In a world where stress permeates our daily lives, the silent menace of hypertension looms large and demands our attention.
With every beat, our hearts fight a quiet battle, silently struggling against the relentless pressure that threatens to consume them.
But fear not, as the quest to conquer this potentially life-threatening condition is underway.
Join us as we unravel the mysteries of hypertension, explore the risk factors, and discover the secrets to maintaining a healthy heart.
Prepare to dive into a world where knowledge is power and where victory over hypertension is within our grasp.
hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, occurs when the pressure in the blood vessels is too high.
It is common but can be serious if left untreated.
Risk factors for hypertension include age, genetics, being overweight or obese, lack of physical activity, high-salt diet, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Lifestyle changes such as eating a healthier diet, quitting tobacco, and being more active can help lower blood pressure.
Hypertension is diagnosed if both systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings on two different days are equal to or greater than 140/90 mmHg.
Treatment options include lifestyle changes and medication.
Hypertension can lead to complications such as heart damage, stroke, and kidney damage.
The prevalence of hypertension is higher in low- and middle-income countries, and the WHO supports efforts to reduce hypertension globally through initiatives like the Global Hearts Initiative.
Key Points:
- Hypertension is when blood pressure in the blood vessels is too high.
- It is common but can be serious if not treated.
- Risk factors include age, genetics, obesity, lack of exercise, high-salt diet, and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Lifestyle changes can help lower blood pressure, such as a healthier diet and increased physical activity.
- Diagnosis requires consistent high blood pressure readings.
- Treatment options include lifestyle changes and medication.
hypertension – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, affects more than 1 billion people worldwide, making it the most common cardiovascular disease globally.
2. Despite its prevalence, approximately 50% of people with hypertension are unaware of their condition, often leading to undiagnosed and uncontrolled high blood pressure.
3. A study conducted by the American Heart Association found that petting a dog or cat for just 10 minutes can lower blood pressure and reduce stress, helping to manage hypertension.
4. Drinking beetroot juice has been found to have a positive effect on blood pressure due to its high nitrate content, which enhances blood flow and widens blood vessels, ultimately promoting lower blood pressure levels.
5. Studies have shown a strong connection between excessive sodium intake and hypertension. However, only about 25% of the sodium we consume comes from the salt shaker, while the majority is hidden in processed and packaged foods.
What Is Hypertension?
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, occurs when the pressure in the blood vessels is consistently elevated, measuring at 140/90 mmHg or higher. This condition affects a significant number of individuals worldwide and is a major health concern.
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it around the body. When this force is consistently too high, it puts strain on the heart and blood vessels, potentially leading to serious health complications.
The silent nature of hypertension is one of its most alarming characteristics. Many people with hypertension do not experience any symptoms, which makes it difficult to detect unless regular blood pressure checks are performed. However, even without noticeable symptoms, hypertension can silently damage blood vessels and organs over time, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
Therefore, it is crucial to understand the consequences of untreated hypertension and the risk factors associated with the development of this condition.
Key points:
- Hypertension, or high blood pressure, occurs when the blood pressure consistently measures at 140/90 mmHg or higher.
- High blood pressure puts strain on the heart and blood vessels, potentially leading to serious health complications.
- Hypertension often has no symptoms, making regular blood pressure checks important for detection.
- Untreated hypertension can silently damage blood vessels and organs, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
Serious Consequences Of Untreated Hypertension
Although hypertension may seem like a common condition, it should not be taken lightly. If left untreated, it can lead to severe health problems and significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. The continuous strain on the heart caused by high blood pressure can gradually weaken the organ, ultimately leading to heart failure. This occurs when the heart becomes unable to efficiently pump blood through the body.
Furthermore, the increased pressure in the blood vessels can damage the arteries, contributing to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits build up, narrowing the arteries and increasing the risk of blood clots.
Untreated hypertension can also lead to kidney damage, as the excessive pressure in the blood vessels strains the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys. Over time, this can result in chronic kidney disease, potentially leading to kidney failure.
Additionally, hypertension is a significant risk factor for stroke, a life-threatening condition that occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted. Without prompt medical intervention, a stroke can cause permanent brain damage or even be fatal.
Considering the serious consequences of untreated hypertension, it becomes essential to identify the risk factors that contribute to the development of high blood pressure.
- Untreated hypertension can lead to heart failure.
- High blood pressure can cause atherosclerosis and increase the risk of blood clots.
- Kidney damage is a consequence of untreated hypertension.
- Hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke.
- Prompt medical intervention is crucial in the case of a stroke.
Risk Factors For Hypertension
Several factors increase an individual’s risk of developing hypertension. While some are modifiable and can be altered through lifestyle changes, others are non-modifiable and cannot be changed.
- Age is a non-modifiable risk factor, as the frequency of hypertension tends to increase with age.
- Genetics also play a role, as having a family history of hypertension raises the likelihood of developing the condition.
Certain lifestyle choices and habits also contribute to the development of hypertension.
- Being overweight or obese increases the risk significantly, as excess weight puts extra stress on the heart and blood vessels.
- Lack of physical activity is another risk factor, as regular exercise helps maintain a healthy cardiovascular system.
- Additionally, consuming a high-salt diet and regularly consuming excessive amounts of alcohol can lead to the development of hypertension.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention and early intervention. By identifying and targeting these factors, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their lifestyle choices and actively lower their blood pressure through various means, including adopting healthier habits and making necessary lifestyle changes.
Lifestyle Changes To Lower Blood Pressure
Fortunately, there are many lifestyle changes that individuals can make to lower their blood pressure and reduce the risk of hypertension. Implementing these changes not only helps manage blood pressure but also improves overall health and well-being.
One key change is adopting a healthier diet. This involves reducing sodium intake, as excessive salt consumption can contribute to high blood pressure. Instead, individuals should focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. These foods are naturally low in sodium, high in essential nutrients, and support a healthy cardiovascular system.
Regular physical activity also plays a crucial role in managing blood pressure. Engaging in aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week can help lower blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health. Weight loss, if necessary, can also lead to a significant reduction in blood pressure. Losing even a small amount of weight can have a positive impact on blood pressure readings.
Furthermore, quitting tobacco use is essential, as smoking or chewing tobacco can raise blood pressure and damage blood vessels. Reducing alcohol consumption or abstaining altogether is also recommended, as excessive alcohol intake can cause hypertension. By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals can take control of their blood pressure and minimize the risk of developing hypertension or its associated complications.
- Adopt a healthier diet with reduced sodium intake
- Engage in regular physical activity for at least 150 minutes per week
- Consider weight loss if necessary
- Quit smoking or chewing tobacco
- Reduce alcohol consumption or abstain altogether
Understanding Blood Pressure Measurements
To fully comprehend the diagnosis and management of hypertension, it is important to understand blood pressure measurements. Blood pressure is measured using two numbers: systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure is the higher number and represents the force exerted on the arteries when the heart contracts and pumps blood. The diastolic pressure is the lower number and represents the force on the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
Blood pressure is expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). The measurement is typically given as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure, with the normal range considered to be below 120/80 mmHg. Hypertension is diagnosed when an individual has two separate blood pressure readings, taken on different days, of 140/90 mmHg or higher.
Understanding these measurements allows healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and manage hypertension, ensuring appropriate treatment and prevention strategies are implemented.
Diagnosis Of Hypertension
Diagnosing hypertension involves carefully monitoring blood pressure readings over time. Rather than relying on a single measurement, healthcare professionals typically assess blood pressure on multiple occasions to determine a consistent pattern. This approach minimizes the potential for false readings caused by temporary factors such as stress.
When diagnosing hypertension, it is important to obtain two separate blood pressure readings, ideally taken on different days. If both measurements consistently indicate levels of 140/90 mmHg or higher, a diagnosis of hypertension is made. This approach ensures accuracy and reduces the likelihood of misdiagnosis.
Regular blood pressure monitoring is vital for the early detection and management of hypertension. It enables individuals to establish a baseline and identify any significant changes that warrant further investigation. Once hypertension is diagnosed, it is crucial to consider the modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors associated with this condition.
Modifiable And Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
When assessing an individual’s risk for hypertension, it is important to consider both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors.
Modifiable risk factors are those that can be altered through lifestyle changes and interventions, whereas non-modifiable risk factors cannot be changed.
Some modifiable risk factors for hypertension include consuming an unhealthy diet, leading a sedentary lifestyle, using tobacco products, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Unhealthy diets, specifically those high in sodium and low in fruits and vegetables, can contribute to high blood pressure. Lack of physical activity can also negatively impact blood pressure. Engaging in regular exercise can help control weight, reduce stress, and improve cardiovascular health, thus lowering the risk of developing hypertension.
Smoking and tobacco use increase blood pressure and damage blood vessel walls, making individuals more susceptible to hypertension. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to high blood pressure and other cardiovascular problems.
On the other hand, non-modifiable risk factors for hypertension include a family history of the condition, age over 65, and the presence of co-existing diseases such as diabetes or kidney disease.
Individuals who have close relatives with hypertension are more likely to develop the condition. Additionally, as individuals age, the risk of developing hypertension increases. Moreover, having certain chronic conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, or certain hormonal disorders can elevate the risk of hypertension.
Understanding these risk factors enables individuals to make informed decisions about their lifestyle choices, actively managing their blood pressure, and minimizing the risk of hypertension and its associated complications.
Symptoms And Complications Of Hypertension
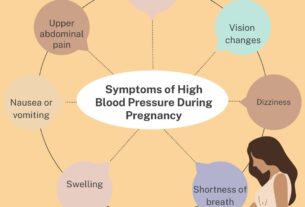
One of the most concerning aspects of hypertension is its silent nature. Most individuals with high blood pressure do not experience any notable symptoms, making it challenging to detect without routine blood pressure checks. However, very high blood pressure can lead to symptoms such as headaches, blurred vision, dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Nevertheless, the absence of symptoms should not be misconstrued as an indication of good health. Even in the absence of noticeable symptoms, hypertension can silently cause damage to blood vessels, the heart, and organs throughout the body.
It is essential to acknowledge the potential complications that can arise from untreated hypertension. Persistently high blood pressure can severely strain the heart and blood vessels, leading to various health conditions. Some potential complications include:
- Kidney disease: The excessive pressure in the blood vessels can damage the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to function properly.
- Heart disease: Hypertension can contribute to the development of heart disease, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure. The increased pressure in the blood vessels can cause damage and narrowing, limiting blood flow to the heart and increasing the risk of heart-related complications.
- Stroke: Untreated hypertension significantly increases the risk of stroke, a life-threatening condition that occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted.
By understanding these potential complications, individuals are motivated to seek timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment for hypertension.
“Even in the absence of symptoms, hypertension can silently cause damage to the body.”
- Silent nature of hypertension
- Symptoms of very high blood pressure
- Potential complications of untreated hypertension
Treatment Options For Hypertension
The management of hypertension involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, the use of medication to control blood pressure. The goals of treatment are to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of associated health complications.
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing and preventing hypertension. These changes include adopting a healthier diet, limiting sodium intake, and incorporating more fruits and vegetables into one’s daily meals. Regular physical activity, such as engaging in aerobic exercises, promotes cardiovascular health and helps lower blood pressure. If necessary, losing weight through a combination of dietary changes and exercise can significantly reduce blood pressure readings. Additionally, eliminating tobacco use and reducing alcohol consumption are essential lifestyle modifications to manage hypertension effectively.
In some cases, lifestyle changes may not be sufficient to control blood pressure. In such instances, healthcare professionals may prescribe medication to complement these lifestyle modifications. Several types of medications are commonly used to treat hypertension, including ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics. The specific medication prescribed depends on the individual’s unique health characteristics and considerations.
It is important to note that the goals for blood pressure control may vary depending on other concomitant health conditions. Individuals with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or a high risk for cardiovascular disease generally have a lower blood pressure target of less than 130/80 mmHg. Regular monitoring, adjustment of medication, and collaboration with healthcare professionals are critical to achieving and maintaining the appropriate blood pressure levels for each individual.
Global Efforts To Combat Hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a significant global health concern, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. To address this issue, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S. CDC) launched the Global Hearts Initiative. This initiative aims to strengthen the prevention and control of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, worldwide.
As part of the Global Hearts Initiative, the WHO and U.S. CDC have developed the HEARTS technical package. This package consists of six modules that provide guidance on improving cardiovascular health. These modules focus on areas such as health system strengthening, the use of standardized treatment protocols, quality improvement methods, and information systems for monitoring and evaluation.
Since its launch in 2017, the initiative has yielded promising results. Over 7.5 million individuals in 31 low- and middle-income countries have received protocol-based hypertension treatment through person-centered models of care. These efforts demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of implementing standardized hypertension control programs, even in resource-limited settings.
In conclusion, hypertension is a prevalent condition with potentially serious health consequences if left untreated. Understanding the risk factors and complications associated with hypertension is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding tobacco and alcohol use, can address modifiable risk factors. Additionally, non-modifiable risk factors, including age, genetic predisposition, and existing health conditions, should be taken into consideration. By implementing lifestyle changes, regularly monitoring blood pressure, and, when necessary, utilizing appropriate medication, individuals can effectively manage hypertension and decrease the risk of associated complications.
Furthermore, the Global Hearts Initiative serves as a powerful example of the importance of addressing hypertension globally. Through education, awareness, and timely interventions, we can combat the silent threat of high blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health worldwide.
- Hypertension is a global health concern
- Prevalence is high in low- and middle-income countries
- World Health Organization (WHO) and U.S. CDC launched the Global Hearts Initiative
- Initiative aims to strengthen prevention and control of cardiovascular diseases
- HEARTS technical package consists of six modules
- Modules focus on key areas such as health system strengthening, treatment protocols, quality improvement, and information systems
- Initiative has shown promising results
- Over 7.5 million people in 31 countries received hypertension treatment
- Promotes feasibility and effectiveness of standardized hypertension control programs
- Hypertension can lead to serious health consequences if untreated
- Understanding risk factors and complications is crucial
- Modifiable risk factors include unhealthy diets, lack of physical activity, tobacco and alcohol use
- Non-modifiable risk factors include age, genetic predisposition, and existing health conditions
- Lifestyle modifications and medication can effectively manage hypertension
- Global Hearts Initiative highlights the importance of addressing hypertension worldwide
- Education, awareness, and timely interventions are crucial.
💡
You may need to know these questions about hypertension
What is the main cause of hypertension?
The primary cause of hypertension is a combination of unhealthy lifestyle choices and certain health conditions. Lack of regular physical activity can contribute to the development of high blood pressure over time. Additionally, conditions like diabetes and obesity can significantly increase the risk of hypertension. These factors can lead to the narrowing of blood vessels, putting extra strain on the heart and ultimately causing high blood pressure.
How do people cope with hypertension?
People cope with hypertension by adopting a range of strategies to manage their condition. One effective method is to embrace a heart-healthy diet that includes reducing salt intake. Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight or striving to lose weight can greatly assist in managing hypertension. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding smoking are essential steps in controlling the condition. Lastly, ensuring an ample duration of restful sleep, ideally between 7 to 9 hours daily, is crucial in coping with hypertension and promoting overall well-being.
How does hypertension make you feel?
Hypertension can have a profound impact on one’s well-being. People with high blood pressure might experience persistent headaches, feelings of anxiety, and shortness of breath, which can significantly affect their day-to-day life. Additionally, nosebleeds, palpitations, and a pulsating sensation in the neck are indications of this condition. It is important to note that these symptoms often emerge at a later stage, emphasizing the significance of regular annual check-ups for all adults to monitor their blood pressure and take necessary steps to maintain their health.
What are 10 warning signs of high blood pressure?
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a medical condition that often remains silent with no obvious symptoms. However, there are warning signs that can indicate elevated blood pressure levels. These signs may include severe headaches, nosebleeds, fatigue or confusion, vision problems, chest pain, difficulty breathing, irregular heartbeat, and blood in the urine. It is crucial to note that these symptoms can also be related to other health issues, so it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. Regular check-ups and monitoring blood pressure levels can help in detecting and managing high blood pressure effectively.
Reference source
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/about.htm
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20373417
https://www.riversideonline.com/patients-and-visitors/healthy-you-blog/blog/w/what-are-the-symptoms-of-high-blood-pressure