In the realm of medical anomalies, hidden within the intricate web of the human body, lies a condition both fascinating and perplexing – interstitial tubal pregnancy.
This enigmatic phenomenon, often eluding early detection, challenges medical professionals and captivates the curious minds of researchers.
Join us as we delve into the mysterious world of interstitial tubal pregnancy, navigating through the complexities and unraveling the secrets that lie within.
interstitial tubal pregnancy
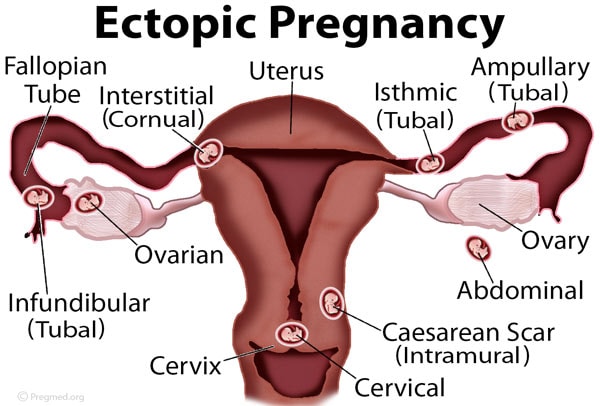
Interstitial tubal pregnancy is a rare and potentially life-threatening condition where a fertilized egg implants in the muscular wall of the fallopian tube, called the interstitial segment.
This type of ectopic pregnancy can be difficult to diagnose and carry a higher risk of uterine rupture compared to other types of tubal pregnancies.
Immediate medical attention is necessary to prevent complications and preserve the woman’s fertility.
Early detection through ultrasound and appropriate management, such as surgical intervention or medical treatment with methotrexate, can lead to successful outcomes and reduce the risk of severe complications.
Key Points:
- Interstitial tubal pregnancy is a rare and life-threatening condition where a fertilized egg implants in the muscular wall of the fallopian tube.
- Diagnosis of interstitial tubal pregnancy can be challenging and carries a higher risk of uterine rupture.
- Urgent medical attention is required to prevent complications and preserve fertility.
- Early detection through ultrasound and appropriate management can lead to successful outcomes.
- Surgical intervention or medical treatment with methotrexate are common approaches to managing interstitial tubal pregnancy.
- These interventions can help reduce the risk of severe complications.
interstitial tubal pregnancy – Watch Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sDPnGo4OJp4
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Interstitial tubal pregnancy, also known as cornual pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants itself in the muscular part of the fallopian tube, rather than in the uterus.
2. Compared to other types of ectopic pregnancies, interstitial tubal pregnancies are extremely rare, representing only about 2-4% of all ectopic pregnancies.
3. Because of its location in the fallopian tube near the uterus, an interstitial tubal pregnancy can often mimic the symptoms of a normal early pregnancy, making it difficult to diagnose.
4. Interstitial tubal pregnancies have a higher risk of serious complications such as rupture and hemorrhage, which can be life-threatening for the mother.
5. Due to the potential risks and difficulties in diagnosing interstitial tubal pregnancies, early detection through thorough ultrasound examinations and close monitoring is crucial for the health and safety of the mother.
Definition Of Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
Interstitial tubal pregnancy, also known as cornual pregnancy, is a rare type of ectopic pregnancy where the fertilized egg implants in the muscular part of the fallopian tube closest to the uterus, called the interstitium. This condition poses a significant risk to maternal health due to the increased vascularity of the interstitial area, which allows the fetus to grow for a longer period compared to other sites of ectopic pregnancy. However, the delayed detection of interstitial tubal pregnancy can lead to severe complications like rupture and internal bleeding. Therefore, it is crucial to promptly diagnose and treat this condition.
- Ectopic pregnancy: implantation of the fertilized egg outside the uterus, commonly in the fallopian tubes
- Interstitial tubal pregnancy: embryo implants in the interstitium of the fallopian tube
- Increased risk to maternal health due to the highly vascularized interstitial area
- Delayed detection can lead to complications like rupture and internal bleeding
Causes Of Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
The cause of interstitial tubal pregnancy is not fully understood at present. However, there are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of its occurrence. These include:
-
Previous pelvic infections, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), can lead to tubal scarring and narrowing. This can hinder the movement of the fertilized egg through the fallopian tube, resulting in implantation in the interstitial region.
-
A history of pelvic or abdominal surgery, as well as endometriosis and congenital anomalies of the fallopian tube, can also increase the risk of interstitial tubal pregnancy.
-
Women who have previously undergone assisted reproductive techniques, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), may be at a higher risk of experiencing interstitial tubal pregnancy.
It is important to remember that early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for managing interstitial tubal pregnancy effectively.
“Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for managing interstitial tubal pregnancy effectively.”
Symptoms And Signs Of Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
Interstitial tubal pregnancy often presents with similar symptoms as other types of ectopic pregnancies, albeit with some distinguishing factors. Women with this condition may experience lower abdominal pain, which can vary in intensity and may be accompanied by bleeding.
One of the key features of interstitial tubal pregnancy is the delayed onset of symptoms, which can make it difficult to diagnose. This delayed presentation is due to the relative distensibility of the interstitial region, allowing the growing pregnancy to go unnoticed until later stages. As the pregnancy progresses, symptoms may worsen, and in some cases, the patient may experience signs of shock due to internal bleeding.
Diagnosis And Detection Methods For Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
Early and accurate diagnosis of interstitial tubal pregnancy is crucial for prompt intervention. Various diagnostic methods can be employed to detect this condition.
-
Transvaginal ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality as it offers high-resolution images and can identify the gestational sac in the interstitial region. An empty uterus and the absence of an intrauterine gestational sac are important clues for diagnosis.
-
Additionally, serial serum beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) levels can be measured to monitor the pregnancy’s progression. A slower rise in beta-hCG levels or plateauing levels may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, including interstitial tubal pregnancy.
-
If there is a high suspicion based on clinical signs and symptoms, laparoscopy may be performed to visualize the fallopian tubes and confirm the diagnosis.
-
Early and accurate diagnosis of interstitial tubal pregnancy is crucial for prompt intervention.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality.
- Serial serum beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) levels can be measured to monitor the pregnancy’s progression.
- Laparoscopy may be performed to visualize the fallopian tubes and confirm the diagnosis.
Potential Complications Of Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
Interstitial tubal pregnancy is a serious condition that can pose several potentially life-threatening complications. One of the main risks is the limited space in the interstitial region that can lead to uterine rupture and result in severe hemorrhage. Immediate surgical intervention is necessary in such cases to control bleeding and preserve the woman’s health. It is important to note that ruptured interstitial tubal pregnancies are considered medical emergencies.
Furthermore, future fertility issues are another concern when it comes to interstitial tubal pregnancies. In certain instances, the affected fallopian tube may need to be surgically removed, which can reduce the woman’s chances of conceiving naturally. Moreover, having an interstitial tubal pregnancy may increase the risk of subsequent ectopic pregnancies.
Given these potential complications, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to be vigilant in diagnosing and managing interstitial tubal pregnancies to ensure the best possible outcomes for women at risk.
Treatment Options For Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
The management of interstitial tubal pregnancy depends on various factors, including the woman’s overall health, the stage of pregnancy, and the presence of complications. The primary treatment options include surgical and medical interventions.
Surgical Approaches For Managing Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
Surgery is commonly used to manage interstitial tubal pregnancy, especially when there are complications. Two surgical options are available: laparoscopic salpingectomy and cornuostomy.
- Laparoscopic salpingectomy involves removing the affected fallopian tube.
- Cornuostomy aims to remove the pregnancy from the interstitial region while preserving the tube.
The choice of surgical approach depends on several factors:
- The extent of the pregnancy.
- The woman’s desire for future fertility.
- The surgeon’s expertise.
Medical Interventions For Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
In some cases, particularly when the condition is detected early and there are no complications, medical interventions may be considered. Methotrexate, a medication that targets rapidly dividing cells, can be used to stop the growth of the pregnancy and prevent further complications. However, careful monitoring is essential during this treatment to ensure its effectiveness and to detect any signs of failed medical management.
Follow-Up Care For Patients With Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
After the initial intervention, women who have undergone treatment for interstitial tubal pregnancy require close follow-up care. Regular monitoring of beta-hCG levels and ultrasound examinations can help ensure that the pregnancy has been effectively resolved and detect any potential complications.
It is also important to address the psychological impact of interstitial tubal pregnancy on the woman and her partner. Counseling and support groups can provide emotional support during this challenging time.
- Regular monitoring of beta-hCG levels and ultrasound examinations
- Counseling and support groups for psychological support during this challenging time.
Prognosis And Long-Term Outcomes Of Interstitial Tubal Pregnancy
The prognosis for interstitial tubal pregnancy depends on several factors, including the time of diagnosis, the presence of complications, and the treatment approach. Early diagnosis and prompt intervention lead to better outcomes and a reduced risk of serious complications.
In terms of future fertility, women who have undergone surgical removal of the affected fallopian tube may have a reduced chance of conceiving naturally. However, with advances in assisted reproductive techniques, such as IVF, many women can still achieve successful pregnancies.
In conclusion, interstitial tubal pregnancy is a rare and potentially life-threatening condition. Early diagnosis, followed by appropriate treatment, is crucial in ensuring the best possible outcomes for affected women. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, healthcare professionals can provide timely interventions and support to women with this condition.
💡
You may need to know these questions about interstitial tubal pregnancy
Can an interstitial pregnancy survive?
Survival of an interstitial pregnancy is exceptionally rare, with only a few documented cases in medical literature. Research conducted until June 2013 identified a mere 10 recorded instances of interstitial pregnancies resulting in a live birth. These cases demonstrate how remarkable it is for an interstitial pregnancy to reach viability, highlighting its rarity and the challenges it presents.
What is the survival rate of interstitial pregnancy?
The survival rate of interstitial pregnancy largely depends on the promptness of treatment and medical intervention. Although the mortality rate associated with ruptured interstitial ectopic pregnancy ranges from 2-5%, early detection and timely medical intervention greatly improve the chances of survival. It is important to note that most cases of interstitial ectopic pregnancy rupture typically occur around 12 weeks of gestation, emphasizing the significance of early diagnosis and intervention to ensure a higher survival rate.
How does an interstitial pregnancy happen?
An interstitial pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants in the interstitial portion of the fallopian tube, which is the part that enters the uterine cavity. This unique location allows the pregnancy to develop within the myometrium, the muscular lining of the uterus. Unlike other ectopic pregnancies, the interstitial ectopic can grow to a larger size before causing symptoms due to being surrounded by the myometrium.
How common is interstitial ectopic pregnancy?
Interstitial ectopic pregnancy is a relatively uncommon form of ectopic pregnancy, comprising only 2–4% of all cases. This specific type of ectopic pregnancy is particularly challenging to diagnose accurately, primarily due to the limited sensitivity and specificity of symptoms and imaging techniques. As a result, early detection and treatment of interstitial ectopic pregnancy can be quite complex and require close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Due to its rarity and diagnostic difficulties, interstitial ectopic pregnancy presents unique challenges in healthcare settings. Clinicians must remain vigilant in considering this condition as a possible diagnosis and utilize a combination of clinical judgment and advanced imaging techniques to accurately identify and manage cases. With a low incidence rate and diagnostic complexities, a multidisciplinary approach is often necessary to provide the best possible care for patients with interstitial ectopic pregnancy.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2700669/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4078107/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9647428/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/interstitial-pregnancy