In the intricate and mysterious realm of the human body, a constant symphony of biological processes unfolds.
Among them, the phenomenon of uterine contractions stands out as a captivating dance of power and rhythm.
Today, we delve into the depths of a specific type of uterine contraction – the enigmatic hypotonic uterine contraction.
Brace yourself, as we embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this mesmerizing force and its impact on the miracle of childbirth.
hypotonic uterine contraction
Hypotonic uterine contraction refers to weak or ineffective contractions of the uterus during labor.
This condition can hinder the progress of labor and delay the delivery of the baby.
The contractions may be irregular, insufficiently strong, or occur too infrequently.
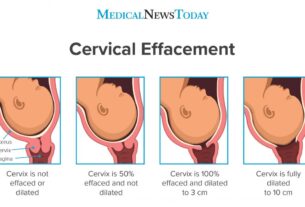
As a result, the cervix may not dilate properly, leading to a prolonged labor and potential complications.
It is important to address hypotonic uterine contractions promptly to ensure a safe delivery for both the mother and baby.
Key Points:
- Hypotonic uterine contraction refers to weak or ineffective contractions of the uterus during labor.
- This condition can hinder the progress of labor and delay the delivery of the baby.
- The contractions may be irregular, insufficiently strong, or occur too infrequently.
- The cervix may not dilate properly, leading to a prolonged labor and potential complications.
- Addressing hypotonic uterine contractions promptly is important.
- Ensuring a safe delivery for both the mother and baby is crucial.
hypotonic uterine contraction – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Hypotonic uterine contractions, also known as “weak contractions,” occur when the muscles of the uterus do not contract adequately during labor and delivery.
2. These contractions can cause prolonged labor, which is often characterized by slow progress in the dilation and effacement of the cervix.
3. Maternal dehydration can contribute to the occurrence of hypotonic uterine contractions. Staying properly hydrated during pregnancy can help prevent their occurrence.
4. In some cases, hypotonic uterine contractions can be managed by administering medications, such as oxytocin, to stimulate more regular and effective contractions.
5. Hypotonic uterine contractions can pose challenges in vaginal delivery, sometimes necessitating the need for interventions like forceps or vacuum extraction to assist with the delivery process.
Definition Of Hypotonic Uterine Contraction
Hypotonic uterine contraction, also known as uterine atony or inadequate uterine contractions, is a condition characterized by weak and ineffective contractions of the uterine muscles during labor and delivery. These contractions are responsible for pushing the baby out of the uterus and into the birth canal. In cases of hypotonic uterine contraction, the contractions may be infrequent, lacking in strength, or both, making it difficult for labor to progress efficiently.
During a normal and effective labor, the uterine muscles contract and tighten, generating enough force to dilate the cervix and expel the baby. However, if the contractions are hypotonic, they may fail to achieve a sufficient level of intensity to achieve these goals. This can lead to a prolonged labor, increased risk for interventions, and potential complications for both the mother and the baby.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for hypotonic uterine contraction is crucial for a successful delivery.
- Hypotonic uterine contraction, also known as uterine atony or inadequate uterine contractions.
- Weak and ineffective contractions of the uterine muscles during labor and delivery.
- Infrequent, lacking in strength, or both contractions make it difficult for labor to progress efficiently.
- Can lead to prolonged labor, increased risk for interventions, and potential complications for both mother and baby.
- Understanding causes, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for a successful delivery.
Causes Of Hypotonic Uterine Contraction
Hypotonic uterine contraction can be caused by various factors, including maternal and fetal conditions. Some common causes include:
- Maternal exhaustion
- Use of certain medications or anesthesia
- Malposition of the baby
- Multiple gestations
- Maternal obesity
- A large baby
- Over-distended uterus due to polyhydramnios (excessive amniotic fluid)
Additionally, factors such as maternal age, previous uterine surgeries, and prolonged labor can contribute to the development of hypotonic uterine contractions.
Poor nutrition and hydration during pregnancy can also affect the strength of uterine contractions. Dehydration or inadequate intake of essential nutrients can lead to inefficient muscle function and contribute to hypotonic uterine contractions.
It is important for expectant mothers to:
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Stay properly hydrated
- Follow proper prenatal care guidelines
This will help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
“Proper nutrition and hydration are vital for maintaining optimal uterine contraction strength and reducing the risk of hypotonic uterine contractions.”
Symptoms And Effects Of Hypotonic Uterine Contraction
The symptoms of hypotonic uterine contraction may include:
- Irregular or weak contractions
- Failure to effectively push the baby downward into the birth canal
- Slow progress of labor
- Frustration and exhaustion for the mother
In some cases, the cervix may not dilate properly or may cease dilating altogether. This can cause a prolonged labor, increasing the risk of medical interventions such as:
- Forceps or vacuum-assisted delivery
- Cesarean section
Hypotonic uterine contractions can also have effects on the baby. Reduced intensity and frequency of contractions may limit the baby’s movement through the birth canal, potentially leading to:
- Fetal distress
- The need for immediate medical intervention
In rare cases, prolonged labor due to hypotonic contractions can increase the risk of:
- Oxygen deprivation to the baby
- Complications such as meconium aspiration or low Apgar scores at birth
Understanding the symptoms and effects of hypotonic uterine contractions can help healthcare providers intervene promptly and effectively to ensure a safe and healthy outcome for both the mother and the baby.
💡
You may need to know these questions about hypotonic uterine contraction
What are hypotonic and hypertonic uterine contractions?
Hypotonic uterine contractions refer to weak or infrequent contractions of the uterus during labor. In this condition, the contractions may not be strong enough to effectively dilate and efface the cervix or facilitate the descent of the baby through the birth canal. Hypotonic uterine dysfunction can prolong labor and make it more challenging for the mother to progress in the delivery process.
On the other hand, hypertonic uterine contractions are characterized by excessive strength or frequency of contractions. These intense and frequent contractions can lead to ineffective cervical dilation or cause the cervix to become overly tense. Hypertonic uterine dysfunction can impede the progress of labor and potentially cause discomfort or distress for both the mother and the baby during the birthing process.
What is hypertonic uterine contraction?
Hypertonic uterine contraction is a medical condition characterized by excessively frequent and painful contractions, accompanied by a high resting tone in the uterus. These intense contractions can lead to maternal exhaustion due to the continuous strain on the body and may also put the fetus at risk of experiencing hypoxia, a condition with reduced oxygen supply. Maternal exhaustion and fetal hypoxia are important concerns associated with hypertonic uterine contractions, underscoring the need for proper management and monitoring during childbirth to ensure the well-being of both mother and baby.
What is the complication of hypotonic contractions?
One potential complication of hypotonic contractions is an increased risk of fetal distress. These contractions may not provide enough force to effectively dilate the cervix or push the baby through the birth canal, leading to prolonged labor and potential deprivation of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus. If not managed promptly, this can result in fetal distress and may require interventions such as cesarean section or instrumental delivery to ensure a safe delivery.
Additionally, hypotonic contractions can contribute to postpartum hemorrhage. These weak contractions may not effectively compress the blood vessels in the placental site, leading to insufficient contraction of the uterus after delivery. This can result in excessive bleeding and put the woman at risk for postpartum hemorrhage, which can be a life-threatening condition if not promptly treated. Close monitoring and appropriate management strategies, such as uterine massage and administration of uterotonics, are crucial in preventing or addressing this complication.
What are 4 characteristics of uterine contractions?
Four characteristics of uterine contractions include contraction strength, duration, baseline tone, and inter-contraction interval. Contraction intensity refers to the strength or force of the contractions, which can vary between individuals and throughout different stages of labor. Duration relates to the length of time each contraction lasts, with contractions typically becoming longer and more frequent as labor progresses. Resting tone represents the baseline tension level of the uterine muscles between contractions, and it is an indicator of the overall uterine activity. Lastly, the inter-contraction interval refers to the duration between contractions, providing insight into the rest time for the uterus and the rhythm of the contractions.
Reference source
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33232073/
https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/abnormalities-and-complications-of-labor-and-delivery/protracted-labor
https://gpnotebook.com/simplepage.cfm?ID=-200933368
https://nurseslabs.com/labor/