– Cervical mucus has two jobs: helping sperm move through the cervix during ovulation and preventing substances from entering the cervix.
– There are different types of cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle, including dry, sticky, creamy, slippery (resembling raw egg whites), and wet.
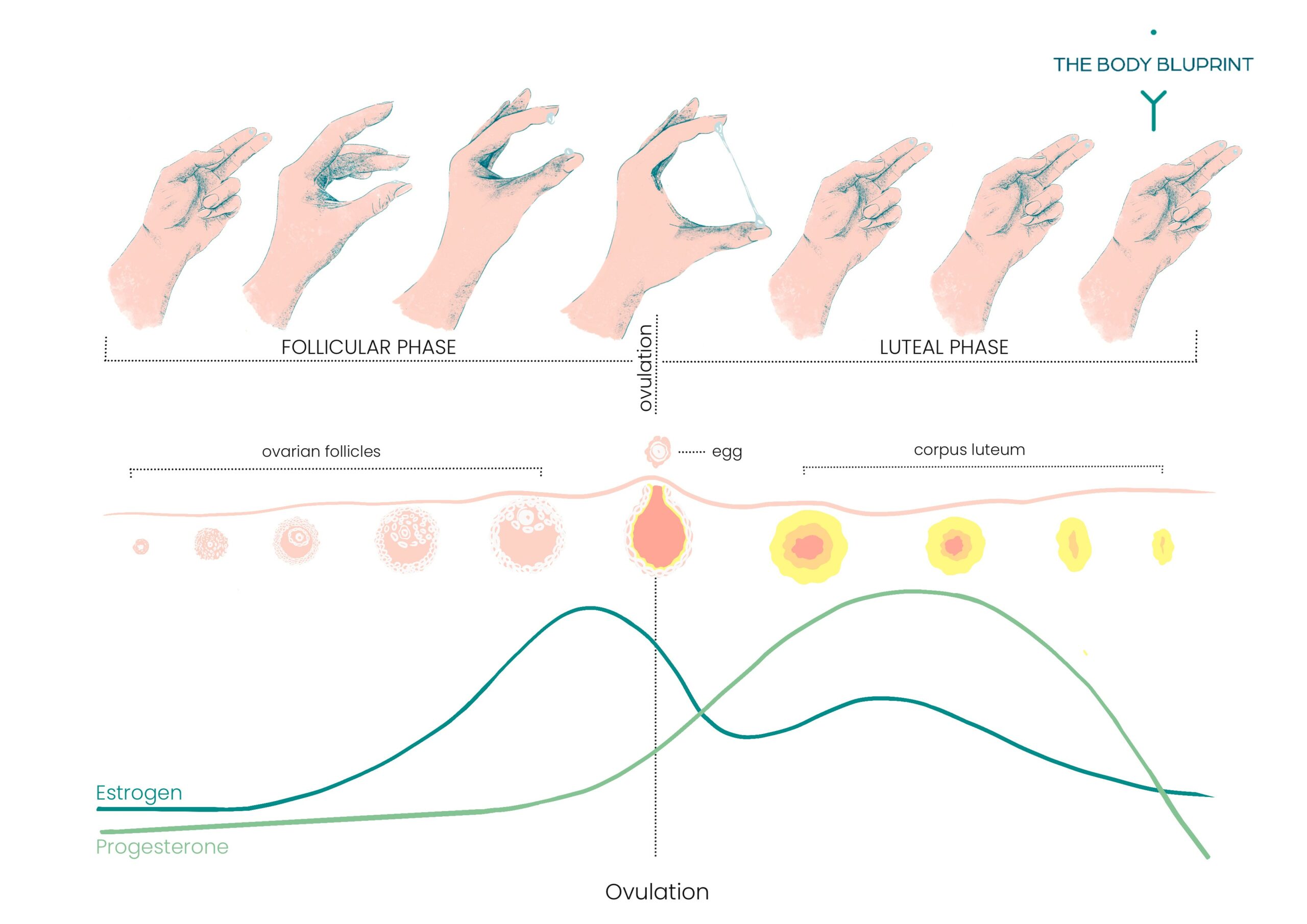
– Cervical mucus changes as hormone levels shift throughout the menstrual cycle. Estrogen increases before ovulation, causing the mucus to become stretchy and slippery, making it easier for sperm to reach the egg.
– After ovulation, estrogen levels drop and progesterone levels rise, causing the mucus to dry up.
– The fertile cervical mucus, resembling raw egg whites, indicates the most fertile time for conception.
– Cervical mucus serves as a medium for sperm to swim through to reach the egg.
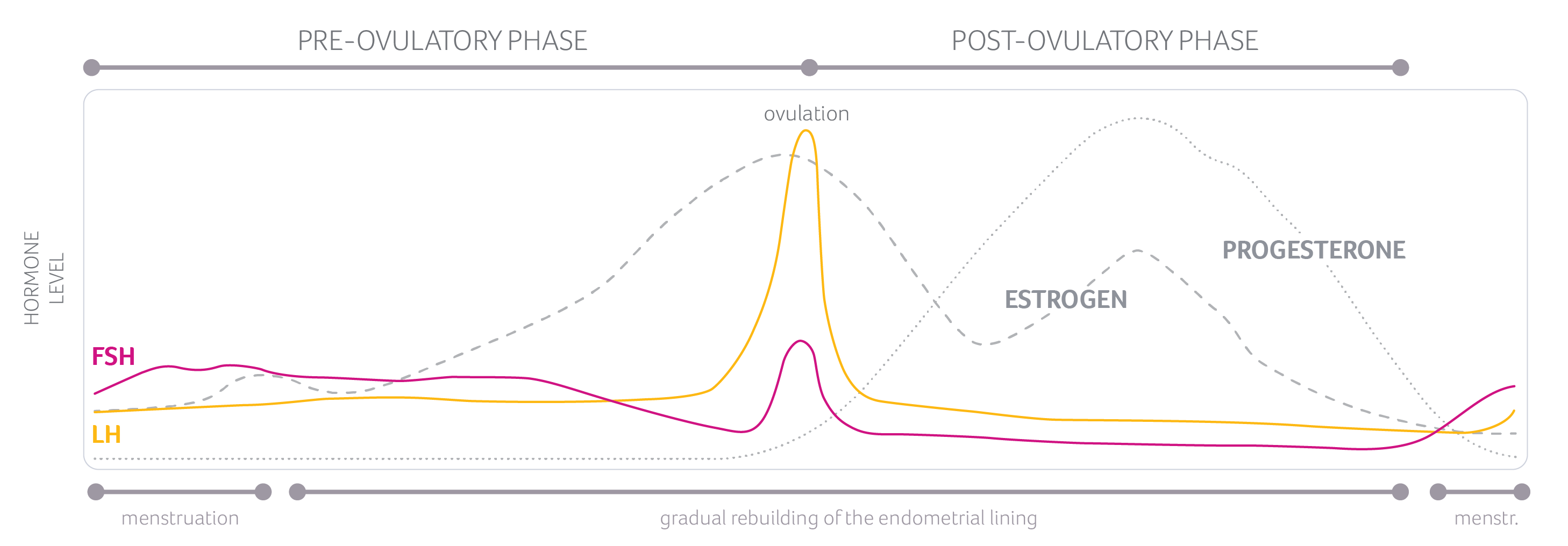
– Estrogen and progesterone are the hormones responsible for the changes in cervical mucus.
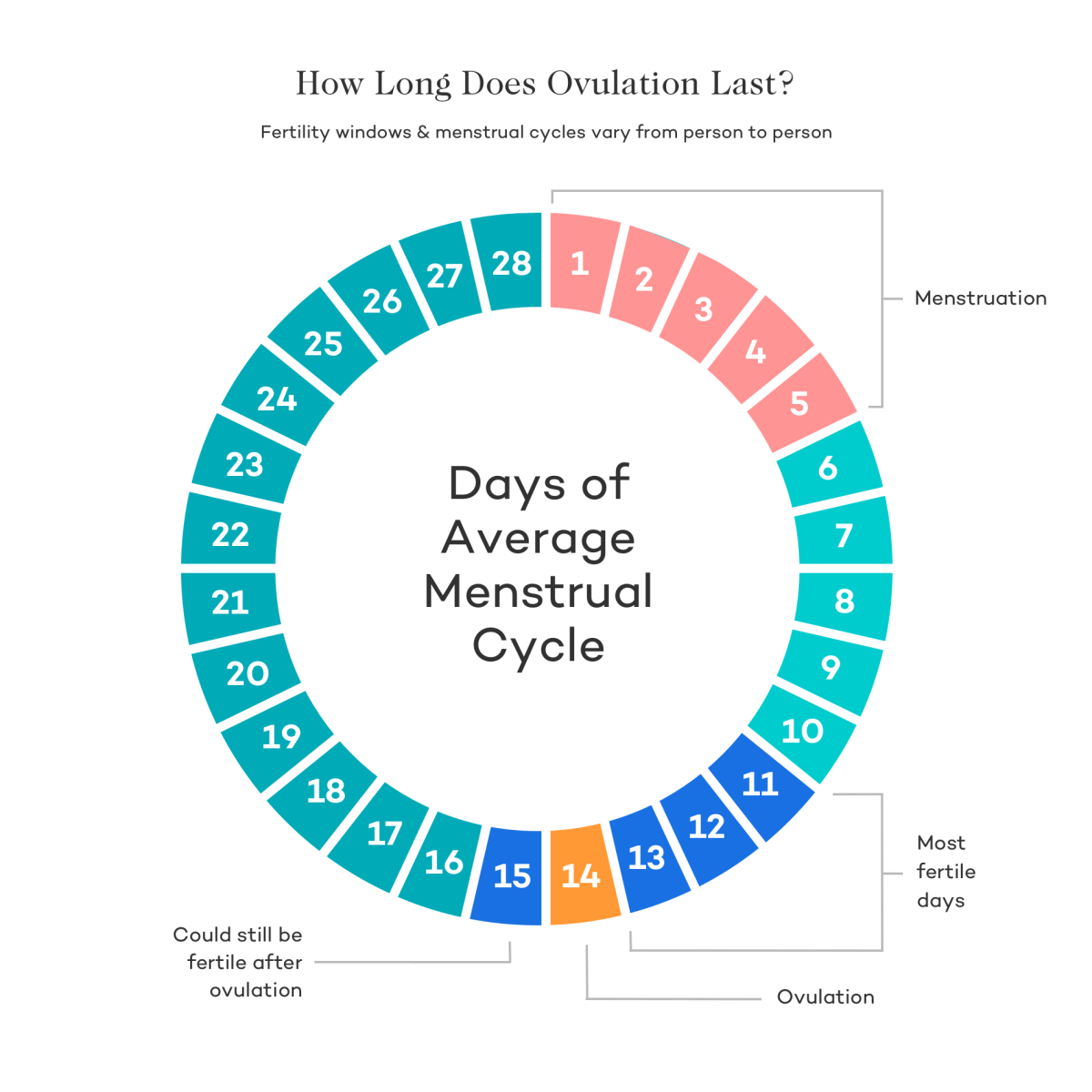
– The article discusses cervical mucus examination and its changes throughout the menstrual cycle and early pregnancy. It states that most women with a 28-day cycle ovulate around day 14, which is when cervical mucus becomes slippery, stretchy, and highly fertile.
– The egg white discharge typically lasts for about four days.
– After ovulation, cervical mucus thickens or dries up until menstruation occurs.
– Some women may still produce cervical mucus if they have conceived at ovulation, and this can indicate pregnancy.
– In some cases, implantation bleeding may occur, which is characterized by brown or pink tinged cervical mucus.
– The cervical mucus method of FAMs helps predict fertility by tracking changes in cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle.
– Hormones control the menstrual cycle and cause the cervix to produce mucus.
– The method involves checking the mucus daily and recording the results on a chart.
– Changes in the mucus indicate when ovulation is likely to occur.
– Unprotected sex is safe during non-fertile days, while another form of birth control should be used during fertile days.
– It is recommended to start this method with the help of a healthcare professional.
– The method is more effective when used in combination with the temperature method.
– Another type of cervical mucus method is the 2-day method.
– Cervical mucus can be checked by wiping the opening of the vagina with a tissue, checking the mucus on underwear, or inserting clean fingers into the vagina.
– The article explains how to examine and chart cervical mucus to determine fertility.
– The consistency and appearance of cervical mucus can change throughout the menstrual cycle.
– During menstruation, cervical mucus is not noticeable.
– After menstruation, there are usually dry days without mucus.
– Before ovulation, mucus becomes sticky or tacky and may be yellow, white, or cloudy.
– The most fertile days are characterized by clear, slippery mucus that resembles raw egg whites and can be stretched between the fingers.
– After ovulation, mucus decreases and becomes cloudy and sticky again.
– The article suggests that safe days for unprotected sex occur after ovulation and before the period, usually lasting for about 11-14 days.
– However, the length of the safe days may vary depending on the individual’s menstrual cycle.
– The article advises avoiding sex during menstruation as it can be considered unsafe due to the presence of blood.
– Cervical mucus examination is a method used to determine safe and unsafe days for sexual activity to prevent pregnancy.
– Unsafe days occur when the body is producing sticky or tacky mucus, and continue until slippery mucus is present leading up to ovulation.
– Unsafe, slippery days last for about 3-4 days.
– Changes to cervical mucus can be caused by activities such as vaginal sex, using lube, certain medications, breastfeeding, surgery on the cervix, douching, early menopause, and recent use of hormonal birth control or the morning-after pill.
– Cervical mucus methods may not be effective for individuals with low discharge production.
– The 2-day method is a simpler approach, where individuals ask themselves if they had cervical mucus on that day and the previous day.
– If the answer is yes to only one question, it is advised to use birth control or avoid vaginal sex.
– Checking cervical mucus can be done at any time of day as long as it is consistent.
Continue Reading