. It also aids in weight loss for the mother, as breastfeeding burns calories and promotes the return of the uterus to its pre-pregnancy size.
Furthermore, breastfeeding has been linked to a decreased risk of developing breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and type 2 diabetes in mothers. The act of breastfeeding stimulates the breast tissue, reducing the accumulation of carcinogens and preventing the overgrowth of cells. These long-term health benefits make early suckling a vital practice for maternal well-being.
- Breastfeeding triggers the release of oxytocin, reducing the risk of postpartum hemorrhage
- Promotes weight loss for the mother
- Decreases the risk of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and type 2 diabetes in mothers
- Stimulates breast tissue, reducing the accumulation of carcinogens and preventing cell overgrowth
“Breastfeeding provides significant health benefits for both newborns and mothers, including reduced risk of postpartum hemorrhage, weight loss for the mother, decreased risk of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and type 2 diabetes in mothers.”
Positive Physical Effects
Beyond its emotional and health benefits, early suckling has positive physical effects on both the mother and the baby. Breastfeeding stimulates the release of the hormone prolactin, which promotes a calming and relaxing effect on the mother. This hormone helps to reduce stress levels and soothe the baby, leading to a more peaceful and content household.
For the baby, breastfeeding helps in the development of the oral muscles, aiding in proper jaw and tooth development. It also promotes the correct alignment of the baby’s palate, reducing the risk of dental issues in the future. Breastfed babies are also less likely to develop early childhood cavities due to the absence of bottle use, prolonged contact with milk, or the consumption of sugary drinks.
Promoting Milk Production
Early suckling is a vital factor in boosting milk production in mothers. Breastfeeding stimulates the mammary glands, prompting the body to produce more milk. By frequently feeding in the early days and weeks after birth, a demand-supply cycle is established, ensuring a steady and ample milk supply for the growing baby.
The feedback mechanism between the baby’s suckling and the mother’s milk production enables the milk composition to adapt and cater to the baby’s nutritional requirements. This intelligent system allows breast milk to provide the exact nutrients needed for the baby’s growth and development at various stages.
- Early suckling promotes milk production in mothers.
- Breastfeeding stimulates the mammary glands.
- Frequent feeding establishes a demand-supply cycle for milk supply.
- The feedback mechanism ensures milk composition adjusts to meet the baby’s needs.
- Breast milk provides precise nutrients for growth and development.
Improving Immune System
One of the most significant advantages of early suckling is its profound impact on the baby’s immune system. Colostrum, the first milk produced after birth, contains a high concentration of antibodies, white blood cells, and other immune-boosting substances. These components act as a shield, protecting the baby from infections and diseases.
Breast milk also contains living cells that enhance the baby’s immune response. It provides a unique array of probiotics and prebiotics that help to colonize the baby’s gut with beneficial bacteria. These friendly microorganisms prevent harmful bacteria from flourishing, reducing the risk of allergies, asthma, eczema, and other immune-mediated conditions.
- Colostrum, the first milk after birth, is rich in antibodies and immune-boosting substances.
- Breast milk contains living cells that aid the baby’s immune response.
- Probiotics and prebiotics in breast milk help colonize the baby’s gut with beneficial bacteria.
“Early suckling and breastfeeding provide vital immune protection for the baby.”
Enhancing Mother-Infant Relationship
The close physical contact and nurturing experience of early suckling enhance the mother-infant relationship, fostering a deep bond of love and trust. Breastfeeding creates a unique opportunity for mothers to connect with their babies on a profound level. The skin-to-skin contact, eye contact, and soothing touch promote emotional closeness, allowing the mother to respond promptly to the baby’s needs.
This enhanced relationship between mother and baby influences the baby’s social, emotional, and behavioral development. Breastfed babies tend to have a greater sense of security, self-regulation, and higher intelligence scores. The constant physical and emotional availability of the mother during breastfeeding fosters a sense of safety and nurturance, promoting a healthy attachment between mother and child.
Long-Term Impact On Child Development
The practice of early suckling has far-reaching consequences beyond infancy. Breastfeeding has been linked to higher IQ scores, improved cognitive development, and better academic achievement. The unique composition of breast milk, in conjunction with the emotional and cognitive stimulation during breastfeeding, contributes to improved brain development in babies.
Breastfed children have also been found to exhibit better social and emotional skills. The bonding experience and the secure attachment formed during breastfeeding create a strong foundation for healthy relationships and emotional regulation later in life. Breastfeeding is associated with lower rates of behavioral problems, including hyperactivity, aggression, and anxiety in children.
Strategies For Encouraging Early Suckling
To encourage early suckling, healthcare providers should educate pregnant women and their families about the benefits of breastfeeding and the importance of early initiation. Antenatal education programs should cover topics such as correct positioning and latch, the establishment of breastfeeding as soon as possible after birth, and the initiation of skin-to-skin contact immediately after delivery.
Healthcare facilities should create a welcoming environment that supports and promotes early suckling. This includes providing privacy, comfortable breastfeeding spaces, and accessible lactation support. Training healthcare providers, midwives, and nurses in lactation support techniques is also crucial in enabling successful early suckling.
“Early suckling plays a vital role in the growth and development of infants.”
The act of breastfeeding within the first hour after birth provides numerous benefits for both the baby and the mother, including:
- Optimal nutrition
- Enhanced bonding
- Improved health outcomes
Understanding the significant positive impact of early suckling is essential for healthcare providers and policymakers to promote and support this crucial practice for the holistic well-being of mother and child.
💡
You may need to know these questions about early suckling
How do I know if my baby is pacifying or nursing?
Distinguishing between pacifying and nursing cues in a baby can be challenging but observing their behaviors provides clues. If your baby is flutter sucking, slowing down, or making little sucks, they may be pacifying and seeking comfort rather than actively nursing for food. Additionally, if they are holding the nipple in their mouth but not actively sucking for milk or looking still and into space while nursing, it suggests they are pacifying. On the other hand, if your baby is rooting and sucking lightly at the breast or displaying behaviors such as arching and grabbing their ears, they are likely actively nursing and seeking nourishment. Understanding and recognizing these cues can help you better respond to your baby’s needs and provide appropriate care and attention.
What is early onset of breastfeeding?
Early onset of breastfeeding refers to the recommended practice of initiating breastfeeding within the first hour after birth. This is a crucial aspect of infant and young child feeding practices, as advised by the World Health Organization (WHO). Despite its significance, the global implementation of early breastfeeding initiation remains inconsistent and far from being a universal practice.
Numerous studies have shown that early initiation of breastfeeding has numerous benefits for both the newborn and the mother. The first hour after birth is a critical window of opportunity, as it allows the newborn to receive essential colostrum, known as the “liquid gold,” which is rich in antibodies and nutrients. This early nourishment boosts the baby’s immune system, protects against infections, and establishes a strong bond between the mother and child. Consequently, promoting early onset of breastfeeding is imperative to improve infant and young child feeding practices worldwide.
Why do you need early initiation when breastfeeding?
Early initiation of breastfeeding is crucial for the well-being of both the newborn and the mother. By starting breastfeeding within one hour of birth, the baby is protected from potential infections and has a decreased risk of mortality. Additionally, early breastfeeding initiation promotes emotional bonding between the mother and the baby, creating a strong foundation for their relationship. This, in turn, positively influences the duration of exclusive breastfeeding, ensuring optimal nutrition and health benefits for the newborn.
Is it OK to let my baby comfort nurse?
Yes, it is absolutely okay to let your baby comfort nurse. Comfort nursing not only provides additional nutrients required for their rapid growth but also stimulates increased milk production, ensuring that your baby gets the nourishment they need. Moreover, this practice promotes a strong bond between you and your little one, as it allows for intimate and comforting moments of closeness during breastfeeding sessions. Embracing comfort nursing can create a nurturing environment for your baby’s development while further strengthening the parent-child relationship.
Reference source
https://www.sangpediatrics.com/how-do-you-tell-if-a-baby-is-hungry-or-wants-comfort
https://www.who.int/tools/elena/commentary/early-breastfeeding
https://www.who.int/data/gho/indicator-metadata-registry/imr-details/early-initiation-of-breastfeeding-(-)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7835117/