In a world where intimacy is an innate part of our lives, there exists a silent and stealthy invader that lurks in the shadows, ready to wreak havoc on our bodies.
Its name is Gonorrhea, a cunning and relentless bacterium, capable of causing catastrophic health issues if left unchecked.
Join us as we delve into the realm of safe sex practices and the importance of regular screenings, in an attempt to ward off this cunning foe and safeguard our well-being.
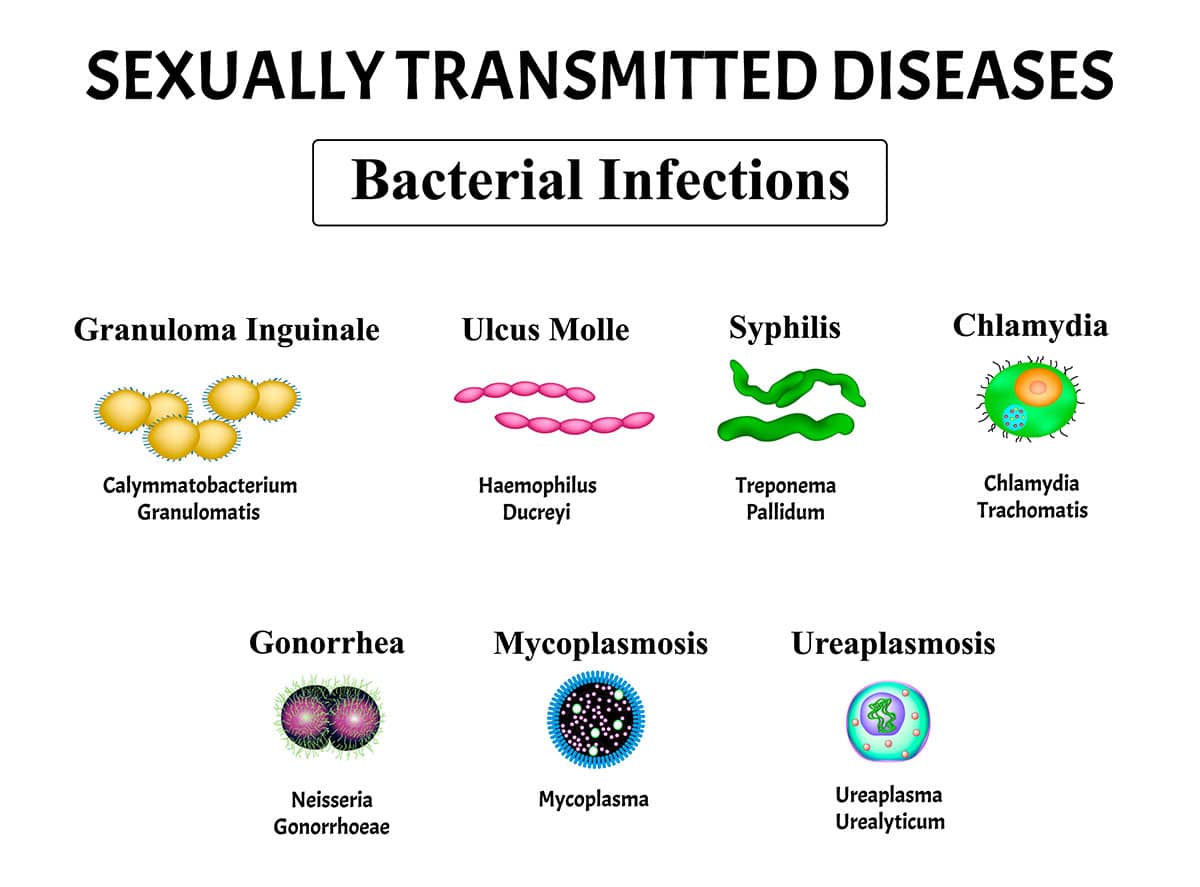
gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by infection with the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium.
It primarily infects the reproductive tract in women and the urethra in both men and women, but it can also infect other mucous membranes.
Approximately 1.6 million new gonococcal infections occurred in the US in 2018, with young people aged 15-24 being the most affected group.
It is the second most commonly reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the US.
Gonorrhea is transmitted through sexual contact with an infected partner and can be spread from mother to baby during childbirth.
It is important for individuals to get tested, as many cases are asymptomatic.
Prompt treatment with antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone, is recommended to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission.
It is also crucial for individuals to inform their recent sexual partners about their diagnosis so that they can seek treatment as well.
Safe sexual practices, such as using latex condoms consistently and correctly, can help reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission.
Abstinence or being in a monogamous relationship with an uninfected partner is the most effective way to prevent transmission.
Key Points:
- Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium.
- It primarily infects the reproductive tract in women and the urethra in both men and women.
- In 2018, there were approximately 1.6 million new gonococcal infections reported in the US, with the highest rates occurring in young people aged 15-24.
- It is the second most commonly reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the US.
- Gonorrhea is transmitted through sexual contact and can also be spread from mother to baby during childbirth.
- It is important for individuals to get tested, as many cases do not show symptoms.
gonorrhea – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Gonorrhea, also known as “the clap,” is believed to have originated in ancient Greece, where it was described in medical texts dating back to the 2nd century AD.
2. A little-known fact about gonorrhea is that it can infect various parts of the body, not just the reproductive organs. In rare cases, it can spread to the throat, eyes, rectum, and even joints, causing a condition known as gonococcal arthritis.
3. The World Health Organization estimates that approximately 78 million people worldwide are infected with gonorrhea each year. Surprisingly, many of these cases go undiagnosed and untreated due to the asymptomatic nature of the infection in some individuals.
4. Antibiotic-resistant strains of gonorrhea have become a growing concern in recent years. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States now lists drug-resistant gonorrhea as one of the most urgent threats to public health.
5. Gonorrhea has been a topic of interest throughout history, even making appearances in famous literary works. In Geoffrey Chaucer’s “The Canterbury Tales,” written in the 14th century, one character, known as the Pardoner, is described as having a face more pocked than “the sail of a small ship filled with holes after being attacked by an army of mice.” This description is believed to be a reference to the scarring caused by untreated gonorrhea.
Introduction To Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an infectious sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. It mainly targets the reproductive tract in women and the urethra in both men and women, but can also infect other mucous membranes. Globally, this disease poses a significant problem, affecting millions of people annually.
Prevalence Of Gonorrhea In The US
In the United States alone, approximately 1.6 million new cases of gonococcal infections occurred in 2018. Alarmingly, more than half of these cases were among young people aged 15-24. Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the US, highlighting the magnitude of the problem.
Modes Of Gonorrhea Transmission
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection that is primarily transmitted through sexual contact with an infected partner. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It is important to note that gonorrhea can also be spread from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth.
It is crucial to understand that any sexually active person can be at risk of contracting gonorrhea. However, teenagers, young adults, and African Americans have been reported to have the highest rates of infection.
Key points:
- Gonorrhea is transmitted through sexual contact with an infected partner.
- It can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
- Pregnant women infected with gonorrhea can pass it on to their babies during childbirth.
- Gonorrhea can affect people of all ages and backgrounds.
- However, sexually active teenagers, young adults, and African Americans are more frequently affected.
“Education is key in preventing the spread of gonorrhea and promoting safer sexual practices.”
Asymptomatic Gonorrhea
One of the concerning aspects of gonorrhea is that many individuals infected with the disease do not display any symptoms. This means that a person can pass on the infection to others unknowingly. Asymptomatic carriers increase the risk of unknowingly spreading the disease and contribute to the silent epidemic nature of gonorrhea.
- Gonorrhea: a sexually transmitted infection.
- Asymptomatic carriers: individuals infected with gonorrhea who do not show any symptoms.
- Silent epidemic: the spread of gonorrhea due to asymptomatic carriers unknowingly passing on the infection.
Symptoms Of Gonorrhea In Men
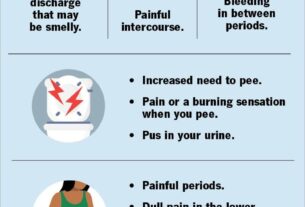
In men, symptoms of gonorrhea may include:
- dysuria (painful or difficult urination)
- urethral discharge (white, yellow, or greenish discharge from the penis)
- testicular or scrotal pain
These symptoms can be distressing and uncomfortable, prompting affected individuals to seek medical attention.
Symptoms Of Gonorrhea In Women
Women with gonorrhea may experience symptoms such as dysuria, increased vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, and lower abdominal pain. Unfortunately, these symptoms are often mistaken for other infections, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. This highlights the importance of regular sexual health check-ups and testing for sexually active individuals.
Complications Of Untreated Gonorrhea
Untreated gonorrhea can result in severe health complications.
- In women, it can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), characterized by abdominal pain, fever, abscesses, chronic pain, and an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Men with untreated gonorrhea are at risk of developing epididymitis, which can potentially lead to infertility.
- Additionally, if left untreated, gonorrhea can spread to the bloodstream, causing a life-threatening condition called disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).
It is crucial to seek timely medical treatment for gonorrhea to prevent these serious health consequences.
“Untreated gonorrhea can have serious health consequences. In women, it can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause abdominal pain, fever, abscesses, chronic pain, infertility, and an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy. Men with untreated gonorrhea can develop epididymitis, which can potentially lead to infertility. Furthermore, untreated gonorrhea can spread to the blood and cause a life-threatening condition known as disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).”
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): abdominal pain, fever, abscesses, chronic pain, infertility, increased risk of ectopic pregnancy
- Epididymitis: potential infertility
- Disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI): life-threatening condition
Prevention And Testing For Gonorrhea
Prevention of gonorrhea is crucial. Consistently and correctly using latex condoms can reduce the transmission risk. Abstaining from sex or being in a monogamous relationship with a tested and uninfected partner is the most effective way to prevent gonorrhea transmission. Testing for gonorrhea is recommended for sexually active individuals, especially those with symptoms or who have a partner with gonorrhea. Yearly screening is recommended for sexually active women younger than 25 years and older women with risk factors.
Treatment Of Gonorrhea
The recommended treatment for gonorrhea is a single 500 mg intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone. Alternative regimens are available if ceftriaxone cannot be used. However, antimicrobial resistance in gonorrhea is a growing concern, making it essential to use the appropriate medications to combat the infection. Individuals treated for pharyngeal gonorrhea should undergo a test-of-cure 7-14 days after treatment. Both men and women with gonorrhea should be retested three months after treatment, regardless of their partner’s treatment status.
Importance Of Partner Notification And Safe Sexual Practices
Important information:
- Individuals diagnosed with gonorrhea should inform their recent sex partners about their diagnosis.
- Open communication and honesty are essential to prevent further spread of the infection.
- It is recommended to avoid sexual activity until completing treatment and being symptom-free.
- Using latex condoms consistently and correctly can help reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission.
- Prompt medical attention is necessary if genital symptoms such as discharge, burning during urination, sores, or rash occur.
- Individuals with a recent sexual partner diagnosed with an STD should seek evaluation for their own sexual health.
- Regular testing and screening are vital in the prevention and control of gonorrhea.
It is crucial for individuals diagnosed with gonorrhea to inform their recent sex partners about their diagnosis so that they can seek treatment. Open communication and honesty are essential in preventing further spread of the infection. It is also recommended to avoid sexual activity until completing treatment and being symptom-free. Safe sexual practices, including using latex condoms consistently and correctly, can help reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission. Prompt medical attention is necessary if genital symptoms such as discharge, burning during urination, sores, or rash occur. Additionally, individuals who have had a recent sexual partner diagnosed with an STD should seek evaluation to ensure their own sexual health. Regular testing and screening are vital in the prevention and control of gonorrhea.
💡
You may need to know these questions about gonorrhea
What is one of the first signs of gonorrhea?
One of the earliest signs of gonorrhea is experiencing a burning sensation during urination. This uncomfortable symptom can serve as an indication that something is amiss and prompt individuals to seek medical advice. Another potential sign is the presence of a pus-like discharge from the genitals or rectum. Identifying these troubling signs or symptoms is crucial in order to receive appropriate treatment and prevent further complications.
What are the 5 symptoms of gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae, can present with several symptoms. Firstly, individuals may experience a watery, creamy, or greenish vaginal discharge. Secondly, there might be pain or burning sensations while urinating. Additionally, an increased urge to urinate more frequently could be observed. Moreover, heavier periods or spotting between periods may occur in some cases. Lastly, pain during penetrative vaginal sex can be another symptom of gonorrhea. It is important to note that these symptoms may vary or be absent in some individuals, and it is necessary to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Does gonorrhea go away?
Yes, gonorrhea can be cured with the appropriate treatment. It is crucial to complete the full course of medication prescribed by your healthcare provider to effectively treat the infection. It is important to note that while the medication can eliminate the infection, it cannot reverse any permanent damage that may have occurred as a result of the disease. Therefore, seeking timely treatment is essential in preventing potential long-term complications.
What is the main cause of gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is primarily caused by the transmission of the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae through sexual fluids during unprotected sexual contact. The bacterium can infiltrate the body via various routes, including the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus. It is this entry of the bacteria into the body’s mucous membranes through sexual fluids that serves as the main cause of gonorrhea.
Reference source
https://www.cdc.gov/std/gonorrhea/stdfact-gonorrhea-detailed.htm
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gonorrhea/symptoms-causes/syc-20351774
https://www.healthline.com/health/gonorrhea
https://www.cdc.gov/std/gonorrhea/stdfact-gonorrhea.htm