Are you familiar with the intricate workings of the female reproductive system?
Brace yourself, for we are about to embark on a fascinating journey into the world of irregular shedding of endometrium.
Unveiling the mysteries of abnormal uterine bleeding, we will unravel its puzzling causes and explore the medical interventions that may hold the key to resolving this perplexing issue.
Prepare to be enlightened and captivated by the hidden secrets of the uterus.
irregular shedding of endometrium
The term “irregular shedding of endometrium” typically refers to abnormal uterine bleeding, which is characterized by heavy or unusual bleeding from the uterus.
This condition can present with symptoms such as vaginal bleeding between periods and extremely heavy bleeding during periods.
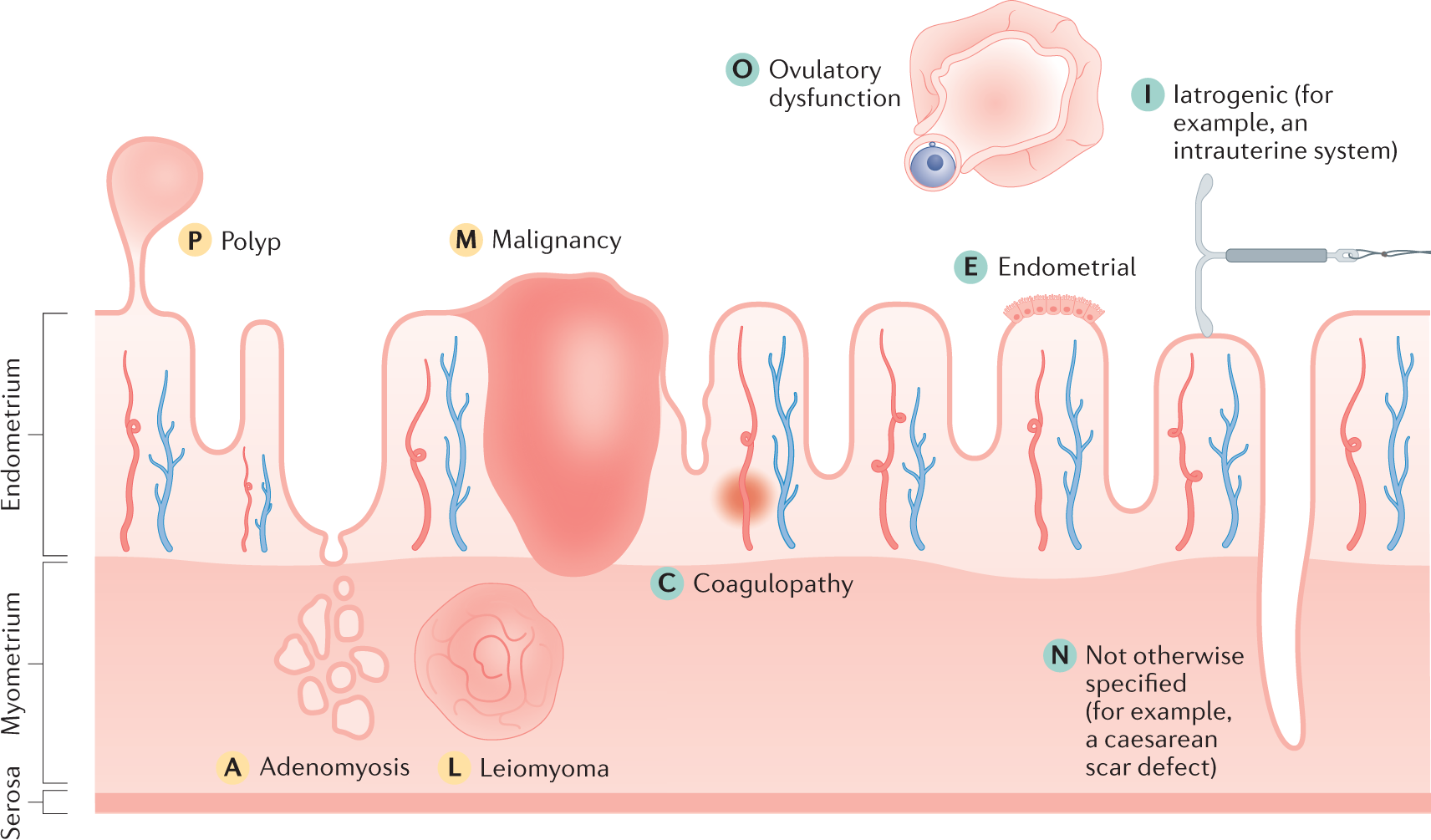
Various factors can contribute to abnormal uterine bleeding, including hormonal imbalances, pregnancy, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), growths in the uterus, infection, liver/kidney/thyroid disease, bleeding disorders, or uterine/cervical cancer.
Causes can vary depending on age, with pregnancy, birth control methods, and hormonal imbalances being common among teenagers and young adults, while lack of ovulation, thickening of the uterine lining, and uterine cancer are more prevalent in individuals in their 40s and early 50s.
After menopause, hormone replacement therapy can also lead to uterine bleeding.
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of pregnancy tests, blood tests, ultrasound exams, endometrial biopsies, and hysteroscopy.
Treatment options may include birth control pills, intrauterine devices, dilation and curettage (D&C) procedures, hysterectomy, endometrial ablation, and management of symptoms such as pain and anemia.
It is important to consult a doctor if experiencing abnormal uterine bleeding, as they can determine the likely cause, severity of the condition, and appropriate treatment options.
Key Points:
- Irregular shedding of endometrium refers to abnormal uterine bleeding characterized by heavy or unusual bleeding from the uterus.
- Symptoms of this condition include vaginal bleeding between periods and extremely heavy bleeding during periods.
- Factors that can contribute to abnormal uterine bleeding include hormonal imbalances, pregnancy, PCOS, growths in the uterus, infection, and various diseases.
- Causes can vary depending on age, with pregnancy and hormonal imbalances being common in teenagers and young adults, and lack of ovulation and uterine cancer more prevalent in individuals in their 40s and early 50s.
- Hormone replacement therapy after menopause can also lead to uterine bleeding.
- Diagnosis involves a combination of pregnancy tests, blood tests, ultrasound exams, endometrial biopsies, and hysteroscopy.
- Treatment options include birth control, D&C procedures, hysterectomy, and symptom management.
irregular shedding of endometrium – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The irregular shedding of endometrium, also known as endometrial disarray, can be caused by hormonal imbalances or certain medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
2. Women who experience irregular shedding of endometrium often face challenges with fertility, as the unpredictable shedding can disrupt the normal menstrual cycle and make it difficult to determine the optimal time for conception.
3. In rare cases, irregular shedding of endometrium can lead to the formation of endometrial polyps—abnormal growths within the uterus. These polyps can cause further irregular bleeding and may require medical intervention to remove.
4. Certain lifestyle factors can contribute to irregular shedding of endometrium, such as excessive stress levels and a lack of physical activity. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing stress can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce the likelihood of irregular shedding.
5. Endometrial ablation, a surgical procedure that destroys the lining of the uterus, is sometimes used as a treatment for women who experience severe and debilitating irregular shedding of endometrium. However, this procedure is generally considered a last resort after other treatment options have been exhausted.
Understanding Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Abnormal uterine bleeding is characterized by heavy or unusual bleeding from the uterus. It is a common condition that can greatly affect the daily lives of women. This type of bleeding can occur at any age and can be attributed to various factors. Understanding the causes and symptoms of abnormal uterine bleeding is crucial in seeking appropriate medical care and finding effective treatment options.
Recognizing The Symptoms Of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
The symptoms of abnormal uterine bleeding can vary depending on the individual and the underlying cause. Some key symptoms include:
- Vaginal bleeding between periods: This can be characterized by spotting or light bleeding that occurs outside of the normal menstrual cycle.
- Extremely heavy bleeding during periods (known as menorrhagia): This can result in the need to change sanitary pads or tampons frequently and may even lead to blood clots being passed.
- Longer or more frequent periods: This may indicate abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Pelvic pain or cramping: This can be one of the symptoms experienced.
- Fatigue or weakness: Due to the loss of blood, fatigue and weakness may occur.
It is important to note that if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is recommended to consult with a medical professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
In summary:
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
- Extremely heavy bleeding during periods (menorrhagia)
- Longer or more frequent periods
- Pelvic pain or cramping
- Fatigue or weakness due to blood loss.
Common Causes Of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
There are numerous factors that can contribute to abnormal uterine bleeding. Hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can disrupt the regular menstrual cycle and lead to irregular shedding of the endometrium. Pregnancy can also cause abnormal bleeding, particularly in the form of implantation bleeding or miscarriage. Other causes may include:
- Presence of growths in the uterus, such as polyps or fibroids
- Infection
- Liver/kidney/thyroid disease
- Bleeding disorders
- Even cancer of the uterus or cervix.
It is important to note that any abnormal uterine bleeding should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
Causes Of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding In Different Age Groups
Causes of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding:
The causes of abnormal uterine bleeding can vary depending on the age group of the individual experiencing the symptoms.
For teenagers and young adults, the common causes include:
- Pregnancy
- Certain birth control methods
- Hormonal imbalances
As women reach their 40s and early 50s, the hormonal changes associated with perimenopause and menopause can lead to irregular shedding of the endometrium. Other causes during this life stage include:
- Lack of ovulation
- Thickening of the uterine lining
- Uterine cancer
To summarize, the causes of abnormal uterine bleeding differ across age groups. Teenagers and young adults may experience abnormal bleeding due to pregnancy, certain birth control methods, or hormonal imbalances. In the 40s and early 50s, hormonal changes, lack of ovulation, thickened uterine lining, and uterine cancer can cause abnormal bleeding.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding After Menopause
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a frequent cause of uterine bleeding in women after menopause. It is crucial for women undergoing HRT to be mindful of the possibility of abnormal bleeding and to seek medical advice if they observe any alterations in their menstrual patterns. Abnormal uterine bleeding after menopause may also indicate the presence of endometrial or uterine cancer, which is more prevalent in older individuals. Additionally, infections, hormonal imbalances, or the presence of growths can contribute to postmenopausal bleeding.
To summarize:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can lead to uterine bleeding after menopause.
- Women on HRT should be vigilant for abnormal bleeding and consult their doctor if changes occur in their menstrual patterns.
- Abnormal uterine bleeding after menopause may indicate endometrial or uterine cancer.
- Other factors such as infections, hormonal imbalances, or growths can also cause postmenopausal bleeding.
Seeking Medical Diagnosis For Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
It is crucial to consult a doctor if you are experiencing abnormal uterine bleeding, as they can help diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Diagnosis may involve:
- Taking a detailed medical history which includes information on menstrual irregularities, pregnancy history, and medication usage.
- A physical examination, including a pelvic exam, to rule out physical changes in the reproductive system.
Additional tests that may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis include:
- Transvaginal ultrasound to check the thickness of the uterine lining.
- A biopsy to examine the uterine cells.
Remember, it’s important to seek medical attention if you notice any abnormal uterine bleeding.
Treatment Options For Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
The treatment options for abnormal uterine bleeding depend on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms.
In some cases, hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills or intrauterine devices (IUDs), may be prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce bleeding.
Non-hormonal medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also be used to relieve pain and cramping.
In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. These can include procedures like endometrial ablation or a dilation and curettage (D&C) to remove or destroy the uterine lining.
In extreme cases, a hysterectomy, the surgical removal of the uterus, may be recommended.
Potential Side Effects Of Hormonal Birth Control
While hormonal birth control can be an effective treatment option for abnormal uterine bleeding, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects. Some women may experience irregular bleeding or spotting when starting hormonal contraceptives, which can normalize over time. Other side effects may include nausea, breast tenderness, and changes in mood. It is important to discuss any concerns or side effects with your doctor in order to find the best treatment option for your individual needs.
- Hormonal birth control is effective for abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Potential side effects: irregular bleeding, spotting, nausea, breast tenderness, changes in mood.
- Side effects may normalize over time.
- Discuss concerns or side effects with your doctor for the best treatment option.
Surgical Procedures For Diagnosing And Treating Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
In cases of uncertain diagnosis, surgical procedures may be required to diagnose and treat abnormal uterine bleeding. One such procedure is dilation and curettage (D&C), which involves stretching the cervix and using a surgical tool to scrape away the uterus lining. D&C can serve the purpose of both diagnosing and treating abnormal bleeding. Another option is hysteroscopy, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the uterus to visually examine the uterine lining and potentially remove any abnormal tissue.
To summarize:
- Dilation and curettage (D&C): stretches the cervix and scrapes away the lining of the uterus
- Hysteroscopy: visually examines the uterine lining and may involve removal of abnormal tissue.
Managing The Impact Of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding On Daily Life
Living with abnormal uterine bleeding can have a negative impact on daily life, including causing anxiety and limiting activities. It is important to seek medical care and explore treatment options to manage the symptoms effectively.
In addition to medical interventions, there are also self-care measures that can help alleviate the impact of abnormal uterine bleeding, such as:
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, during periods to reduce pain and cramping.
- Ensuring adequate iron intake through a balanced diet or supplements to prevent anemia, a common complication of heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Communicating openly with healthcare providers and asking questions to understand the likely cause of the abnormal bleeding, the seriousness of the condition, recommended treatment options, and the impact on future pregnancy chances.
“Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for seeking appropriate medical care.”
Abnormal uterine bleeding is a common condition that can significantly impact the lives of women. Whether it is hormonal imbalances, pregnancy, growths, or other underlying conditions, identifying the cause of abnormal bleeding is essential in order to find an effective treatment plan. By working closely with healthcare providers and exploring various treatment options, women can manage the impact of abnormal uterine bleeding and improve their quality of life.
💡
You may need to know these questions about irregular shedding of endometrium
What causes irregular shedding of endometrium?
The irregular shedding of endometrium can be attributed to various factors, one of which is hormonal imbalances. When there is an imbalance in hormones, particularly those involved in the menstrual cycle, the body may struggle to accurately determine when to shed the lining. As a result, this can lead to irregular bleeding or spotting between periods. This occurrence is more common in the years before menopause and during the onset of menopause, as ovulation may not occur regularly during these stages.
How do you treat irregular ripening of the endometrium?
To address irregular ripening of the endometrium, a tailored treatment approach is needed. Progesterone is commonly used as the primary remedy in such cases, facilitating the synchronization and regulation of the endometrium’s ripening process. By administering progesterone, hormonal balance can be restored, allowing for a more regular and coordinated development of the endometrium.
Alternatively, in instances of irregular shedding and decidual reaction, oestrogens are typically prescribed. By introducing oestrogens, the shedding process can be regulated, promoting proper shedding of the endometrial lining and supporting the necessary decidual reaction. This approach ensures that the endometrium maintains its optimal functionality and facilitates a more harmonious menstrual cycle.
What is irregular endometrium?
Irregular endometrium refers to an abnormal thickening of the uterine lining, a condition known as endometrial hyperplasia. This condition poses a potential risk as it is considered precancerous. Women with irregular endometrium may experience symptoms such as heavy menstrual periods, postmenopausal bleeding, and anemia due to excessive bleeding. It is important for individuals with this condition to receive proper medical attention and monitoring to prevent the development of uterine cancer.
What is normal endometrial shedding?
Normal endometrial shedding refers to the natural process in which the upper two-thirds of the endometrium, known as the functional layer, is shed during menstruation. This shedding occurs as a result of hormonal fluctuations within the menstrual cycle. The basal layer, located in the lower third of the endometrium, remains intact and does not shed during menses. This shedding process allows for the renewal of the endometrium and prepares the uterus for potential pregnancy.
Reference source
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0002937850904236/pdf?md5=e12dfbadc68fc2d7283cc01d0d762f33&pid=1-s2.0-0002937850904236-main.pdf
https://familydoctor.org/condition/abnormal-uterine-bleeding/
https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/j.1879-3479.1964.tb00093.x
https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/endometrial-hyperplasia