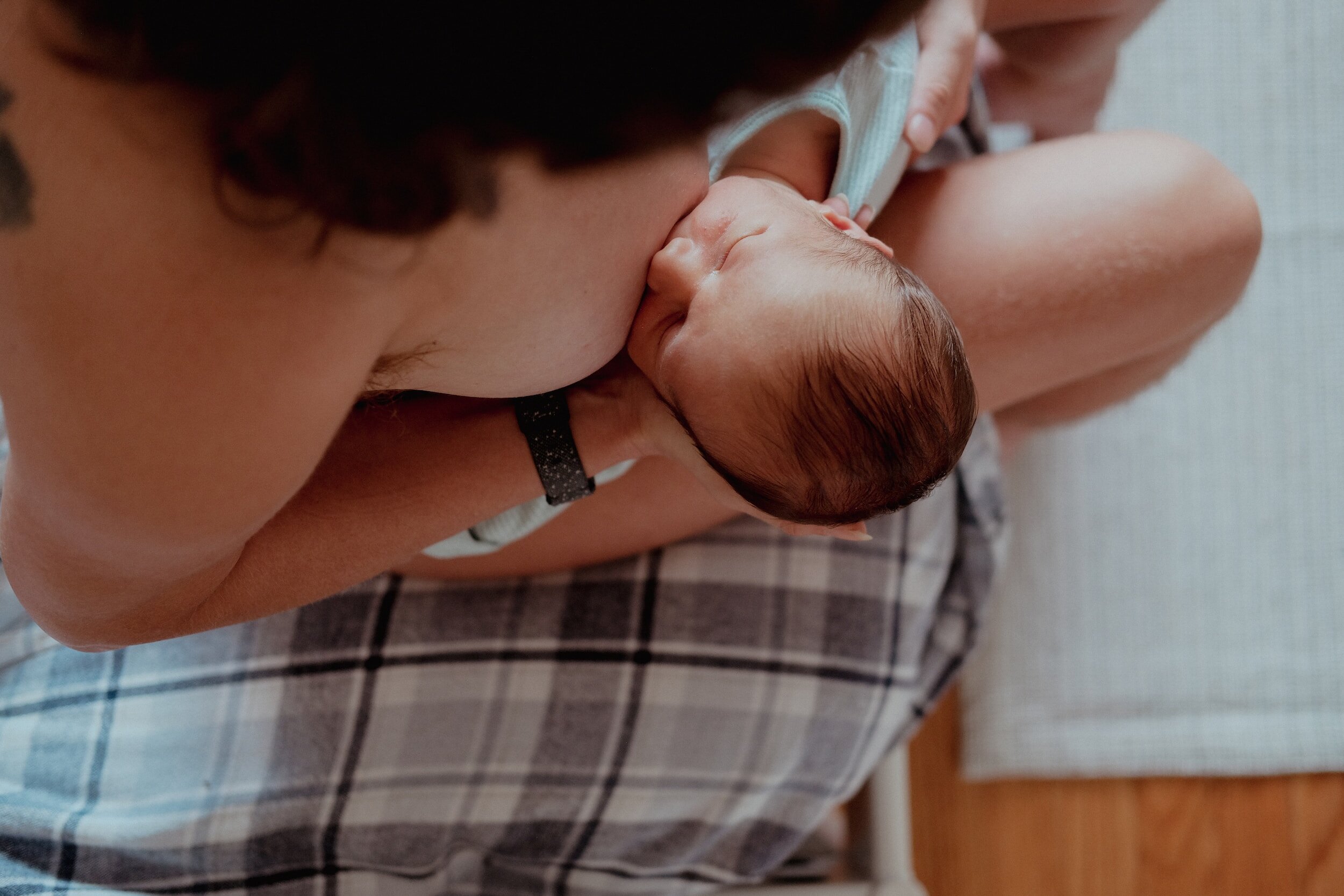
Discover the fascinating role that breast milk plays in a baby’s growth and development.
From providing crucial nutrients and water to cultivating good bacteria, breast milk is truly a miracle elixir.
But did you know that an imbalance between foremilk and hindmilk can impact digestion?
Join us as we unravel the secrets of breast milk’s incredible benefits!
fore milk
Foremilk refers to the initial milk that is produced in the mother’s breast during breastfeeding.
It contains a lower concentration of fat compared to hindmilk, which is the milk that is produced towards the end of a feeding session.
The purpose of foremilk is to provide hydration and essential nutrients to the baby, including lactose and other nutrients necessary for their growth and development.
However, an imbalance between foremilk and hindmilk can occur if the baby does not receive enough hindmilk, leading to potential digestion issues such as gas and symptoms of lactose overload.
It’s important to ensure proper breastfeeding techniques, avoid overfeeding, and promote the consumption of both foremilk and hindmilk for the baby’s optimal health, including the development of the brain, nerve tissues, and the digestive system.
Key Points:
- Foremilk is the initial milk produced during breastfeeding
- It contains a lower concentration of fat compared to hindmilk
- Foremilk provides hydration and essential nutrients to the baby
- Imbalance between foremilk and hindmilk can lead to digestion issues and lactose overload
- Proper breastfeeding techniques and avoiding overfeeding are important
- Foremilk and hindmilk are both needed for the baby’s optimal health and development
fore milk – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Fore milk, the initial milk produced during breastfeeding, has a lower fat content than hind milk, which is released toward the end of a feeding session.
2. In ancient times, fore milk was considered a cherished remedy for eye infections and was even used as an ingredient in various medicinal preparations.
3. Fore milk typically has a higher lactose content than hind milk, making it a valuable source of energy for a breastfeeding baby.
4. Certain factors, such as stress or improper latch, can affect the composition of fore milk, leading to an imbalance in the ratio of fat to lactose.
5. The taste of fore milk can vary depending on various factors, including the mother’s diet, resulting in different flavors for babies to experience during feeding.
Fore Milk – Breast Milk
Breast milk is the perfect source of nutrition for newborn babies. It provides all the necessary elements for their growth and development during the first few months of life. One important component of breast milk is the fore milk, also known as the initial milk. This milk is produced at the beginning of a feeding session and differs in composition from the hind milk, which is produced towards the end of a feeding.
- Breast milk is ideal for newborns’ nutrition.
- Fore milk is the initial milk produced during feeding.
- Hind milk is produced towards the end of a feeding.
“Breast milk provides essential nutrition for newborns, with fore milk and hind milk differing in composition.”
Foremilk
Foremilk is the milk that is released first during breastfeeding. It is generally high in lactose, a type of sugar, and contains lower levels of fat. This milk appears thinner and more watery in consistency compared to hind milk. The lactose in foremilk provides the baby with an easily digestible source of energy.
In addition to lactose, foremilk also contains important nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antibodies. These substances play a significant role in supporting the baby’s immune system, promoting healthy growth, and protecting against infections.
- Foremilk is released first during breastfeeding
- High in lactose, a type of sugar
- Lower levels of fat compared to hind milk
- Thinner and more watery in consistency
- Provides easily digestible source of energy for the baby
“Foremilk contains important nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antibodies, which support the baby’s immune system, promote healthy growth, and protect against infections.”
Hindmilk
Hindmilk is the milk produced at the end of a feeding session and is higher in fat content than foremilk. The fat in hindmilk provides the baby with a concentrated source of calories, promoting weight gain and proper growth.
During breastfeeding, babies naturally receive both foremilk and hindmilk to ensure they get a balanced combination of nutrients, including lactose and fat, for their growing needs.
Lactose
Lactose is a crucial component of breast milk, present in higher amounts in foremilk. It is a type of sugar that acts as the primary carbohydrate source for babies. Lactose provides energy for growth and supports brain development.
Furthermore, lactose also contributes to the absorption of calcium and other minerals, ensuring the baby’s overall bone health. It also plays a role in the development of a healthy digestive system, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Lactose is a primary carbohydrate source in breast milk
- Provides energy for growth and brain development
- Absorption of calcium and other minerals is facilitated by lactose
- Supports overall bone health
- Promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria
“Lactose is a crucial component of breast milk, providing energy and supporting development. It also helps with calcium absorption, bone health, and the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.”
Nutrients
Breast milk is an essential source of nutrients for a baby’s healthy development. It contains a wide range of important components, including lactose, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients are crucial for supporting the overall growth of the baby, particularly during the early stages of life when rapid development occurs.
One significant benefit of breast milk is its high levels of antibodies, which play a vital role in protecting the baby against infections and boosting their immune system. Additionally, breast milk provides essential fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin A, D, E, and K. These vitamins are critical for promoting good vision, maintaining healthy skin, strengthening bones, and facilitating blood clotting.
Water
Breast milk is primarily made up of water, which plays a crucial role in keeping the baby hydrated. This is particularly important during the early months when the baby’s kidneys are still developing. Breast milk provides the necessary fluids to maintain proper hydration for the baby.
To support a sufficient milk supply, it is essential for mothers to ensure they are well-hydrated. Drinking an adequate amount of water is crucial as it helps in producing enough breast milk and maintaining its hydration properties for the baby.
- Breast milk is primarily composed of water
- Adequate hydration is vital for the baby’s well-being
- Proper hydration supports the development of the baby’s kidneys
- Drinking enough water is essential for mothers to produce sufficient breast milk and maintain its hydration properties.
Fat
Fat in breast milk plays a vital role in the growth and development of a baby. Its concentration gradually increases during feeding sessions, providing essential calories and facilitating steady weight gain. Moreover, this fat also contributes to the development of the brain and nerve tissues.
Notably, the fatty acids present in breast milk are particularly crucial for the baby’s brain and nervous system development. These healthy fats promote cognitive growth and enhance the baby’s intelligence.
Growth and Development
Breast milk, which includes foremilk and hindmilk, is crucial for a baby’s growth and development. It supplies vital nutrients, vitamins, and antibodies necessary for the baby’s rapid growth in the early months of life.
The balanced composition of lactose, fat, and other nutrients in breast milk aids in healthy weight gain, promotes proper bone development, and boosts the baby’s immune system. Furthermore, it plays a vital role in the maturation of the digestive system and facilitates the absorption of essential nutrients.
- Breast milk provides necessary nutrients, vitamins, and antibodies for babies.
- The combination of lactose, fat, and other nutrients supports healthy weight gain and proper bone development.
- Breast milk strengthens the baby’s immune system.
- It contributes to the healthy maturation of the digestive system and absorption of essential nutrients.
Foremilk/Hindmilk Imbalance
An imbalance between foremilk and hindmilk can occur under certain circumstances. This imbalance can result in the baby receiving an excess of foremilk, which is higher in lactose and lower in fat compared to hindmilk.
This imbalance may lead to symptoms such as gassiness, colic, and loose stools. It is important for breastfeeding mothers to ensure that their baby is getting a proper balance of foremilk and hindmilk during each feeding session to avoid any potential issues.
Digestion
Breast milk, including both foremilk and hindmilk, is easily digested by the baby’s immature digestive system. The presence of lactose in foremilk promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, supporting a healthy digestive system.
The enzymes present in breast milk aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, ensuring that the baby can extract the necessary energy and nutrients from each feeding. This ease of digestion is one of the many advantages of breastfeeding over formula feeding.
Breast milk remains the gold standard of infant nutrition, providing everything a baby needs for a strong start in life.
- Breast milk contains a unique balance of nutrients, including lactose and fat, that support the baby’s growth, brain development, and immune system.
- Ensuring a proper balance of these milk components is important to prevent any potential issues and to promote optimal digestion.
Breast milk is truly a remarkable source of nutrition for infants, offering numerous benefits with its easily digestible nature and rich composition.
💡
You may need to know these questions about fore milk
What is fore milk and hindmilk?
Foremilk and hindmilk are two distinct types of breast milk produced by breastfeeding mothers. Foremilk is the initial milk that a baby receives during feeding, while hindmilk follows thereafter. Foremilk is primarily composed of water with additional nutrients, while hindmilk is notably high in fat content. This differentiation in composition allows babies to benefit from both hydration and essential nutrients throughout their feeding session.
Is fore or hind milk better?
Both foremilk and hindmilk play important roles in a baby’s feeding process. While hindmilk is often thought to be more nutritious due to its higher fat content, it is crucial to understand that the emphasis should be on allowing the baby to feed until they are satisfied. This ensures that they receive an adequate volume of milk, which ultimately contributes to their weight gain. The key here is to focus on the continuous supply and demand process by allowing babies to nurse until they are full, rather than solely fixating on the differences between foremilk and hindmilk.
What causes too much foremilk?
An excessive amount of foremilk can be caused by an overabundant supply of breast milk, particularly when both breasts are offered during each feeding. This can result in the baby receiving predominantly foremilk from the first side, followed by even more foremilk from the other breast.
How long does it take for a baby to get hindmilk?
The time it takes for a baby to get hindmilk can vary depending on several factors. These factors include your milk supply, the time of day, and the last time you expressed milk. While some babies may get hindmilk immediately during a nursing session, others may require up to 45 minutes. It is important to remember that each baby’s feeding pattern is unique, and what matters most is that the baby is well-nourished and comfortable during the feeding process.
Reference source
https://www.webmd.com/parenting/baby/what-to-know-about-foremilk-and-hindmilk
https://www.healthline.com/health/breastfeeding/hindmilk
https://www.verywellfamily.com/foremilk-431991
https://balancedbreastfeeding.com/foremilk-vs-hindmilk/