Childbirth is a miraculous yet challenging journey, during which a woman’s strength and resilience are truly tested.
One aspect that has long been debated in the medical field is the use of episiotomy – a surgical cut made during delivery.
However, recent research has shed light on the truth behind this once-believed “beneficial” procedure.
So, let us dive into the world of episiotomy, uncover its flaws, and explore the better alternatives that exist today.
episioitis
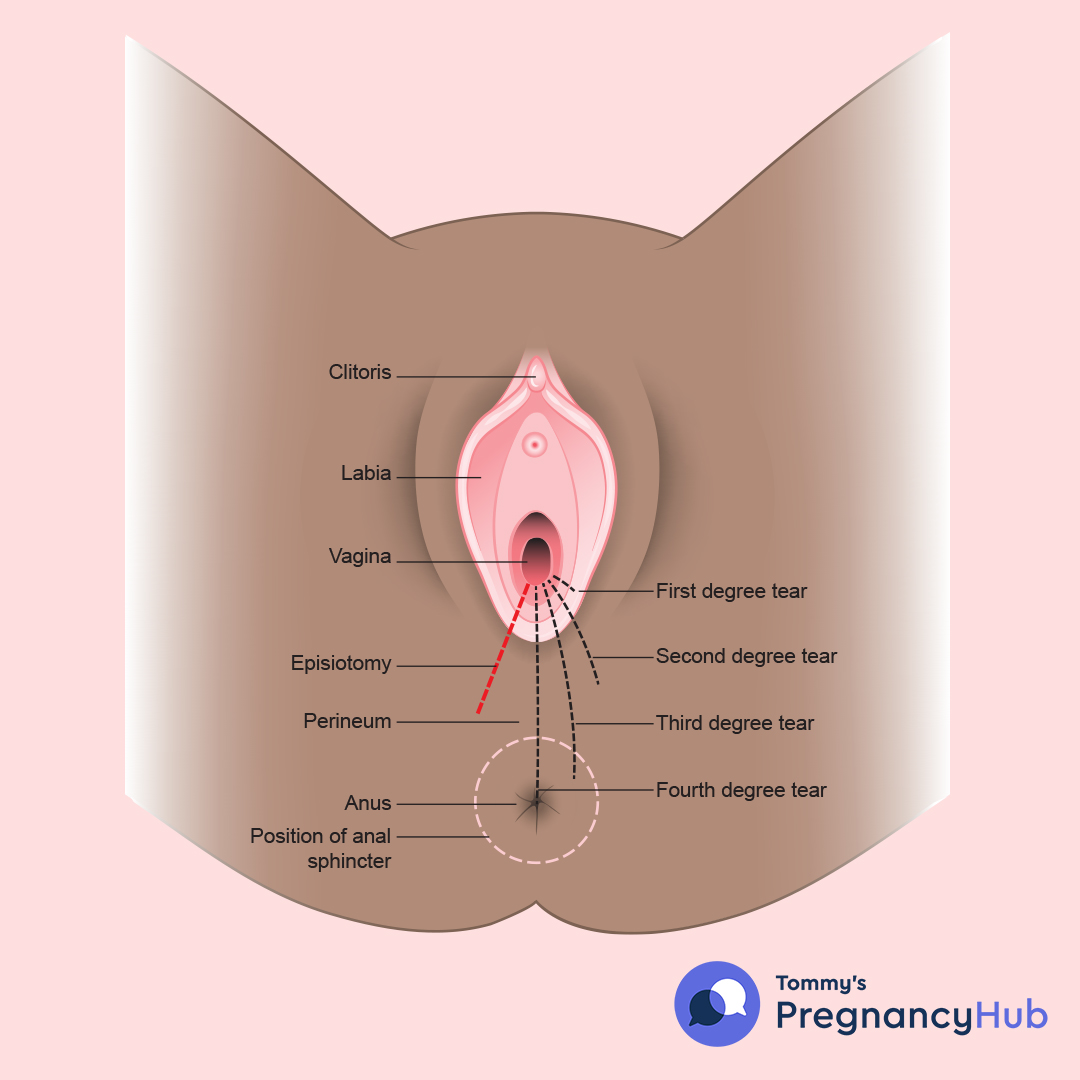
Episiotomy is a surgical procedure performed during childbirth that involves making a cut between the vaginal opening and the anus.
It was once believed to prevent larger tears and preserve pelvic floor muscles, but research shows it does not prevent problems.
Nowadays, routine episiotomies are no longer recommended.
However, there are situations where an episiotomy may be necessary, such as if a baby needs to be quickly delivered due to complications.
There are two types of episiotomy incisions: midline and mediolateral.
Midline incisions are easier to repair but have a higher risk of extending into the anal area, while mediolateral incisions are less likely to cause extended tears into the anal area but are more painful and challenging to repair.
Episiotomy recovery is uncomfortable, and there is a possibility of infection.
Some women may also experience pain during sex after having an episiotomy.
It’s important to note that a midline episiotomy puts women at a higher risk of fourth-degree vaginal tearing.
Key Points:
- Episiotomy is a surgical procedure performed during childbirth to make a cut between the vaginal opening and the anus.
- Research shows that episiotomies do not prevent problems and routine episiotomies are no longer recommended.
- Episiotomies may be necessary in certain situations, such as if there are complications requiring a quick delivery.
- There are two types of episiotomy incisions: midline and mediolateral.
- Midline incisions are easier to repair but have a higher risk of extending into the anal area, while mediolateral incisions are less likely to cause extended tears into the anal area but are more painful and harder to repair.
- Episiotomy recovery can be uncomfortable, with a possibility of infection and potential pain during sex.
episioitis – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Episiotis is a relatively common childbirth injury, occurring in about 60-70% of vaginal deliveries.
2. The term “episiotomy” comes from the Greek words “epison” meaning “vulva” and “tomē” meaning “incision.”
3. Due to advances in obstetric care, the rate of episiotomy has significantly decreased over the past few decades.
4. Episiotis can be classified into four degrees, with the severity increasing from first to fourth degree.
5. Factors that may increase the risk of episiotis include an instrumental delivery (such as forceps or vacuum), a large baby, short perineum, and previously having an episiotomy.
1. Episiotomy: Definition And Purpose
Childbirth is a beautiful and miraculous process, but it can also be an intense and physically demanding experience for women. During vaginal delivery, there is a risk of tears occurring around the perineum, which is the area between the vaginal opening and the anus. To mitigate these potential tears, medical professionals have historically performed episiotomies, which involve making a deliberate cut in this area to create an opening. The purpose is to prevent larger tears and preserve the muscles and connective tissue in the pelvic floor.
2. Research Debunks The Effectiveness Of Episiotomies
In recent years, research has questioned the effectiveness of episiotomies in preventing problems during childbirth. Multiple studies have indicated that routine episiotomies do not offer clear benefits and may actually cause more harm than good. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have both revised their recommendations and no longer advocate for the routine use of episiotomies. Instead, it is now believed that allowing natural tears to occur, rather than performing an incision, is a more favorable approach.
- Episiotomies are no longer recommended by ACOG and WHO.
- Research suggests that routine episiotomies may do more harm than good.
- Allowing natural tears during childbirth is now favored.
3. Update In Recommendations: No More Routine Episiotomies
Based on the research findings, healthcare professionals have shifted their approach to episiotomies. The updated recommendations emphasize that episiotomies should not be performed routinely unless there is a clear medical indication. This change reflects a more evidence-based approach to childbirth and acknowledges the potential risks associated with unnecessary interventions.
- Healthcare professionals have changed their approach to episiotomies
- Updated recommendations state that episiotomies should not be performed routinely
- Clear medical indication is required for performing an episiotomy
“Episiotomies should not be performed routinely unless there is a clear medical indication.”
4. Indications For An Episiotomy In Childbirth
Although routine episiotomies are no longer recommended, there are still situations where an episiotomy may be necessary. These indications include instances when:
- A baby needs to be quickly delivered due to a stuck shoulder
- An unusual heart rate pattern is detected
- Forceps or vacuum extraction is required
In such cases, a carefully performed episiotomy can facilitate the safe delivery of the baby.
However, it is important to note that episiotomies should only be performed when absolutely necessary and after careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits.
5. Midline Vs. Mediolateral Episiotomy Incisions
When an episiotomy is deemed necessary, two common types of incisions can be made: midline and mediolateral.
- A midline incision involves cutting straight downwards toward the anus from the vaginal opening.
- On the other hand, a mediolateral incision is made at an angle, starting from the vaginal opening and extending towards the buttocks.
The choice between these two types of incisions depends on various factors, such as the position of the baby and the experience of the healthcare provider.
6. Balancing Ease Of Repair And Risk Of Anal Area Extension
The type of incision used during an episiotomy can have an impact on both the ease of repair and the risk of extending into the anal area. Midline incisions are generally easier to repair, but they have a higher risk of extending into the anal area, which can result in more significant complications. On the other hand, mediolateral incisions are less likely to cause an extended tear into the anal area, but they are often more painful and difficult to repair. Therefore, healthcare providers must carefully consider the potential trade-offs when deciding which type of incision to use during an episiotomy.
7. The Unpleasant Road To Episiotomy Recovery
Recovery from an episiotomy can be a challenging experience for most women. The incision site may be sore, swollen, and may require stitches. To alleviate the discomfort, there are several pain management strategies that can be helpful:
- Applying ice packs
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers
- Using sitz baths
However, it is crucial for women to discuss their pain management options with their healthcare providers. They should also follow any recommended postpartum care instructions to ensure proper healing.
It is important to take these steps seriously in order to effectively recover from an episiotomy.
8. Impact On Sexual Intimacy: Post-Episiotomy Pain
One of the concerns women may have after an episiotomy is the impact on their sexual intimacy. It is not uncommon for women to experience pain or discomfort during sex for some time after childbirth. The healing process, scar tissue formation, and changes in the pelvic floor muscles can all contribute to this discomfort. Open communication with a healthcare provider, along with the support and understanding of one’s partner, can play a crucial role in addressing these issues and finding ways to restore sexual well-being.
9. The Risk Of Fourth-Degree Vaginal Tearing With Midline Episiotomies
While episiotomies are intended to prevent severe tears, it is important to note that a midline episiotomy can increase the risk of a more extensive tear known as a fourth-degree tear. This type of tear extends through the perineal muscles, anal sphincter, and rectal mucosa. Fourth-degree tears require specialized repair and can have long-term consequences on bowel function and quality of life.
Hence, the decision to perform a midline episiotomy should be carefully considered, weighing the potential benefits against the risks involved.
- Episiotomies can prevent severe tears but have their own risks
- Midline episiotomy can lead to a fourth-degree tear
- Fourth-degree tears impact bowel function and quality of life
- Deciding to perform a midline episiotomy should be carefully considered.
Remember to prioritize the well-being of the patient and their long-term health
10. Conclusion: Weighing The Pros And Cons Of Episiotomies
The use of episiotomies during childbirth has evolved significantly in recent years. Research has debunked the once-held belief in their effectiveness, leading to updated recommendations against routine episiotomies. While episiotomies are no longer considered standard practice, they may still be necessary in certain circumstances. Healthcare providers must weigh the potential benefits and risks when making decisions about incision types and interventions during childbirth. Understanding the recovery process and addressing any concerns about sexual intimacy are crucial aspects of post-episiotomy care. Ultimately, each woman’s unique circumstances should guide the choices made for a safe and successful childbirth experience.
💡
You may need to know these questions about episioitis
1. What are the common causes and risk factors for developing episiotomy complications like episiotisitis?
Episiotomy is a surgical cut made in the perineum, the area between the vagina and anus, during childbirth to enlarge the vaginal opening. While the procedure is commonly performed to facilitate delivery, it is not without potential complications. Episiotisitis, the inflammation or infection of the episiotomy site, can occur due to a variety of factors.
One common cause of episiotisitis is poor wound care hygiene. Inadequate cleaning or not keeping the episiotomy site dry can lead to infection. Additionally, excessive pressure or friction on the wound, such as from prolonged sitting or walking, can also increase the risk of infection. Another risk factor is the presence of certain bacteria in the vaginal or rectal area, which can introduce infection to the episiotomy site. The use of medical instruments, like forceps or vacuum extractors, during delivery can also contribute to the development of episiotisitis.
In summary, some common causes and risk factors for developing episiotomy complications like episiotisitis include poor wound care hygiene, pressure or friction on the wound, presence of specific bacteria, and the use of medical instruments during delivery. It is important for healthcare professionals to provide thorough postpartum guidelines and education to assist in preventing and managing these complications.
2. What are the typical symptoms and signs of episiotisitis, and how is it diagnosed?
Episiotisitis refers to inflammation or infection of the perineal area, which is the area between the vagina and anus in females. Common symptoms include pain, tenderness, and swelling in the perineal region. There may also be redness, warmth, and the presence of pus or discharge. Some individuals may experience discomfort or pain during urination or bowel movements. If left untreated, episiotisitis can lead to more severe complications, such as abscess formation or difficulty healing of the episiotomy or tear site.
To diagnose episiotisitis, a healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination of the perineal area. They will look for signs of inflammation, swelling, or infection. The provider may also collect a swab sample to test for the presence of bacteria in cases of suspected infection. Proper diagnosis is essential to ensure appropriate treatment is administered promptly, including antibiotics if necessary, to prevent further complications and promote healing.
3. What are the available treatment options for episiotisitis, and are there any home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms?
The available treatment options for episiotisitis typically involve medical interventions. These may include pain medication for relief, antibiotics to prevent infection, and sitz baths to promote healing and reduce discomfort. The doctor may also provide instructions for proper hygiene and wound care. In severe cases, surgical repair may be necessary.
While medical treatment is the most effective approach, there are some home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Keeping the area clean and dry is essential. Using warm water and mild soap during cleansing can help prevent infection. Applying ice packs or warm compresses to the area may help reduce swelling and discomfort. Additionally, sitting on a cushion or using a donut-shaped pillow can provide relief while sitting. However, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and recommendations before attempting any home remedies.
4. What are the potential long-term effects or complications that can arise from untreated episiotisitis, and how can they be prevented?
Untreated episiotisitis, which is the inflammation or infection of the perineal area following childbirth, can lead to several potential long-term effects or complications. These may include chronic pain and discomfort, delayed wound healing, scarring, urinary incontinence, sexual dysfunction, and psychological distress. In severe cases, it can even result in the formation of fistulas, which are abnormal connections between organs.
To prevent these complications, it is crucial to ensure proper management and treatment of episiotisitis. This includes timely recognition and diagnosis, appropriate wound care, pain management, and administration of antibiotics if needed. Additionally, practicing good perineal hygiene, regular pelvic floor exercises, and avoiding excessive strain on the perineum during subsequent pregnancies can help prevent the occurrence of episiotisitis and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Reference source
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/labor-and-delivery/in-depth/episiotomy/art-20047282
https://wordinfo.info/unit/746
https://www.almaany.com/en/dict/ar-en/episioitis/
https://www.spellchecker.net/meaning/episioitis