In the realm of Alzheimer’s disease treatment, where hope is sought and breakthroughs are treasured, a curious substance called lecithin has emerged as a potential game-changer.
While the name might not ring a familiar bell, its amalgamation with tacrine has sparked excitement among researchers.
Join us on a journey through the labyrinthine world of medical innovation as we unravel how lecithin could enhance the efficacy of tacrine in the fight against Alzheimer’s.
lecithin
Lecithin is a natural substance that has been studied for its potential therapeutic effects in various medical conditions.
It has shown beneficial effects in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia, with promising results in both persistent and non-persistent cases.
Lecithin has also been explored in the context of memory improvement in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease patients.
When used in combination with anticholinesterase treatment or thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), it has shown modest facilitation of memory.
Additionally, high-dose phosphatidylcholine, a component of lecithin, has demonstrated early positive results in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial for Alzheimer’s disease.
Lecithin has also shown potential in the treatment of other conditions such as alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis and Friedreich’s ataxia.
Overall, lecithin has been studied for its therapeutic potential in various medical conditions, with promising outcomes in several cases.
Key Points:
- Lecithin has potential therapeutic effects in various medical conditions
- Beneficial effects in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia, including persistent and non-persistent cases
- Explored for memory improvement in dementia and Alzheimer’s patients, especially when combined with anticholinesterase treatment or thyrotropin-releasing hormone
- High-dose phosphatidylcholine, a component of lecithin, has shown positive results in an Alzheimer’s trial
- Potential in treating alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis and Friedreich’s ataxia
- Overall, promising outcomes in the therapeutic potential of lecithin in multiple medical conditions
lecithin – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Lecithin, a natural emulsifier derived from soybeans or egg yolks, is widely used in the chocolate industry to prevent cocoa butter separation.
2. Did you know that lecithin plays a key role in brain health? It is a vital component of the brain’s cell membranes and is crucial for proper signaling between nerve cells.
3. Lecithin can be found in various skincare products, as it helps to enhance the texture and effectiveness of creams and lotions by improving their ability to spread and penetrate the skin.
4. Lecithin is commonly used in the food industry to prevent the sticking of food items during processing, such as preventing cheese from clumping or maintaining the smoothness of sauces and dressings.
5. Lecithin is also used in the production of certain medications, as it helps to increase the absorption of various active ingredients in the body. It is often included in vitamins and supplements to aid in their digestion and effectiveness.
Artificial Surfactant Containing Lecithin For Preventing Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Lecithin, a naturally occurring phospholipid, has shown potential in the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). A controlled trial investigated the effectiveness of artificial surfactant containing lecithin in preventing RDS. Surfactant plays a crucial role in reducing surface tension in the alveoli, allowing for efficient gas exchange in the lungs. The trial found that the use of artificial surfactant with lecithin resulted in a significant reduction in the incidence and severity of RDS in preterm infants. This promising outcome suggests that lecithin could be an important component in the management and prevention of respiratory distress syndrome.
Lecithin Treatment For Tardive Dyskinesia
Tardive dyskinesia is a neurological disorder characterized by repetitive, involuntary movements primarily affecting the face and mouth. Lecithin has been explored as a potential therapeutic agent for this condition. Research has indicated that lecithin treatment shows beneficial effects in reducing the severity and frequency of tardive dyskinesia symptoms.
By enhancing neurotransmitter activity and improving neuronal membrane stability, lecithin presents a promising avenue for the management of this debilitating disorder.
Further studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage and long-term effects of lecithin treatment in tardive dyskinesia patients.
- Lecithin has shown promise as a potential therapeutic agent for tardive dyskinesia.
- Research indicates that lecithin treatment can reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms.
- Lecithin enhances neurotransmitter activity and improves neuronal membrane stability.
- Additional studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage and long-term effects of lecithin treatment.
“By enhancing neurotransmitter activity and improving neuronal membrane stability, lecithin presents a promising avenue for the management of this debilitating disorder.”
Combined Use Of Lecithin And Anticholinesterase Treatment For Memory Facilitation In Dementia Patients
Dementia patients often struggle with memory impairment, and finding effective treatment options is crucial. The combined use of lecithin and anticholinesterase treatment has shown modest facilitation of memory in individuals with dementia. Lecithin acts as a precursor to acetylcholine, a key neurotransmitter involved in memory and cognition. By increasing acetylcholine levels through lecithin supplementation and inhibiting its breakdown through anticholinesterase drugs, a synergistic effect may be achieved, leading to enhanced memory function in dementia patients. While the results are encouraging, more research is needed to fully understand the efficacy, safety, and long-term effects of this combined treatment approach.
Lecithin As A Potential Therapeutic Agent In Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline. Lecithin has been extensively studied as a potential therapeutic agent in the management of Alzheimer’s disease, with promising results. In particular, studies have shown that lecithin supplementation can improve cognitive performance, memory function, and overall brain health in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. These positive outcomes may be attributed to lecithin’s ability to support neuronal membrane integrity, enhance neurotransmission, and reduce oxidative stress. Continued research is needed to determine optimal dosages and identify specific subgroups of Alzheimer’s patients who may benefit the most from lecithin treatment.
Some key points on lecithin and Alzheimer’s disease:
- Lecithin is a potential therapeutic agent for managing Alzheimer’s disease.
- Lecithin supplementation can improve cognitive performance and memory function.
- Lecithin supports neuronal membrane integrity and enhances neurotransmission.
- Lecithin treatment may reduce oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s patients.
“Continued research is needed to determine optimal dosages and identify specific subgroups of Alzheimer’s patients who may benefit the most from lecithin treatment.”
Lecithin Co-Administration With Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone For Alzheimer’s Disease
One approach to address the complexities of Alzheimer’s disease is the co-administration of lecithin with thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). TRH is a peptide hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal activity and improving cognitive function.
When combined with lecithin, TRH has shown potential as a therapeutic option in Alzheimer’s disease. Lecithin’s ability to support neurotransmission and neuronal membrane integrity, coupled with TRH’s neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties, may lead to improved outcomes for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Further research and clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of this combined treatment approach.
Long-Term Administration Of Physostigmine And Lecithin For Improved Memory In Alzheimer’s Disease
Memory impairment is a key feature of Alzheimer’s disease, highlighting the need to enhance memory function. Promising results have been observed with the long-term use of physostigmine, an anticholinesterase drug, in conjunction with lecithin supplementation. This combination therapy aims to improve memory by inhibiting acetylcholine breakdown and providing a precursor through lecithin. Encouragingly, preliminary studies suggest that long-term administration of physostigmine and lecithin can enhance memory and overall cognitive performance in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. However, further research is required to confirm these findings and determine the optimal dosage and treatment duration.
- Memory impairment is a hallmark feature of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Long-term administration of physostigmine, an anticholinesterase drug, in combination with lecithin supplementation, has shown promise in improving memory in Alzheimer’s patients.
- This combination therapy aims to inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine and provide a precursor through lecithin supplementation.
- Preliminary studies indicate encouraging results for long-term administration of physostigmine and lecithin, leading to improved memory and overall cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s patients.
- Further research is necessary to confirm findings and establish optimal dosage and treatment duration.
High-Dose Phosphatidylcholine In Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
Phosphatidylcholine, a crucial component of lecithin, has shown promising results in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial revealed that high-dose phosphatidylcholine supplementation resulted in early positive outcomes in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Phosphatidylcholine has been suggested to enhance brain function by improving neuronal membrane integrity, facilitating neurotransmission, and reducing inflammation.
The findings highlight the potential of high-dose phosphatidylcholine as an adjunct therapy for Alzheimer’s disease, offering hope for improved cognitive function and quality of life for affected individuals. Further research is needed to establish the optimal dosage, duration, and long-term effects of this treatment.
- Phosphatidylcholine is a crucial component of lecithin.
- High-dose phosphatidylcholine supplementation showed early positive outcomes in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
- Phosphatidylcholine enhances brain function by improving neuronal membrane integrity, facilitating neurotransmission, and reducing inflammation.
“The findings highlight the potential of high-dose phosphatidylcholine as an adjunct therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.”
Lecithin Attenuation Of Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to hepatic fibrosis, a condition characterized by the accumulation of fibrous tissue in the liver. Lecithin, with its hepatoprotective properties, has been investigated as a potential treatment to attenuate alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis. Studies have shown that lecithin supplementation can reduce oxidative stress, inhibit inflammatory processes, and improve liver function in individuals with alcohol-induced liver damage. By promoting liver regeneration and supporting cellular integrity, lecithin holds promise as a therapeutic agent in the management of hepatic fibrosis associated with chronic alcohol abuse. Further research is needed to confirm these findings and determine optimal dosing and treatment protocols.
Lecithin Treatment In Friedreich’s Ataxia
Friedreich’s ataxia is a rare genetic disorder characterized by progressive neurodegeneration, resulting in impaired coordination and muscle strength. Lecithin treatment has been studied in relation to Friedreich’s ataxia and has shown positive effects. By providing essential phospholipids, lecithin supplementation may improve the integrity of neuronal membranes, enhance neuronal function, and potentially slow disease progression. However, further research is needed to determine the optimal dosage, treatment duration, and long-term effects of lecithin in individuals with Friedreich’s ataxia.
Lecithin Combined With Tacrine Treatment
Tacrine and Lecithin Combination Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease
Tacrine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, is commonly used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. One potential approach to enhancing the treatment outcomes of Alzheimer’s is the combination of tacrine with lecithin supplementation.
Lecithin, an essential phospholipid, acts as a precursor for acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in cognitive function. Tacrine, on the other hand, inhibits the breakdown of acetylcholine. When these two components are combined, a synergistic effect occurs, potentially improving cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Promising results from preliminary studies have indicated that the combination therapy of tacrine and lecithin leads to improved memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s patients. These findings suggest that this treatment approach may hold potential in enhancing the lives of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
However, it is important to note that further research is necessary to establish the optimal dosage, treatment duration, and long-term effects of this combined treatment approach. More comprehensive studies are needed to fully understand the effectiveness and safety of this therapy.
In conclusion, lecithin offers multiple potential benefits for various neurological conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease. It shows promise as a therapeutic agent, not only for improving memory and cognitive function but also for preventing respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants and providing protective effects in alcohol-induced liver damage. Furthermore, lecithin has shown positive impacts on rare genetic disorders such as Friedreich’s ataxia. However, additional research is required to determine the optimal dosages, treatment regimens, and long-term effects of lecithin for each specific condition. Through continued investigation, lecithin may emerge as a valuable tool for promoting optimal brain function and improving the quality of life for individuals with neurological disorders.
Key points:
- Tacrine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor commonly used in Alzheimer’s disease treatment.
- Combining tacrine with lecithin supplementation has shown potential to enhance treatment outcomes.
- Lecithin acts as a precursor of acetylcholine, while tacrine inhibits its breakdown, resulting in a synergistic effect.
- Preliminary studies have suggested improved memory, attention, and cognitive performance in patients receiving the combined therapy.
- Further research is needed to determine the optimal dosage, treatment duration, and long-term effects of this approach.
💡
You may need to know these questions about lecithin
What is the lecithin used for?
Lecithin serves various purposes due to its role in the body’s metabolic process and fat transportation. When consumed, lecithins convert into choline, contributing to the production of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This neurotransmitter plays a crucial role in the brain and nervous system communication. In addition, lecithin finds common use as a food additive, particularly for its ability to bind and emulsify different ingredients together, combining foods effectively. This function makes it a practical and popular choice in various food products.
Who Cannot take lecithin?
It is important to note that individuals with a severe allergic reaction to lecithin, its ingredients, or derivatives such as eggs, soy, fish, or sunflower should avoid taking lecithin. If you are uncertain about the ingredients, consulting with your pharmacist or healthcare provider for a complete list is recommended. Additionally, pregnant individuals should exercise caution with lecithin consumption as it can break down into choline.
Does lecithin help lose belly fat?
While there is no conclusive evidence to directly support the effectiveness of lecithin in losing belly fat, choline, a minor constituent of lecithin, could potentially aid in weight loss. Choline has been associated with improving metabolism and fat metabolism in the body, which suggests it might have a positive impact on reducing belly fat. Nevertheless, further research is needed to ascertain the direct correlation between lecithin, choline, and its effectiveness in losing belly fat.
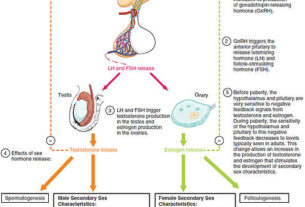
Does lecithin increase estrogen?
While soy lecithin does contain phytosterols that have been found to exert estrogenic effects in the human body, it is important to note that the extent to which lecithin increases estrogen levels still requires further research. These phytosterols have been used in the past by pharmaceutical companies to create human sex hormones. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before drawing any conclusions or making any significant dietary changes regarding estrogen levels in the body.
Reference source
https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-966/lecithin
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=19&contentid=lecithin
https://www.verywellhealth.com/lecithin-benefits-and-nutrition-4771091
https://www.vinmec.com/en/news/health-news/nutrition/can-lecithin-help-you-lose-weight/