Imagine waking up one day and feeling completely drained, as if all your energy has been sapped away.
Your body feels weak, your emotions erratic, and your weight steadily climbing despite your best efforts.
This bewildering condition, known as hypopituitarism, is a rare yet fascinating disorder that disrupts the delicate balance of hormones in our bodies.
Join us as we delve into the mysteries of this condition and explore the challenges faced by those living with it.
hypopituitarism
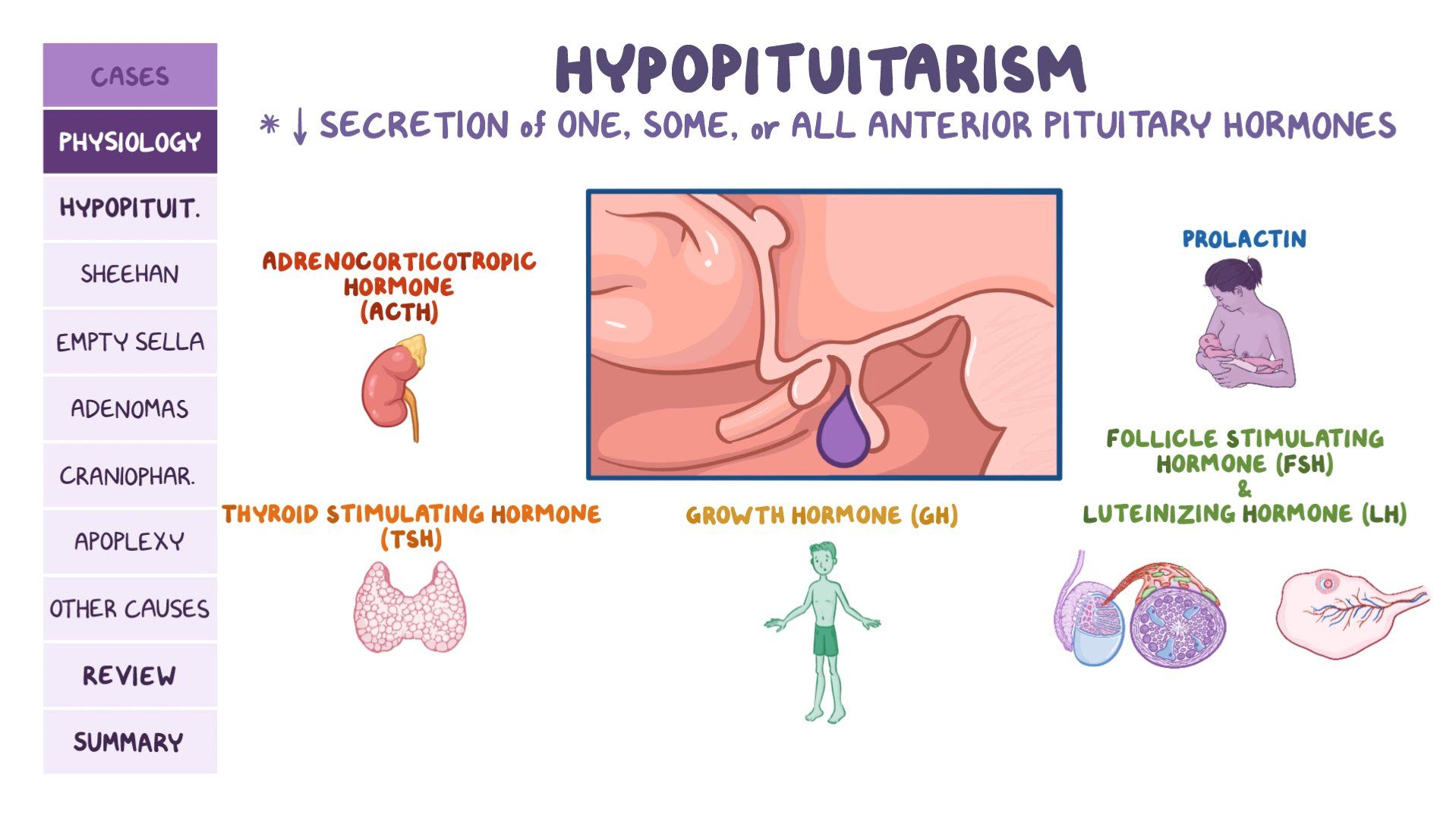
Hypopituitarism is a rare condition where the pituitary gland does not produce enough hormones.
It can affect various bodily functions, resulting in symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, changes in body fat, and infertility.
Treatment typically involves hormone replacement therapy.
Some important facts about hypopituitarism include the potential for severe tiredness, low blood pressure, and confusion.
Symptoms that occur suddenly or are accompanied by a severe headache or changes in vision could indicate a medical emergency called pituitary apoplexy.
Common causes of hypopituitarism include tumors, head injuries, radiation treatment, and genetic factors.
It is worth noting that diseases or tumors of the hypothalamus can also lead to hypopituitarism.
Key Points:
- Hypopituitarism is a rare condition characterized by insufficient hormone production in the pituitary gland.
- Symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, changes in body fat, and infertility.
- Treatment involves hormone replacement therapy.
- Severe tiredness, low blood pressure, and confusion are potential symptoms.
- Pituitary apoplexy is a medical emergency associated with sudden symptoms, severe headache, or vision changes.
- Common causes include tumors, head injuries, radiation treatment, genetic factors, and hypothalamic diseases or tumors.
hypopituitarism – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Hypopituitarism is a rare condition that occurs when the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, fails to produce adequate amounts of one or more hormones.
2. The most common cause of hypopituitarism is a pituitary tumor, which can compress the gland and disrupt hormone production.
3. Hypopituitarism can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, low blood pressure, infertility, and decreased libido.
4. In some cases, hypopituitarism can be caused by conditions beyond tumors, such as head trauma, infections, radiation therapy, or autoimmune diseases.
5. Treatment for hypopituitarism usually involves hormone replacement therapy to supplement the deficient hormones and manage symptoms.
1. Overview Of Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is a rare condition characterized by the insufficient production of hormones by the pituitary gland. This gland, situated at the base of the brain, is responsible for the regulation of various bodily functions. The pituitary gland, often compared in size to a kidney bean, is part of the endocrine system, which includes other glands like the thyroid and adrenal glands.
When the pituitary gland fails to produce enough hormones, it can have a significant impact on crucial bodily functions, including growth, blood pressure regulation, and fertility.
While hypopituitarism is a relatively uncommon condition, its effects can be far-reaching. The symptoms experienced by individuals with hypopituitarism vary depending on which hormones are deficient. Fatigue, muscle weakness, changes in body fat distribution, loss of interest in activities, and infertility are among the potential symptoms.
Furthermore, both men and women may experience specific symptoms related to hormonal imbalances: hot flashes, irregular periods, loss of pubic hair, and erectile dysfunction. Other symptoms can include mood changes, tiredness, weight gain, dry skin, constipation, and sensitivity to cold.
2. Importance Of The Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is a crucial component in maintaining the balance of hormones in the body. Often referred to as the “master gland,” it controls the functions of other endocrine glands. These glands communicate with each other to ensure that hormones are produced in the right quantities and at the appropriate times.
The pituitary gland has a significant role in the production and regulation of essential hormones. Some of these hormones include:
- Growth hormone (GH)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Prolactin (PRL)
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
These hormones are responsible for various bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, reproduction, and the maintenance of body fluids.
However, when the pituitary gland fails to function properly, it can lead to disruptions in the hormonal balance and the development of hypopituitarism.
3. Functions Impacted By Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism has a wide-ranging impact on various bodily functions due to the significant role played by the pituitary gland in hormone production. Some key effects of hypopituitarism include:
-
Growth hormone deficiency: In children, this can lead to stunted growth and delayed sexual maturation. In adults, it may result in a decrease in bone density and an increased risk of fractures.
-
Blood pressure regulation: Insufficient production of ACTH, the hormone that stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol, can cause low blood pressure, fatigue, and frequent infections.
-
Fertility and reproductive functions: In women, deficient levels of FSH and LH can lead to irregular periods or even amenorrhea (absence of menstruation). In men, it can result in decreased testosterone levels, causing infertility, erectile dysfunction, and reduced sexual desire.
-
Body fluid regulation: Inadequate production of ADH can lead to frequent urination, excessive thirst, and dehydration.
It is essential to note that the impact of hypopituitarism can vary from person to person, and treatment options are available to manage specific symptoms and hormone imbalances.
- Hypopituitarism affects a multitude of bodily functions due to the wide range of pituitary gland hormones.
- Growth hormone deficiency leads to stunted growth and delayed sexual maturation in children and decreased bone density and increased fracture risk in adults.
- Insufficient production of ACTH causes low blood pressure, fatigue, and frequent infections.
- In women, deficient levels of FSH and LH can result in irregular periods or even amenorrhea.
- In men, it can cause decreased testosterone levels, leading to infertility, erectile dysfunction, and reduced sexual desire.
- Inadequate production of ADH causes frequent urination, excessive thirst, and dehydration.
4. Common Symptoms Of Hypopituitarism
The symptoms experienced by individuals with hypopituitarism depend on which hormones are deficient. However, some common symptoms can help identify the condition.
- Fatigue is a prevalent symptom, often accompanied by muscle weakness and changes in body fat distribution.
Emotional and psychological changes may also occur, including a loss of interest in activities and mood disturbances.
Infertility is a significant concern, manifesting as irregular periods and hot flashes in women, and loss of pubic hair and erectile dysfunction in men.
Other symptoms may include tiredness, weight gain, dry skin, constipation, and sensitivity to cold.
It is essential to note that these symptoms can overlap with other medical conditions, so it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Changes in body fat distribution
- Loss of interest in activities
- Mood disturbances
- Infertility (irregular periods and hot flashes in women, loss of pubic hair and erectile dysfunction in men)
- Tiredness
- Weight gain
- Dry skin
- Constipation
- Sensitivity to cold
5. Importance Of Replacing Missing Hormones
Treatment for hypopituitarism involves replacing the hormones that are deficient. The specific hormone replacement therapy required will depend on the individual’s hormone levels and the functions affected.
For example, individuals with growth hormone deficiency may need daily injections of synthetic growth hormone. Those experiencing adrenal insufficiency may require cortisol replacement therapy. Hormone replacement therapy can help alleviate symptoms, restore hormonal balance, and improve quality of life for individuals with hypopituitarism.
Close monitoring of hormone levels and symptoms is necessary throughout treatment to ensure optimal hormone replacement. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to adjust doses as needed.
6. Recognizing Pituitary Apoplexy As A Medical Emergency
Hypopituitarism leading to Pituitary Apoplexy
In some cases, hypopituitarism can lead to a medical emergency known as pituitary apoplexy. This condition occurs when there is bleeding into the pituitary gland, resulting in sudden symptoms that require immediate medical attention.
Individuals experiencing the following symptoms should seek urgent medical care:
- severe tiredness
- sudden low blood pressure
- frequent infections
- nausea
- vomiting
- abdominal pain
- confusion
- changes in vision
- drop in blood pressure
These symptoms can indicate pituitary apoplexy, which necessitates prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent further complications.
It is important to note that people experiencing these symptoms should not delay seeking medical help as pituitary apoplexy can be a life-threatening condition.
7. Common Causes Of Hypopituitarism
Various causes contribute to the development of hypopituitarism, including:
-
Pituitary tumors: These tumors commonly disrupt the normal function of the pituitary gland.
-
Hypothalamic tumors: Tumors located in the hypothalamus, just above the pituitary gland, can also lead to hypopituitarism.
-
Head injuries: Traumatic head injuries can result in hypopituitarism.
-
Brain surgery: Surgical procedures involving the brain can contribute to the development of hypopituitarism.
-
Radiation treatment: Radiation therapy targeting the head or neck region is another potential cause.
-
Stroke or brain bleeding: Impairments in blood flow to the brain or bleeding within the brain can result in hypopituitarism.
-
Certain medications: Some medications can impact the function of the pituitary gland and lead to hypopituitarism.
-
Inflammation of the pituitary gland: Conditions characterized by inflammation of the pituitary gland can cause hypopituitarism.
-
Infections of the brain: Certain brain infections can contribute to the development of hypopituitarism.
-
Systemic diseases: Diseases that affect multiple organs of the body may also be a factor.
-
Significant blood loss during childbirth: Excessive blood loss during childbirth can lead to hypopituitarism.
-
Genetic factors: In some cases, genetic factors play a role in the development of hypopituitarism.
Diagnosing the underlying cause of hypopituitarism is crucial for effective treatment and management.
- It is essential to identify the cause to provide appropriate treatment.
“Diagnosing the underlying cause of hypopituitarism is crucial for effective treatment and management.”
8. Role Of Tumors And Diseases Of The Hypothalamus
Tumors or diseases of the hypothalamus, a region located above the pituitary gland, can significantly impact the development of hypopituitarism.
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating the function of the pituitary gland by releasing hormones that influence its activity.
Tumors in the hypothalamus can disrupt the communication between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland, impacting the production and regulation of hormones.
Such disruptions can ultimately lead to the development of hypopituitarism.
It is important for healthcare professionals to evaluate both the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland when diagnosing and managing hypopituitarism.
- Tumors or diseases of the hypothalamus can impact hypopituitarism.
- The hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland through hormones.
- Disruptions in communication between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland can lead to hypopituitarism.
- Healthcare professionals should evaluate both the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland in diagnosing and managing hypopituitarism.
9. Other Factors Contributing To Hypopituitarism
In addition to pituitary tumors and hypothalamic diseases, there are other factors that can contribute to the development of hypopituitarism. These include:
- Brain injuries: Accidents or trauma can disrupt the normal function of the pituitary gland and lead to hormonal deficiencies.
- Radiation therapy: Especially when targeted to the head or neck, it can damage the pituitary gland, impairing its ability to produce and regulate hormones effectively.
- Brain surgeries: Surgeries performed near the pituitary gland can cause damage and result in hypopituitarism.
- Certain medications: Medications used for chemotherapy or immunosuppression in autoimmune disorders can impact pituitary function if used over a long period.
- Genetic factors: Some individuals may be born with certain conditions that make them more prone to hormonal deficiencies.
Note: It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
10. Conclusion And Treatment Options
Hypopituitarism is a rare condition characterized by the insufficient production of hormones by the pituitary gland. It can have far-reaching effects on various bodily functions, including growth, blood pressure regulation, and fertility.
Identifying the symptoms of hypopituitarism is crucial for obtaining an accurate diagnosis. Treatment options typically involve hormone replacement therapy, which aims to restore hormonal balance and alleviate symptoms. Close monitoring by healthcare professionals is necessary to ensure optimal hormone replacement and adjust doses as needed.
In cases of severe symptoms occurring suddenly, such as those accompanied by a bad headache, changes in vision, confusion, or a drop in blood pressure, immediate medical attention is necessary, as it may indicate pituitary apoplexy.
Understanding the common causes of hypopituitarism can aid in diagnosing and managing the condition effectively. These causes include:
- Pituitary tumors
- Head injuries
- Radiation therapy
- Genetic factors
In conclusion, hypopituitarism is a complex condition that requires proper medical management to restore hormonal balance and improve quality of life for affected individuals. With appropriate treatment and support, individuals with hypopituitarism can lead fulfilling and healthy lives.
💡
You may need to know these questions about hypopituitarism
What happens when you have hypopituitarism?
Hypopituitarism, an underactive pituitary gland, leads to a deficiency of one or more pituitary hormones, giving rise to various symptoms. Since the manifestation of hypopituitarism depends on the specific hormone deficiency, individuals may experience a range of effects. This can include stunted growth, hindered fertility, sensitivity to cold temperatures, fatigue, and the inability to produce breast milk. It is crucial to address these hormone imbalances to mitigate the adverse impacts on a person’s overall health and well-being.
What is the most common cause of hypopituitarism?
The most common cause of hypopituitarism is pituitary adenoma, a tumor that arises in the pituitary gland. This tumor can disrupt the normal functioning of the gland, leading to a deficiency in one or more hormone levels. Additionally, complications from surgery or radiation therapy used to treat pituitary adenoma can also result in the development of hypopituitarism. These procedures may inadvertently damage the pituitary gland, impairing its ability to produce and release hormones effectively.
What is the life expectancy of someone with hypopituitarism?
Individuals with hypopituitarism have a normal life expectancy with the appropriate lifelong treatment. Hypopituitarism is a condition that necessitates ongoing medication to balance hormone levels and manage symptoms. With proper medical care and adherence to treatment, individuals with hypopituitarism can anticipate a regular lifespan, enabling them to lead fulfilling lives with the condition. The prognosis of hypopituitarism highlights the importance of timely diagnosis and continued medical management to ensure optimal health outcomes for affected individuals.
What is hypopituitarism treated with?
To treat hypopituitarism, hormone replacement therapy is used to elevate hormone levels. This involves administering medications to restore the hormone levels that would be naturally produced by the body if it did not have a pituitary issue. The dosage is carefully determined to replicate the body’s normal hormone production, and in certain instances, individuals with hypopituitarism may require lifelong medication to manage their condition.
Reference source
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hypopituitarism/symptoms-causes/syc-20351645
https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/hormonal-and-metabolic-disorders/pituitary-gland-disorders/hypopituitarism
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4722397/
https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/hypopituitarism