In the realm of pregnancy, where joy and anticipation intertwine, a lurking menace silently awaits – gestational trophoblastic tumor.
This elusive and rare form of cancer emerges from placenta cells, unleashing a cascade of unsettling symptoms.
However, fear not, for this enigma can often be conquered through a variety of treatments, illuminating the path to hope and recovery.
gestational trophoblastic tumour
A gestational trophoblastic tumor is a type of cancer that develops from the cells that form the placenta during pregnancy.
It is a rare condition that typically affects women of childbearing age.
The tumor can be benign or cancerous and may present symptoms such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, nausea, vomiting, and pelvic pain.
Treatment options for gestational trophoblastic tumors include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Clinical trials are continually being conducted to discover new and improved ways to treat this form of cancer.
It is crucial to receive care from a medical team with expertise in managing gestational trophoblastic tumors.
While this disease is rare, it can generally be cured with appropriate treatment.
The 5-year survival rate for women with low-risk disease is close to 100%, while for women with high-risk disease, it is around 90%.
In some cases, the tumor can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs, which can complicate treatment.
Key Points:
- Gestational trophoblastic tumor is a cancer that develops from placental cells during pregnancy.
- It typically affects women of childbearing age and can be benign or cancerous.
- Symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, nausea, vomiting, and pelvic pain.
- Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
- Clinical trials are ongoing to improve treatment methods for this type of cancer.
- It is crucial to seek care from experts in managing gestational trophoblastic tumors.
gestational trophoblastic tumour – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Gestational trophoblastic tumors (GTTs) are rare and usually benign tumors that develop from abnormal growth of cells in the uterus during pregnancy.
2. One form of GTT called complete hydatidiform mole occurs when the placenta develops abnormally, resulting in a mass of cysts without a viable fetus. This condition is characterized by a complete lack of fetal tissue development.
3. GTTs can sometimes be associated with abnormal hormonal activity, leading to symptoms such as rapid enlargement of the uterus, severe morning sickness, and high blood pressure.
4. Despite being largely benign, some forms of GTT can develop into a malignant tumor called choriocarcinoma. This aggressive cancer can spread to other organs and tissues.
5. GTTs are more commonly diagnosed in women of Asian descent, with highest rates found in countries like Indonesia, the Philippines, and parts of East Asia.
What Is Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor?
Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor
Gestational trophoblastic tumor is a unique form of cancer that originates from the cells responsible for developing the placenta during pregnancy. This tumor can be categorized as either benign or cancerous, impacting women of childbearing age. Although rare, understanding its diagnosis, treatment, and recovery process is crucial for those affected.
The tumor develops when there are abnormal growths or changes in the trophoblast cells, which are normally responsible for forming the placenta. These cells nourish the embryo and eventually develop into the placenta, providing essential support during pregnancy. However, in the case of gestational trophoblastic tumor, these cells become abnormal and rapidly multiply, forming a mass or tumor within the uterus.
Occurrence And Prevalence
Gestational trophoblastic tumor primarily affects women of childbearing age, typically between the ages of 20 and 40. Understanding the prevalence of this condition and its impact on reproductive health is essential. It can occur after any type of pregnancy, including molar pregnancies, miscarriages, and normal pregnancies.
The incidence of gestational trophoblastic tumor varies across different populations and regions. In some parts of the world, such as Southeast Asia, it occurs more frequently. This disparity may be influenced by genetic or environmental factors. However, it is crucial to note that gestational trophoblastic tumor can occur in women of any ethnic background or geographic location.
Differentiating Between Benign And Cancerous Tumor
Gestational trophoblastic tumor can manifest as either a benign or cancerous growth. It is important to distinguish between the two to determine the appropriate treatment approach. Benign tumors, also known as gestational trophoblastic disease, do not spread to other parts of the body and are generally less aggressive. Conversely, cancerous tumors, referred to as gestational trophoblastic neoplasia, have the potential to metastasize to other organs, such as the lungs, making treatment more challenging.
To differentiate between benign and cancerous tumors, healthcare professionals rely on various diagnostic tools, including ultrasound, blood tests, and biopsy. These tests help assess the size, location, and characteristics of the tumor, providing crucial information for staging and treatment decisions.
Recognizing Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of gestational trophoblastic tumor is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. While some women may experience no symptoms, others may present with certain signs indicative of this condition. Common symptoms include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as heavy or persistent bleeding
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic region
- Nausea and vomiting
- Enlarged uterus
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other conditions, highlighting the significance of seeking medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Any concerns should be addressed with a healthcare professional, who can guide individuals through the necessary evaluations and determine the appropriate course of action.
- Seek medical attention if experiencing abnormal vaginal bleeding or pelvic pain
- Other conditions can also cause these symptoms, so it’s important to get a proper diagnosis
- Healthcare professionals can provide guidance and determine the best course of action
Available Treatment Options
When it comes to gestational trophoblastic tumor, a range of treatment options exists. Determining the most suitable approach depends on factors such as the tumor type, stage, and potential spread to other organs.
-
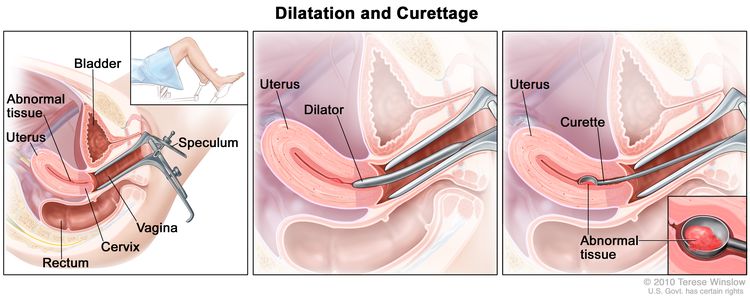
Surgery is often the preferred initial treatment for gestational trophoblastic tumor. The primary goal of surgery is to remove the tumor and any surrounding tissue that may contain cancerous cells. In some cases, a hysterectomy may be recommended, particularly if the tumor is cancerous or has severely impacted the uterus.
-
Chemotherapy is another vital treatment option for gestational trophoblastic tumor. It utilizes strong medications to destroy cancer cells and prevent their growth. Chemotherapy can be administered orally or intravenously, allowing the drugs to reach cancer cells throughout the body.
-
Radiation therapy may also be used in certain cases. It uses high-energy X-rays or other radiation sources to kill cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Radiation therapy is often recommended when cancer has spread or is at high risk of recurrence.
Often, a combination of these treatment modalities is employed to maximize the chances of a successful outcome. The specific treatment plan will be tailored to the individual’s needs and circumstances, taking into account factors such as overall health and desires regarding future pregnancy.
- The primary goal of surgery for gestational trophoblastic tumor is to remove the tumor and any surrounding tissue that may contain cancerous cells.
- In some cases, a hysterectomy may be recommended if the tumor is cancerous or has severely impacted the uterus.
- Chemotherapy is a vital treatment option that utilizes strong medications to destroy cancer cells and prevent their growth.
- It can be administered orally or intravenously, allowing the drugs to reach cancer cells throughout the body.
- Radiation therapy may also be used, especially when the cancer has spread or is at high risk of recurrence.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other radiation sources to kill cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
- A combination of these treatment modalities is often employed to maximize the chances of a successful outcome.
- The specific treatment plan will be tailored to the individual’s needs, taking into account factors such as overall health and desires regarding future pregnancy.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Continual advancements in medical research have led to the ongoing exploration of new and improved methods to treat gestational trophoblastic tumor. Clinical trials play a crucial role in evaluating innovative treatments, identifying potential breakthroughs, and improving patient outcomes.
These trials involve the investigation of experimental therapies, such as new drugs or treatment regimens. By participating in clinical trials, patients can access cutting-edge treatments that may not yet be widely available. Furthermore, contributing to these trials helps enhance medical knowledge and improve future treatment options for individuals diagnosed with gestational trophoblastic tumor.
- Clinical trials are vital for evaluating new treatments for gestational trophoblastic tumor.
- Experimental therapies, such as new drugs or treatment regimens, are investigated in these trials.
- Participation in clinical trials allows patients to access cutting-edge treatments.
- Contributing to clinical trials helps improve future treatment options for individuals with gestational trophoblastic tumor.
“By participating in clinical trials, patients can access cutting-edge treatments that may not yet be widely available and contribute to improving medical knowledge.”
Causes And Risk Factors
The exact causes of gestational trophoblastic tumor are not fully understood. However, certain risk factors have been identified that may increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Some factors include a history of molar pregnancies, a previous gestational trophoblastic tumor, or a family history of the disease. Additionally, women of Asian descent, particularly those from Southeast Asian countries, have an increased risk compared to other ethnic populations.
While these risk factors can provide insight into the development of gestational trophoblastic tumor, it is important to note that the condition can occur in individuals without any identifiable risk factors. Regular prenatal care and early detection remain crucial in managing and treating gestational trophoblastic tumor.
Potential For Complete Cure
The prognosis for women diagnosed with gestational trophoblastic tumor is generally optimistic, with an excellent chance of a complete cure. The overall prognosis depends on factors such as the tumor type, stage, and the presence of any metastasis.
For women with low-risk disease, the 5-year survival rate is nearly 100%. This high survival rate is attributed to the efficacy of treatment approaches such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy in eliminating cancerous cells. Even for women with high-risk disease, the 5-year survival rate remains at approximately 90%, emphasizing the potential for successful treatment outcomes.
Importance Of Specialized Medical Care
Receiving care from a specialized medical team experienced in diagnosing and treating gestational trophoblastic tumor is crucial. Due to the rarity and unique nature of this condition, specialized care can ensure accurate diagnosis, seamless treatment planning, and comprehensive support throughout the journey.
Specialized medical professionals have the expertise and skills necessary to employ the most advanced diagnostic tools and develop individualized treatment plans. Their familiarity with the complexities of gestational trophoblastic tumor can provide patients with the confidence and reassurance they need to navigate their treatment and recovery successfully.
Survival Rates And Potential Spread To Other Organs
While the overall survival rates for gestational trophoblastic tumor are high, it is important to be aware that the disease can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, increasing the complexity of treatment. The most common site of metastasis is the lungs, although other organs may also be affected.
When gestational trophoblastic tumor spreads to other organs, it is considered more challenging to treat. However, with the appropriate medical care and ongoing advancements in treatment options, managing metastasis and achieving positive outcomes are still possible. Regular follow-up appointments and continued surveillance play a crucial role in detecting any potential spread and ensuring early intervention.
In conclusion, understanding gestational trophoblastic tumor is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals. Recognizing the symptoms, accessing specialized care, and exploring available treatment options are vital components of a successful diagnosis, treatment, and recovery process. By staying informed and proactive, individuals diagnosed with gestational trophoblastic tumor can approach their journey with confidence and optimism, supported by the latest advancements in medical knowledge and specialized care.
- Awareness of potential metastasis
- Focus on regular follow-up
- Emphasis on early intervention
💡
You may need to know these questions about gestational trophoblastic tumour
Is gestational trophoblastic disease a cancer?
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) encompasses a range of conditions involving abnormal cell growth in the tissue formed during pregnancy. While GTD is generally rare, it can manifest as both benign and malignant tumors. Hence, some forms of GTD can indeed be classified as cancerous, indicating the potential for malignancy within this unique group of diseases. It is essential for medical professionals to diagnose and differentiate between the various types of GTD to provide appropriate treatment and care for affected individuals.
What are the symptoms of a trophoblastic tumor?
Trophoblastic tumors can manifest through a variety of symptoms. One of the key indicators is abnormal vaginal bleeding, occurring either during or after pregnancy. Additionally, the presence of a uterus larger than expected for the given stage of pregnancy may serve as a sign of a trophoblastic tumor. Other symptoms to be vigilant about include severe nausea or vomiting during pregnancy, accompanied by high blood pressure, which may manifest through headaches and swelling of the extremities. If any of these symptoms arise, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What is the survival rate for gestational trophoblastic disease?
The survival rate for gestational trophoblastic disease is generally quite high. Even in cases of metastatic, low-risk GTD or non-metastatic, high-risk GTD, women still have a good prognosis. With intensive treatment that often involves a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and possibly surgery, cure rates range from 80% to 90%. Thus, despite the faster growth of GTD, the chances of survival remain promising for patients.
What causes trophoblastic tumor?
Trophoblastic tumors are primarily caused by abnormalities in fertilization processes. These tumors often arise when an empty egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell or when a normal egg cell is fertilized by two sperm cells. Age also plays a significant role, as gestational trophoblastic disease commonly occurs in women of childbearing age. These factors increase the risk of developing trophoblastic tumors.
Reference source
https://www.cancer.gov/types/gestational-trophoblastic/patient/gtd-treatment-pdq
https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/gestational-trophoblastic-disease-gtd/about
https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/gestational-trophoblastic-disease/symptoms-and-signs
https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-types/gestational-trophoblastic-disease/prognosis-and-survival