Have you ever wondered how women manage the symptoms of menopause?
Hormone replacement therapy, or HRT, might just be the answer.
This medication, containing female hormones, helps alleviate symptoms and prevent bone loss.
But, like any treatment, it comes with its own set of risks and considerations.
Step into the world of HRT, where individualized care and regular monitoring are vital for a balanced and healthy life.
hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a medication that contains female hormones used to replace estrogen during menopause.
It is primarily used to treat menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal discomfort.
HRT has been proven to prevent bone loss and reduce fractures in postmenopausal women.
There are risks associated with HRT, including an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, blood clots, and breast cancer.
The optimal dosage, duration, and route of administration of HRT should be individualized for each woman based on her symptoms, medical history, and risk factors.
Regular follow-up care and screenings, as well as healthy lifestyle choices, are recommended alongside HRT.
Nonhormonal approaches and alternative medications may also help manage menopausal symptoms.
It is important to have regular conversations with a doctor to determine if HRT is a suitable treatment option.
Key Points:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to replace estrogen during menopause
- HRT treats menopausal symptoms like hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal discomfort
- HRT prevents bone loss and reduces fractures in postmenopausal women
- Risks associated with HRT include heart disease, stroke, blood clots, and breast cancer
- The dosage, duration, and administration route of HRT should be personalized for each woman
- Regular follow-up care, screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices are recommended with HRT
hormone replacement therapy – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) was first introduced in the 1940s as a treatment for menopausal symptoms, but its origin can be traced back to ancient Egyptian times when women would consume licorice root to relieve menopausal discomfort.
2. Hormone replacement therapy is not limited to postmenopausal women; it is also sometimes used in transgender individuals to align their hormone levels with their gender identity.
3. The practice of hormone replacement therapy gained significant popularity after the publication of a landmark study called the Women’s Health Initiative in 2002, which raised some concerns about the risks and benefits of HRT.
4. Hormone replacement therapy has been found to have potential benefits beyond symptom relief in menopausal women. Studies suggest that it may lower the risk of developing osteoporosis, colorectal cancer, and heart disease.
5. While hormone replacement therapy primarily uses synthetic hormones to replace those declining with age or transitioning, compounded bioidentical hormones can also be custom-made in a compounding pharmacy to mimic the molecular structure of hormones naturally produced by the human body.
Introduction To Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
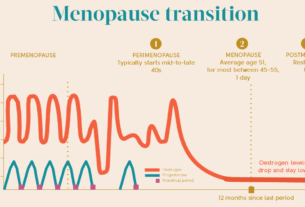
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a medication that contains female hormones and is used to replace estrogen during menopause. Menopause, which typically occurs between the ages of 45 to 55 in women, is a natural process where the ovaries stop producing eggs and estrogen levels decrease. This hormonal shift can lead to symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal discomfort.
The main goal of HRT is to alleviate these symptoms and improve the overall quality of life for women going through menopause.
Treating Menopausal Symptoms With HRT
One of the primary uses of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is to manage menopausal symptoms. These symptoms can be distressing and have a significant impact on a woman’s daily life. Hot flashes, characterized by sudden feelings of warmth and flushing of the skin, can be intense and disruptive. Night sweats can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and irritability. Vaginal discomfort, including dryness and thinning of the vaginal walls, can cause pain during intercourse and discomfort in daily activities.
HRT has been shown to be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of these symptoms. By replenishing estrogen levels in the body, HRT can help regulate body temperature and reduce the intensity of hot flashes. It can also restore moisture to the vaginal tissues, alleviating discomfort and improving overall vaginal health. By addressing these menopausal symptoms, HRT can enhance a woman’s overall well-being and improve her quality of life during this transitional phase.
HRT’s Benefits In Preventing Bone Loss
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has been proven to have significant benefits in preventing bone loss and reducing fractures in postmenopausal women. As estrogen levels decline during menopause, women become more susceptible to osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
Estrogen is crucial for maintaining healthy bone density, and HRT can help to replenish and maintain estrogen levels. Studies have shown that women who undergo estrogen therapy have a significantly reduced risk of developing osteoporosis and experiencing fractures. By preserving bone density, HRT can protect against fractures and minimize the impact of osteoporosis, ultimately promoting skeletal health and reducing the risk of mobility issues later in life.
Risks And Potential Side Effects Of HRT
While hormone replacement therapy (HRT) offers significant benefits, it is important to acknowledge and understand the potential risks and side effects associated with this treatment. Studies have shown that long-term use of HRT, particularly estrogen-progestin therapy (EPT), may increase the risk of certain health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, blood clots, and breast cancer.
It is essential for women considering HRT to have an open and honest conversation with their healthcare provider. Factors such as age, overall health, and individual risk factors should be taken into account when weighing the potential risks and benefits of HRT. For women with a history of heart disease, stroke, blood clots, or breast cancer, alternative treatment options may be recommended.
It is also worth noting that the risks associated with HRT may vary depending on the type of therapy. Estrogen-only therapy (ET), which is recommended for women who have had a hysterectomy, may carry a lower risk of certain health complications compared to EPT. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to assess individual risks and determine the most suitable form of HRT based on each woman’s unique circumstances.
💡
You may need to know these questions about hormone replacement therapy
What are the signs that you need hormone replacement therapy?
Hormone replacement therapy may be necessary when experiencing certain signs and symptoms. Hot flashes, characterized by sudden heat waves and sweating, are one of the common menopausal symptoms indicating the potential need for hormone replacement therapy. Night sweats, another menopausal symptom leading to excessive sweating during sleep, may also indicate the necessity for this treatment. Additionally, vaginal atrophy and dryness, fatigue, mood swings, sleeplessness, hair loss, and weight gain are further signs that hormone replacement therapy may be beneficial. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to assess individual symptoms accurately and determine the appropriate course of action.
What are the side effects of hormone replacement therapy?
Some potential side effects of hormone replacement therapy include tiredness and fatigue, which may be more pronounced while taking hormone therapy. Additionally, hormone therapy can potentially lead to digestive system issues, such as discomfort or irregularity. Other possible side effects may include experiencing menopausal symptoms, thinning of hair, changes in muscle and bone density, weight gain, headaches, and memory problems. Overall, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional about individualized risks and potential side effects before starting hormone replacement therapy.
What is the most common hormone replacement therapy?
The most common hormone replacement therapy is through the use of patches. These small adhesive patches are applied to the skin and slowly release hormones over time. They offer a convenient and consistent method of hormone delivery, as they eliminate the need for daily pill intake. Patches can be applied to different areas of the body and are often changed every few days or once a week, depending on the specific therapy. They provide a steady and controlled dosage, allowing for better hormone regulation. Additionally, patches minimize the risk of gastrointestinal side effects that may be associated with tablets, making them a preferred choice for many individuals.
What is given in hormone replacement therapy?
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) involves providing women with a supplement of hormones that are typically lost during menopause. It aims to alleviate the symptoms associated with this natural transition by including both estrogen and progesterone components. By mimicking the hormones produced by the human ovary, HRT helps to balance hormone levels and improve overall well-being during menopause.
Reference source
https://www.bodylogicmd.com/blog/what-are-the-signs-that-you-need-hormone-replacement-therapy/
https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/treatment/hormone-therapy/side-effects-women
https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/hormone-replacement-therapy-hrt/types-of-hormone-replacement-therapy-hrt/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493191/