Imagine the exhilaration of bringing life into the world, the anticipation and joy that fill the air.
But amidst this precious moment, a sudden wave of concern emerges – the possibility of hypertonic uterine contractions.
In the world of labor induction, this phenomenon can pose serious risks.
Yet fear not, for medical advancements and alternative methods offer hope and solutions.
Join us as we uncover the complexities and explore the ways in which this condition can be effectively managed.
hypertonic uterine contraction
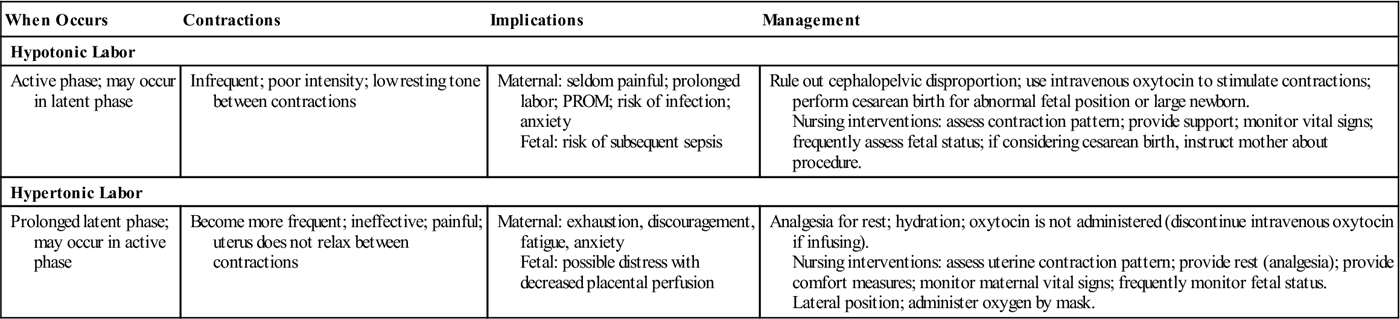
Hypertonic uterine contraction, which is also known as uterine hyperstimulation, can occur as a complication of labor induction.
It is characterized by frequent contractions (more than five in 10 minutes) or contractions lasting more than two minutes.
This condition can result in fetal heart rate abnormalities, uterine rupture, or placental abruption.
Drugs such as Misoprostol used for peptic ulcers can cause uterine hyperstimulation when used to induce labor.
However, there are treatment options available for uterine hyperstimulation, including the use of Terbutaline, which is commonly used to treat this condition.
Prostaglandin E2 can also be administered before labor to minimize the risk of hyperstimulation and its effects on the fetal heart rate.
Tocolytic treatment with β2-adrenergic drugs has been used to stabilize uterine contractions and lower fetal heart rate.
Additionally, using a balloon catheter for labor induction instead of Prostaglandin E2 can reduce the risk of uterine hyperstimulation and its impact on the fetal heart rate.
Key Points:
- Hypertonic uterine contraction is a complication of labor induction.
- It is characterized by frequent or prolonged contractions.
- It can lead to fetal heart rate issues, uterine rupture, or placental abruption.
- Certain drugs, such as Misoprostol, can cause this condition when used for labor induction.
- Treatment options include the use of Terbutaline and Prostaglandin E2.
- Tocolytic treatment with β2-adrenergic drugs can stabilize uterine contractions and lower fetal heart rate.
- Using a balloon catheter for labor induction can reduce the risk of uterine hyperstimulation and its impact on fetal heart rate.
hypertonic uterine contraction – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Hypertonic uterine contractions can sometimes result in a condition called “tetanic contraction,” where the muscle fibers remain rigid and completely fail to relax.
2. In some cases, the use of oxytocin (a hormone that induces uterine contractions) can lead to hypertonic contractions, causing distress for both the mother and baby during labor.
3. Hypertonic uterine contractions are more commonly observed in first-time mothers, as their uterine muscles may be less toned and more prone to excessive contractions.
4. Some natural remedies, such as warm baths and relaxation techniques, have been found to be effective in relieving hypertonic uterine contractions and promoting a more optimal labor process.
5. Hypertonic contractions can impede the progress of labor and potentially lead to complications like decreased oxygen supply to the baby or uterine rupture, necessitating prompt medical intervention.
Definition And Causes Of Hypertonic Uterine Contraction
Hypertonic Uterine Contraction:
Hypertonic uterine contraction, also known as uterine hyperstimulation, is a condition that can occur as a complication of labor induction. It is characterized by abnormally frequent contractions, with more than five contractions occurring within a 10-minute period, or contractions lasting more than two minutes. This excessive uterine activity can put both the mother and the fetus at risk.
Causes of Hypertonic Uterine Contraction:
- The use of the drug Misoprostol, typically used for the treatment of peptic ulcers but also used off-label to induce labor, is a common cause of hypertonic uterine contraction. Misoprostol can lead to hyperstimulation of the uterus, resulting in the onset of strong and frequent contractions.
- Excessive use of synthetic oxytocin can contribute to hypertonic uterine contraction.
- Dehydration and uterine malformations are also factors that can contribute to this condition.
Bullet points are used to provide clear and concise information, while bold highlights the important points. A blockquote is not necessary for this passage.
Frequency And Duration Of Contractions In Uterine Hyperstimulation
In cases of hypertonic uterine contraction, the frequency and duration of contractions are significantly increased compared to normal labor. Contractions occur more frequently than usual, with more than five contractions happening within a 10-minute period. This excessive uterine activity can lead to increased stress on the mother’s body and cause difficulties in the progression of labor.
Furthermore, the duration of contractions in hypertonic uterine contraction is prolonged, lasting more than two minutes. These prolonged contractions can result in inadequate relaxation of the uterine muscle between contractions, leading to reduced blood flow to the placenta and an increased risk of fetal distress.
Key points:
- Frequency of contractions increases significantly
- More than five contractions within a 10-minute period
- Prolonged contractions lasting more than two minutes
- Inadequate relaxation of uterine muscle between contractions
- Reduced blood flow to the placenta
- Increased risk of fetal distress
“Hypertonic uterine contraction can lead to increased stress on the mother’s body and difficulties in labor progression. Prolonged contractions can also result in reduced blood flow to the placenta and an increased risk of fetal distress.”
Potential Complications Of Hypertonic Uterine Dysfunction
Hypertonic uterine dysfunction can have several potential complications that pose risks to both the mother and the fetus. One of the most concerning complications is fetal heart rate abnormalities. The excessive uterine contractions can cause changes in the fetal heart rate pattern, such as decelerations or prolonged decelerations, indicating fetal distress.
Another significant complication is uterine rupture, which can occur due to the excessive force exerted by the hyperstimulated uterus. Uterine rupture is a life-threatening condition that requires emergency intervention and poses serious risks to both the mother and the fetus.
Additionally, hypertonic uterine dysfunction can also lead to placental abruption, a condition where the placenta separates from the uterine wall prematurely. Placental abruption can cause severe bleeding and deprive the fetus of oxygen and nutrients, potentially leading to fetal distress, preterm birth, or even fetal demise.
It is crucial to recognize and manage hypertonic uterine contraction promptly to minimize the potential complications and ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Misoprostol And Its Association With Uterine Hyperstimulation
One of the contributing factors to uterine hyperstimulation is the use of Misoprostol, a medication primarily used for peptic ulcer treatment. Misoprostol is also used off-label to induce labor due to its ability to stimulate uterine contractions. However, the use of Misoprostol for labor induction carries the risk of hyperstimulation, especially when administered in high doses or at frequent intervals.
The prostaglandin-like properties of Misoprostol can cause uterine hyperactivity, leading to excessive uterine contractions. The hyperstimulated uterus can result in inadequate relaxation between contractions, compromising blood flow to the placenta and increasing the risk of fetal distress.
It is essential for healthcare providers to exercise caution when using Misoprostol for labor induction and closely monitor the mother and the fetus for signs of hyperstimulation. Proper dosing and timing are crucial to minimize the risks associated with uterine hyperstimulation.
- Contributing factor: Use of Misoprostol
- Misoprostol is primarily used for peptic ulcer treatment
- Off-label use for inducing labor
- Risk of hyperstimulation with high doses or frequent intervals
- Prostaglandin-like properties cause uterine hyperactivity
- Hyperstimulated uterus leads to inadequate relaxation between contractions
- Compromised blood flow to placenta and increased risk of fetal distress
- Healthcare providers must exercise caution and monitor for signs of hyperstimulation
- Proper dosing and timing crucial to minimize risks
Treatment Options For Uterine Hyperstimulation
When hypertonic uterine contraction occurs, prompt intervention is necessary to manage the condition and minimize potential complications. One commonly used treatment option is the administration of terbutaline, a medication that acts as a uterine relaxant. Terbutaline helps to reduce uterine activity, allowing for better blood flow to the placenta and reducing the risk of fetal distress.
Another preventive measure for hyperstimulation is the administration of Prostaglandin E2 before labor induction. Prostaglandin E2 helps to prime the cervix and prepare it for labor while minimizing the risk of hyperstimulation and its effects on the fetal heart rate. This proactive approach ensures a smoother labor process while protecting the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
In cases where uterine contractions are difficult to control, tocolytic treatment with β2-adrenergic drugs may be necessary. β2-adrenergic drugs, such as ritodrine or nifedipine, act as uterine relaxants and can help stabilize the contractions, reducing the risk of complications.
Moreover, using a balloon catheter for labor induction instead of Prostaglandin E2 has shown promising results in reducing the risk of uterine hyperstimulation and its impact on the fetal heart rate. The balloon catheter helps to gradually dilate the cervix and induce labor, providing a safer alternative for women at risk of hypertonic uterine contraction.
Minimizing Risk To Fetal Heart Rate In Uterine Hyperstimulation
When dealing with hypertonic uterine contraction, protecting the fetal heart rate is of utmost importance. Continuous monitoring of the fetal heart rate is essential to detect any abnormalities or signs of distress promptly. If significant changes in the fetal heart rate pattern occur, immediate interventions may be needed to mitigate the risks.
Healthcare providers should closely monitor the progress of labor and adjust interventions accordingly. The goal is to maintain uterine contractions within a safe range and ensure proper relaxation between contractions to allow adequate blood flow to the placenta.
By using appropriate medications and treatment options, such as terbutaline or Prostaglandin E2, healthcare providers can manage hypertonic uterine contraction effectively, minimizing the risks to the fetal heart rate and ensuring a safe and successful delivery.
In conclusion, hypertonic uterine contraction or uterine hyperstimulation can occur as a complication of labor induction. It is characterized by frequent and prolonged contractions, posing risks to the mother and the fetus. Prompt identification, proper treatment, and close monitoring can help manage this condition effectively and minimize the potential complications. By using alternative methods, such as balloon catheter induction, and taking preventive measures, healthcare providers can ensure a safe labor process while protecting the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
💡
You may need to know these questions about hypertonic uterine contraction
How do you manage hypertonic uterine contractions?
Managing hypertonic uterine contractions can be a challenging task. However, a multimodal approach can be adopted for effective management. Firstly, repositioning the patient can help alleviate the contractions by promoting better blood flow to the uterus. Additionally, short-acting tocolytics such as terbutaline administered intravenously can be utilized to relax the uterine muscles. If oxytocin is being used, discontinuing its administration may also be beneficial. Finally, providing analgesics can provide pain relief and potentially aid in reducing uterine contractions. It is important to tailor the management approach to each individual case to ensure the best possible outcome.
What is hypotonic uterine contraction?
Hypotonic uterine contractions refer to a condition during labor where the strength and frequency of contractions are insufficient to effectively progress the birthing process. This pattern of inadequate uterine contractions often occurs during the active phase of labor and can lead to prolonged or protracted delivery. When the uterine contractions are weak and unable to cause cervical dilation, effacement, and fetal descent, it becomes challenging for the delivery to occur in a timely manner.
What is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic uterine contractions?
Hypotonic uterine contractions refer to contractions that are weak or infrequent during labor. These contractions may not provide enough force to effectively progress labor, leading to prolonged delivery. On the other hand, hypertonic uterine contractions involve contractions that are excessively strong or close together. These intense contractions can cause distress for both the baby and the mother, potentially resulting in complications or the need for medical intervention.
What is a hypertonic phase of labor?
During the hypertonic phase of labor, contractions occur more frequently than every 2 minutes, potentially jeopardizing both the fetus and the placenta. These intense and rapid contractions can lead to fetal distress and pose a risk for placental abruption, highlighting the need for medical intervention to ensure the well-being of both mother and baby. Medical professionals closely monitor the progress of labor during this phase, employing appropriate measures to manage and mitigate the potential complications associated with hypertonic contractions.
Reference source
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterine_hyperstimulation
https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/abnormalities-and-complications-of-labor-and-delivery/protracted-labor
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33232073/
https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/abnormalities-and-complications-of-labor-and-delivery/protracted-labor