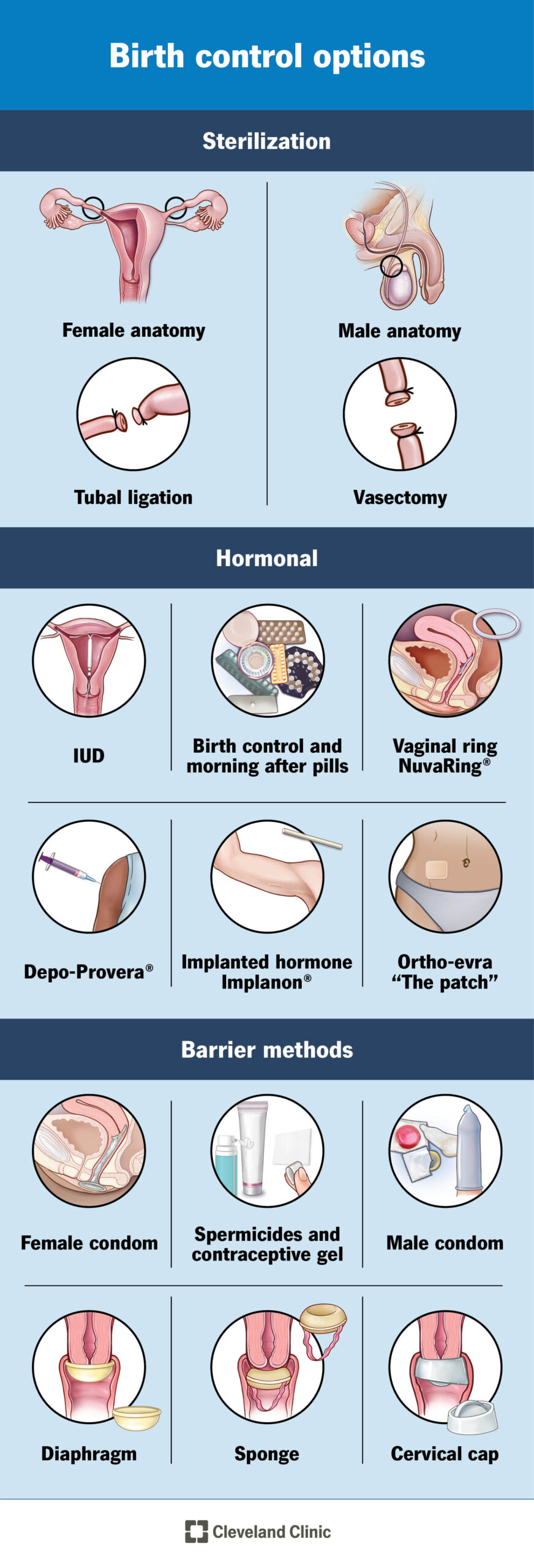
In a world where contraception options abound, one tiny device has proven its worth by standing the test of time.
Enter the intrauterine device (IUD), a T-shaped guardian that offers up to a decade of pregnancy protection.
But is this ultimate contraceptive superhero without its quirks and caveats?
Join us as we explore the fascinating realm of IUDs, where mysteries linger and truths unravel.
intrauterine devic
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small T-shaped plastic and copper device that is inserted into the womb to prevent pregnancy.
It is over 99% effective when inserted correctly and can last for 5 to 10 years.
IUDs can be inserted at any time during the menstrual cycle if the person is not pregnant and can be removed at any time by a trained medical professional.
They do not protect against sexually transmitted infections and may have side effects such as heavier periods and a small risk of infection.
It is important to check the IUD regularly and consult a healthcare professional if there are any problems or concerns.
Contraception services are free and confidential, even for individuals under 16, and healthcare professionals will only disclose information if there is a risk of harm.
Key Points:
- An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small T-shaped plastic and copper device inserted into the womb to prevent pregnancy.
- IUDs are over 99% effective when inserted correctly and can last for 5 to 10 years.
- IUDs can be inserted or removed at any time by a trained medical professional, as long as the person is not pregnant.
- They do not protect against sexually transmitted infections and may have side effects, like heavier periods and a small risk of infection.
- Regular checking and consultation with a healthcare professional is important if there are any problems or concerns with the IUD.
- Contraception services are free and confidential, including for individuals under 16; healthcare professionals will only disclose information if there is a risk of harm.
intrauterine devic – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The intrauterine device (IUD) was first introduced in 1909 by German physician Dr. Ernst Gräfenberg, who also developed the controversial sexual pleasure zone called the “G-spot.”
2. Cleopatra, the Egyptian queen known for her beauty and power, is believed to have used an early form of an IUD made from a hollowed-out gourd filled with crocodile dung. This primitive method likely acted as a barrier against pregnancy.
3. In 1974, a sheep named Dolly became the first mammal to be successfully cloned. The scientists who carried out this groundbreaking experiment used a tiny IUD-like device called a pipette to remove and transfer genetic material from one sheep to another.
4. The Mona Lisa, the iconic masterpiece of Leonardo da Vinci, was discovered to have a hidden secret during a high-resolution scan in 2004. An IUD-like object was found beneath the paint layers in the abdomen of the famous portrait, indicating that the subject might have been pregnant.
5. In the world of music, legendary guitarist Jimi Hendrix reportedly used an IUD as a pick during some of his performances. He believed that the copper-coated IUD produced a unique sound when struck against the strings, adding a distinct texture to his electric guitar solos.
Introduction to Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are a popular and highly effective form of contraception. They consist of a small T-shaped plastic device that is inserted into the womb to prevent pregnancy.
The IUD is a long-lasting method that provides continuous protection, making it a convenient option for individuals who are looking for a reliable contraceptive method.
The IUD is inserted into the uterus by a trained medical professional. Once in place, it can stay there for several years, providing a high level of effectiveness.
Some key points regarding IUDs include:
- IUDs are an attractive option for many individuals due to their ease of use and minimal maintenance required.
- They do not require daily attention like some other forms of birth control.
- IUDs are a discreet and reliable choice for those seeking effective family planning.
“IUDs offer a convenient and highly effective contraception method with its long-lasting protection and minimal maintenance required.”
Effectiveness and Duration of IUDs
IUDs are highly effective and have a success rate of over 99% when inserted correctly. This means that fewer than 1 out of 100 women will become pregnant while using this form of contraception. The effectiveness of IUDs makes them one of the most reliable methods of birth control available.
The duration of effectiveness for IUDs varies depending on the type. Some IUDs can last up to 5 years, while others can be effective for up to 10 years. The long duration of protection offered by IUDs makes them an attractive choice for individuals who are looking for a long-term contraceptive solution.
- IUDs have a success rate of over 99% when inserted correctly.
- Fewer than 1 out of 100 women will become pregnant while using an IUD.
- IUDs are one of the most reliable methods of birth control available.
- Some IUDs can last up to 5 years, while others can be effective for up to 10 years.
- The long duration of protection makes IUDs an attractive choice for individuals seeking a long-term contraceptive solution.
“IUDs are highly effective and have a success rate of over 99% when inserted correctly. This means that fewer than 1 out of 100 women will become pregnant while using this form of contraception.”
Timing and Availability of IUD Insertion and Removal
IUDs can be inserted at any time during the menstrual cycle, as long as the person is not pregnant. This flexibility in timing allows individuals to choose the most convenient time for insertion.
Likewise, IUDs can be removed at any time by a trained medical professional. This feature provides flexibility to those who decide to discontinue using the IUD or wish to switch to a different contraceptive method.
IUDs can be obtained from various sources, including contraception clinics, sexual health or genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinics, GP surgeries, and some young people’s services. These facilities offer IUD insertion and removal services, ensuring accessibility to individuals seeking an IUD as their preferred form of contraception.
Common Side Effects of IUDs
While IUDs are generally safe and effective, some individuals may experience side effects. These side effects can include:
- Heavier, longer, or more painful periods
- Spotting or bleeding between periods
- A small risk of infection
It is important to note that the IUD does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Therefore, individuals using an IUD should consider additional protection if they are at risk of contracting STIs. Using condoms alongside the IUD can provide comprehensive protection against both unplanned pregnancies and STIs.
It’s worth mentioning that the side effects of IUDs are generally well-tolerated and fade over time. If an individual experiences persistent or severe side effects, they should consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
Limitations of IUDs in Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections
It is essential to recognize that IUDs do not provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
-
Individuals using an IUD should be aware of this limitation and take additional precautions, such as using condoms, to reduce the risk of contracting STIs.
-
While IUDs are highly effective at preventing pregnancy, they do not have an impact on the transmission of STIs.
-
It is crucial for individuals to be proactive about their sexual health and engage in open and honest conversations with their partners about STI prevention.
-
Understanding the limitations of IUDs in preventing STIs can empower individuals to make informed decisions and take the necessary steps to protect their sexual health.
The Mechanism of Action of Copper IUDs
Copper IUDs work by releasing copper into the womb, which alters the cervical mucus and makes it difficult for sperm to reach an egg and implant itself. The presence of copper creates a hostile environment for sperm, reducing the likelihood of fertilization.
Copper IUDs are a non-hormonal form of contraception, which makes them a suitable option for individuals who prefer to avoid hormonal methods. The absence of hormones in copper IUDs minimizes the risk of hormonal side effects often associated with other contraceptive methods.
Understanding the mechanism of action of copper IUDs can help individuals make an informed decision about whether this form of contraception aligns with their personal preferences and needs.
- Key points:
- Copper IUDs release copper into the womb.
- Copper alters cervical mucus to inhibit sperm.
- Copper creates a hostile environment for sperm.
- Non-hormonal contraception option.
- Minimizes risk of hormonal side effects.
- Helps make an informed decision.
Recommendations for Long-Term Use of IUDs
IUDs can be left in place until menopause or when contraception is no longer needed. For individuals over 40 years old, IUDs can provide long-term protection against unplanned pregnancies. This longevity makes IUDs an attractive option for those who desire a reliable contraceptive solution without the need for regular maintenance or replacement.
Before the insertion of an IUD, a general practitioner or nurse will assess the position and size of the womb and may test for existing infections. This evaluation is essential to ensure the suitability of IUD use and minimize the risk of complications.
Once the IUD is inserted, individuals may experience period-type cramps and bleeding for a few days. However, these symptoms are usually temporary and should subside over time. If any problems or concerns arise, or if removal of the IUD is desired, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for guidance and support.
- IUDs can be left in place until menopause or when contraception is no longer needed
- For individuals over 40 years old, IUDs can provide long-term protection against unplanned pregnancies
- IUD insertion requires assessment of the position and size of the womb, as well as tests for existing infections
- Period-type cramps and bleeding may occur for a few days after IUD insertion
- Consult a healthcare professional for any problems, concerns, or if removal of the IUD is desired.
Preparing for IUD Insertion and Possible Complications
Prior to IUD insertion, it is crucial to have a discussion with a general practitioner or nurse to address any concerns and prepare for the procedure. Professionals will check the position and size of the womb and may test for existing infections to ensure the suitability of IUD use.
The fitting process takes approximately 20 to 30 minutes, with the IUD being inserted through the cervix into the womb. It is normal to experience some discomfort or pain during the procedure. However, local anesthesia can be used to minimize discomfort and maximize comfort during insertion.
It is important to note that, while rare, complications may occur during or after IUD insertion. These can include infection, expulsion of the IUD, or the IUD moving out of position. If any complications are suspected, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to address the concerns and ensure appropriate follow-up.
- Prior to IUD insertion, have a discussion with a general practitioner or nurse.
- Professionals will check the position and size of the womb and may test for existing infections.
- The fitting process takes approximately 20 to 30 minutes.
- Discomfort or pain may be experienced during the procedure, but local anesthesia can be used for comfort.
- Complications are rare but can include infection, expulsion of the IUD, or the IUD moving out of position.
- Consult a healthcare professional if complications are suspected.
Monitoring and Follow-Up After IUD Insertion
After having an IUD fitted, it is recommended to schedule a check-up with a general practitioner after 3 to 6 weeks. This follow-up appointment allows healthcare professionals to ensure that the IUD is in the correct position and functioning properly. It also provides an opportunity to address any questions or concerns that may arise.
Individuals using an IUD should regularly check the two thin threads attached to the device to ensure it is still in place. If the threads cannot be felt or if the IUD has moved, there may be a risk of pregnancy, and additional contraception should be used until a healthcare professional can confirm the IUD’s position.
Furthermore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional if the partner can feel the IUD during sex. This may indicate that the IUD has become dislodged or shifted and requires medical attention.
Special Considerations and Contraindications for IUD Use
Although most individuals with a womb can use an IUD, there are certain factors that may impact its suitability. These include:
- Pregnancy
- Untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or pelvic infections
- Issues with the womb or cervix
- Unexplained bleeding
- History of ectopic pregnancy
- Presence of an artificial heart valve
It is important to consult a general practitioner or healthcare professional to evaluate any individual concerns or medical conditions that may affect the safe and appropriate use of an IUD. In such cases, alternative contraceptive methods or specific management plans can be discussed to ensure optimal health outcomes.
IUDs are a safe and effective form of contraception. They offer a long-term solution for individuals seeking reliable family planning options. With proper knowledge and guidance, individuals can make informed decisions about the use of an IUD and take steps to protect their sexual health and well-being.
–Most individuals with a womb can use an IUD.
–Factors that may impact its suitability include pregnancy, untreated STIs or pelvic infections, issues with the womb or cervix, unexplained bleeding, a history of ectopic pregnancy, or the presence of an artificial heart valve.
–Consult a general practitioner or healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance.
–Alternative contraceptive methods or specific management plans can be discussed.
–IUDs are a safe and effective form of contraception.
–They offer a long-term solution for reliable family planning.
-*Individuals can make informed decisions about the use of an IUD to protect their sexual health and well-being.
Note: It is important to keep in mind that each individual’s situation may vary, and it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
💡
You may need to know these questions about intrauterine devic
Can my partner feel my IUD?
The IUD, an intrauterine device, typically does not cause any discomfort or interfere with sexual activities due to its thin plastic strings. However, there may be rare instances where your partner might feel these strings during sex. If this becomes a concern, it is advisable to consult with your ob-gyn who can potentially trim the strings to address the issue.
How much does the IUD cost?
The cost of an IUD can vary greatly, ranging from $0 to $1,300. The good news is that many health insurance plans, as well as Medicaid and some government programs, offer IUDs for free or at a low cost. Additionally, the price can differ depending on the specific type of IUD chosen.
Can I finger my girlfriend if she has an IUD?
If your girlfriend has an IUD, it is generally safe to finger her. However, the presence of the IUD strings may be more noticeable during fingering compared to intercourse. It is important to communicate with your partner and discuss any potential discomfort or concerns with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance on how to make the strings less noticeable or offer alternative solutions if needed. Remember, open communication and seeking professional advice is crucial to ensure a pleasurable and safe experience for both partners.
Can my boyfriend finish inside me with an IUD?
Yes, your boyfriend can safely finish inside you with an IUD. The IUD is highly effective at preventing pregnancy, even when semen is present. Its design ensures that the sperm cannot reach and fertilize an egg, providing reliable contraception. You can enjoy the intimacy of your relationship without worrying about the risk of pregnancy.
Reference source
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/iud-coil/
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/experts-and-stories/ask-acog/will-my-partner-feel-my-iud-during-sex
https://www.chicagoobgyn.com/blog/pros-and-cons-of-an-iud
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/birth-control/iud/how-can-i-get-an-iud