In the miraculous journey of pregnancy, the concept of fetal maturity holds a paramount significance.
As expectant parents eagerly await the arrival of their little one, thoughts of the delicate stages of development and the readiness of their baby’s tiny body become a constant source of wonder.
Join us on an enlightening exploration as we delve into the captivating realm of fetal maturity, uncovering the awe-inspiring milestones that pave the way for new life.
fetal maturity
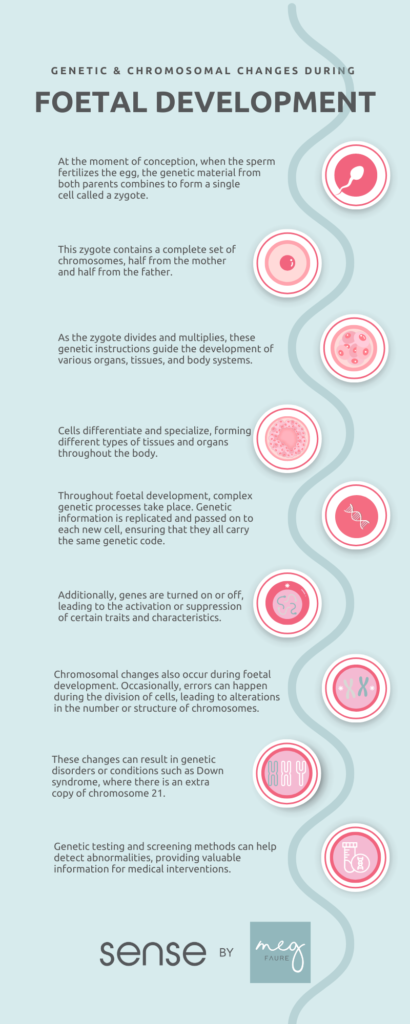
Fetal maturity refers to the stage of development at which a fetus has reached a point where it has a high chance of survival outside the womb.
This milestone is typically determined by the gestational age of the fetus, which is measured in weeks.
The more mature a fetus is, the more developed its organs and systems are, increasing its ability to function independently.
Fetal maturity is an important consideration in medical decision-making regarding potential interventions, such as elective delivery or the administration of certain treatments, to ensure the best outcomes for both the fetus and the mother.
Key Points:
- Fetal maturity refers to the stage of development where a fetus can survive outside the womb.
- It is determined by the gestational age of the fetus, measured in weeks.
- The more mature a fetus is, the more developed its organs and systems are.
- Fetal maturity affects medical decision-making, such as elective delivery or treatment administration.
- It is important for optimal outcomes for both the fetus and the mother.
- Fetal maturity increases the fetus’s ability to function independently.
fetal maturity – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Fetal bones are composed mostly of cartilage until around the 12th week of development, when they start to harden into solid bone structures.
2. By the end of the second trimester, around week 26, a fetus can already hear sounds from the outside world, responding to loud noises and even recognizing their mother’s voice.
3. Toward the end of the third trimester, fetal brain waves resemble those of a newborn, indicating that the brain is becoming increasingly mature.
4. Fetal hiccups are a common occurrence during pregnancy and can be felt by the mother. They are thought to be beneficial for the development of the baby’s diaphragm muscles.
5. Premature babies born as early as 23-24 weeks gestation can survive with the help of advanced neonatal medical care, but their lungs may not be fully mature, making it challenging for them to breathe on their own.
The Stages Of Fetal Development
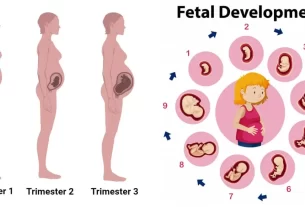
Fetal development is a complex and fascinating process that begins at conception and continues until the moment of birth. Understanding the stages of fetal development is essential in monitoring the maturation and growth of the fetus.
The first trimester of pregnancy is a critical period for fetal development as the organs and body systems begin to form. During this time, the fertilized egg implants itself into the uterine lining, and the placenta begins to develop to nourish and support the growing fetus. By the end of the first trimester, all major organs have formed, and the fetus is around three inches long.
In the second trimester, the fetus continues to grow and develop rapidly. This is the period when the mother can start to feel the baby moving, known as quickening. The fetus’s body proportions start to become more defined, and by the end of the second trimester, the eyes can open and close, and the lungs are capable of breathing movements.
The third trimester sees further growth and maturation of the fetal organs, especially the brain and lungs. The fetus develops a layer of fat under the skin to help regulate body temperature and prepares for life outside the womb.
Assessing Fetal Maturity
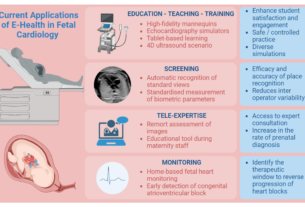
Assessing fetal maturity is essential in prenatal care and involves evaluating various factors to determine the readiness of the fetus for birth. One method is ultrasound imaging, which measures the size of fetal structures and monitors organ development. Another common method is a fetal non-stress test, which measures the baby’s heart rate and movement in response to stimuli. Evaluating the level of amniotic fluid and its composition can also provide insights into fetal maturity.
In addition to these diagnostic techniques, healthcare professionals may assess fetal maturity based on the mother’s perception of fetal movement, which tends to increase as the fetus reaches maturity. Fetal weight gain and measurements of fundal height (the distance between the top of the uterus and the pubic bone) can also indicate fetal maturation. Collectively, these assessments help medical professionals determine the most appropriate timing for delivery and ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Factors Affecting Fetal Maturation
Several factors influence fetal maturation, including genetics, maternal health, and environmental factors. Genetic factors play a significant role in determining the pace of fetal development, as they influence the blueprint of an individual’s growth and maturation. Maternal health is another crucial factor, as certain conditions such as gestational diabetes or hypertension can impact fetal maturation.
Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or maternal substance abuse, can also affect fetal development. Smoking, for example, can restrict oxygen supply to the fetus and impair lung development. Adequate nutrition is essential for fetal maturation, and a well-balanced diet during pregnancy can support healthy growth. Additionally, the presence of certain infections can interfere with fetal development. It is important for expectant mothers to prioritize their health and seek appropriate prenatal care to optimize fetal maturation.
The Importance Of Fetal Lung Development
Fetal lung development is of utmost importance as it directly impacts the baby’s ability to survive after birth. The development of the lungs starts early in pregnancy, but it reaches full maturity towards the end of the third trimester. Surfactant, a substance that reduces surface tension and prevents the collapse of alveoli (the tiny air sacs responsible for oxygen exchange), plays a key role in this process. It is crucial for normal lung function and enables the baby to take its first breath outside the womb.
During pregnancy, the amniotic fluid provides a protective environment for the developing lungs. Additionally, the fetus engages in “breathing” movements that help strengthen the respiratory muscles and prepare the lungs for the transition to breathing air. Premature babies who are born before their lungs have fully matured may require respiratory support such as supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation. Hence, monitoring fetal lung development and ensuring sufficient surfactant production are critical for assessing fetal maturity and preparing for a successful childbirth.
Some key points to keep in mind about fetal lung development:
- Fetal lung development impacts the baby’s ability to survive outside the womb.
- Complete lung maturation occurs towards the end of the third trimester.
- Surfactant production is essential for normal lung function and allows the baby to breathe after birth.
- Amniotic fluid provides a protective environment for the developing lungs.
- “Breathing” movements help strengthen respiratory muscles and prepare the lungs for breathing air.
- Premature babies may need respiratory support due to insufficient lung maturity.
“Among all the organs, fetal lung development holds exceptional significance as it directly relates to the baby’s ability to survive outside the womb.”
Gestational Age And Fetal Maturity
Gestational age, determined by counting the number of weeks since the first day of the mother’s last menstrual period, is crucial in evaluating fetal maturity. It helps determine the expected milestones and readiness for birth. However, it’s important to understand that even babies of the same gestational age can have variations in their development.
Some babies may be more advanced while others may be slower in their development. These differences can be influenced by genetics, maternal health, and environmental factors. Therefore, relying solely on gestational age to assess fetal maturity may not provide a complete picture. Healthcare professionals take into account multiple factors, including ultrasound measurements, physical examinations, and fetal movement patterns, to comprehensively evaluate fetal development and readiness for birth.
- Gestational age is the number of weeks since the first day of the mother’s last menstrual period.
- Variations in fetal development can occur even among babies of the same gestational age.
- Factors like genetics, maternal health, and environment contribute to these variations.
- Healthcare professionals consider ultrasound measurements, physical examinations, and fetal movement patterns for a comprehensive assessment.
“Gestational age plays a key role in determining fetal maturity, but it is important to consider other factors for a complete evaluation.”
Indications Of Fetal Readiness For Birth
Several signs indicate that a fetus is nearing readiness for birth. One common observation is the “lightening” or “dropping” sensation experienced by the mother when the baby’s head settles into the pelvis in preparation for delivery. This relieves pressure on the mother’s diaphragm and allows for easier breathing. The cervix also undergoes changes, becoming softer and beginning to thin out (efface) in preparation for labor.
Braxton Hicks contractions, also known as “practice contractions,” may increase in frequency and intensity as the body prepares for labor. The presence of mucus plug discharge, which can occur days or weeks before labor, is another indication that the cervix is preparing for delivery by “plugging” the opening of the uterus. Monitoring these signs along with the advancement of gestational age and fetal maturity assessments helps healthcare professionals determine the optimal timing for delivery.
Understanding Fetal Organ Development
Fetal organ development is a synchronized and intricate process that involves the formation of all the major organ systems. The heart starts beating at just three weeks and continues to develop throughout pregnancy. The brain and nervous system also undergo extensive growth and differentiation, leading to the formation of complex neural networks.
The digestive system, including the liver and intestines, begins to develop early and facilitates nutrient absorption essential for fetal growth. The kidneys play a crucial role in fluid balance and waste elimination, while the skeletal system provides support for the developing fetus. Muscles, skin, and the body’s reproductive system also undergo growth and maturation during fetal development.
Understanding the milestones and processes involved in fetal organ development is vital for healthcare professionals monitoring the maturation of the fetus. It allows them to identify any abnormalities or potential complications that may require intervention to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Monitoring Fetal Growth And Maturation
Monitoring fetal growth and maturation is a crucial aspect of prenatal care and involves various methods and examinations. Regular ultrasound scans are commonly used to assess the size and growth of the fetus, as well as the development of individual organs. These scans can also help detect any abnormalities or potential issues that may require further evaluation or intervention.
Fundal height measurements, taken by measuring the distance from the top of the uterus to the pubic bone, provide an indication of fetal growth. These measurements are typically assessed during routine prenatal visits and can help identify any discrepancies in growth or potential concerns.
Additionally, fetal movement counting is a simple technique where the mother tracks the number of movements felt within a certain timeframe. Changes in fetal movement patterns may indicate a need for further assessment.
Combining these monitoring methods with overall maternal health assessments, including blood pressure, weight gain, and urine analysis, can provide a comprehensive evaluation of fetal growth and maturation. Regular prenatal visits and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential in ensuring appropriate monitoring and timely intervention if necessary.
- Regular ultrasound scans assess the size, growth, and organ development of the fetus
- Fundal height measurements indicate fetal growth and help identify discrepancies
- Fetal movement counting can be used to track changes in movement patterns
- Overall maternal health assessments, such as blood pressure, weight gain, and urine analysis, provide a comprehensive evaluation
“Monitoring fetal growth and maturation is a crucial aspect of prenatal care and involves various methods and examinations.”
Promoting Fetal Maturation For Premature Babies
Premature birth, defined as delivery before 37 weeks of gestation, can pose challenges as the baby’s organs may not have fully matured. However, medical advancements and interventions allow healthcare professionals to promote fetal maturation and improve outcomes for premature babies. One significant factor in promoting fetal maturation is administering corticosteroids to the mother before delivery.
Corticosteroids accelerate fetal lung development and stimulate the production of surfactant. This helps improve lung function and reduces the risk of respiratory distress syndrome, a common complication in premature babies. Other interventions may include providing respiratory support, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or mechanical ventilation, to aid breathing in premature babies who have not fully developed their lungs.
In addition to medical interventions, creating a safe and nurturing environment in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is vital for promoting fetal maturation. Temperature regulation, infection prevention, and proper nutrition all contribute to the healthy development of premature babies. The combined efforts of healthcare professionals and specialized care in neonatal units help optimize fetal maturation and support the journey to optimal health for premature infants.
Complications Associated With Fetal Immaturity
Fetal immaturity is a critical factor that can lead to various complications, especially in cases of premature birth. Premature babies often have underdeveloped organs, such as the lungs, brain, and digestive system, which puts them at higher risk for respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage (brain bleeding), and necrotizing enterocolitis (inflammation of the intestinal tissue).
In addition to organ immaturity, premature babies may struggle with maintaining body temperature, putting added stress on their bodies and disrupting thermoregulation. Furthermore, their immune systems may be compromised, making them more susceptible to infections. Long-term effects can include developmental delays, learning disabilities, and ongoing health issues.
To mitigate these complications, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to provide close monitoring and specialized care for premature babies. Early intervention, respiratory support, and a multidisciplinary approach to care can significantly improve outcomes for babies born with fetal immaturity.
Understanding fetal maturity and the various stages of development is essential for ensuring optimal prenatal care and promoting healthy childbirth. Assessing fetal maturity through diagnostic techniques and monitoring methods allows healthcare professionals to determine the readiness of the fetus for birth. Factors such as genetics, maternal health, and environmental influences can impact fetal maturation. Fetal lung development is particularly important as it directly affects the baby’s ability to breathe after birth. Gestational age, indications of fetal readiness for birth, and organ development are crucial considerations in assessing fetal maturity.
Monitoring fetal growth and maturation, promoting fetal maturation for premature babies, and addressing complications associated with fetal immaturity are vital aspects of prenatal care and neonatal medicine. By understanding and addressing these factors, healthcare professionals can support healthy fetal development and improve outcomes for both mother and baby.
💡
You may need to know these questions about fetal maturity
How do you determine fetal maturity?
Fetal maturity can be determined through a technique called fluorescent polarization. By measuring the ratio of surfactant to albumin, this method can indicate the level of lung maturity in the fetus. Higher values in fluorescent polarization suggest high surfactant levels and mature lungs, whereas lower values indicate immaturity. This technique offers several advantages, including its simplicity, automation, and enhanced precision compared to the traditional L/S ratio method. Thus, fluorescent polarization is a reliable approach to assess fetal maturity.
What is the meaning of BPD in fetal maturity?
BPD in fetal maturity refers to the biparietal diameter, which indicates the diameter of the baby’s head. It is an important measurement used to assess the growth and development of the baby during pregnancy. Along with other measurements such as head circumference (HC) and crown-rump length (CRL), BPD helps healthcare providers determine the fetal maturity and monitor any potential abnormalities or delays in growth. These measurements are especially crucial in the first trimester when CRL is taken, providing early insights into the baby’s development and ensuring appropriate care and interventions if needed.
Can ultrasound determine age of fetus?
Yes, ultrasound can determine the age of a fetus with a high degree of accuracy. By measuring various fetal parameters, such as crown-rump length, head circumference, and femur length, physicians can estimate the gestational age of the fetus. This information is crucial for ensuring accurate dating in research studies and collecting vital statistics. The precise determination of fetal age through ultrasound aids in establishing appropriate investigational protocols and contributes to improved healthcare outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
How does ultrasound calculate fetal age?
Ultrasound technology plays a crucial role in determining fetal age during various stages of pregnancy. During the initial trimester, the gestational sac mean diameter and crown-rump length measurements are pivotal in evaluating the gestational age. As the pregnancy progresses into the second and third trimesters, ultrasound examinations focus on measuring the fetal head, body, and extremities to assess gestational age. By comparing these measurements to established growth charts and reference values, ultrasound enables medical professionals to calculate fetal age with remarkable accuracy.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK11382/
https://wardelab.com/warde-reports/assessment-of-fetal-lung-maturity/
https://www.webmd.com/baby/fetal-biometry
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/fetus-maturity