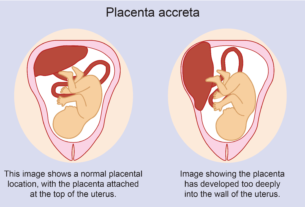
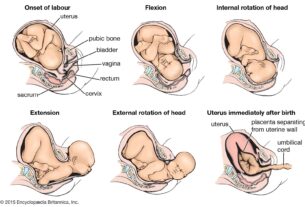
Are you curious about the mysterious and awe-inspiring journey of pregnancy?
Have you ever wondered how doctors are able to calculate the expected due date for a baby with remarkable accuracy?
Enter the world of the Last Menstrual Period, or the LMP, a key to unraveling the enigma of childbirth.
Embark on a fascinating exploration as we delve into the realm of this crucial marker, where science and miracle converge.
lmp
The acronym “LMP” stands for “last menstrual period.” It is used to calculate the expected date of delivery for a human baby, as pregnancy is typically measured in weeks.
By determining the first day of a woman’s last menstrual period, healthcare professionals can estimate when the baby might be due.
A typical human pregnancy is expected to last around 40 ?? 2 weeks from the LMP.
Key Points:
- LMP stands for “last menstrual period” and is used to calculate the expected date of delivery for a human baby
- Healthcare professionals use the first day of a woman’s last menstrual period to estimate the due date
- Pregnancy is typically measured in weeks
- A typical human pregnancy lasts around 40 ?? 2 weeks from the LMP
- LMP is important for determining the timeline of a pregnancy
- The acronym LMP is commonly used in the medical field
lmp – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The acronym “LMP” stands for “Last Menstrual Period” and is an essential piece of information used in estimating the due date of a pregnant woman.
2. In aviation, “LMP” can also refer to the “Last Maintenance Period,” which represents the time when an aircraft underwent its most recent comprehensive maintenance check.
3. “LMP” could stand for “Lunar Mapping and Photography,” a term used by astronauts to document and capture images of the moon’s surface during space missions.
4. In the world of music production, “LMP” is an abbreviation for “Low-Mid Frequencies,” indicating a specific range of sound frequencies that affect the overall tone and warmth of a recording.
5. LMP, or “Lowest Maintainable Population,” refers to a scientific concept that estimates the minimum number of individuals needed in a particular species or population to ensure long-term survival and prevent genetic deterioration.
1. What Is LMP?
The first step towards unraveling the mysteries of female fertility begins with understanding the concept of LMP, or Last Menstrual Period. LMP refers to the start date of a woman’s most recent menstrual cycle before conception. It denotes the beginning of the menstrual cycle and is crucial in calculating the expected date of delivery (EDD), commonly known as the due date.
2. Importance Of Calculating EDD
Calculating the Estimated Date of Delivery (EDD) is crucial for pregnant women and their healthcare providers. It plays a vital role in ensuring proper prenatal care, monitoring fetal growth, and preparing for childbirth. The EDD serves as a reference point throughout the gestational period, allowing expectant mothers to prepare themselves mentally and physically for the arrival of their precious baby.
3. Defining The First Day Of Last Menstrual Period
The first day of the last menstrual period (LMP) is the initial day of bleeding during the menstrual cycle. It is important to note that this date does not correspond to the date of ovulation or conception. Accurately determining the LMP is crucial for calculating the estimated due date (EDD). While the average cycle length for women is around 28 days, it is important to consider that variations are common. Healthcare professionals rely on tracking the LMP to estimate the gestational age.
4. Understanding The Pregnancy Timeline
Pregnancy is a journey that typically lasts for approximately 40 weeks or 280 days, starting from the first day of the woman’s last menstrual period. The entire pregnancy can be divided into three trimesters, each lasting for around 13 weeks.
The first trimester is an especially crucial stage in the development of the baby, as this is when major organs begin to form. During this period, the baby’s heart, brain, and other vital organs take shape, laying the foundation for future growth.
Moving on to the second trimester, this period is characterized by rapid growth and movement for the baby. The mother may start feeling the baby’s movements, and significant physical changes, such as weight gain and a visible baby bump, become more noticeable.
Finally, the third trimester is a time of final preparations for birth. The baby continues to grow and develop, with the lungs and other essential systems maturing in preparation for independent life outside the womb. The mother may experience discomfort due to the baby’s size and position, as well as increased frequency of doctor visits to ensure a smooth delivery.
Overall, understanding the different stages and milestones of pregnancy helps to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
5. The Role Of LMP In Estimating Delivery Date
LMP plays a crucial role in estimating the delivery date as ovulation and conception dates are often difficult to accurately determine.
-
Healthcare professionals rely on the LMP to make rough estimates based on the average length of a woman’s menstrual cycle.
-
However, it’s important to remember that this calculation method assumes a regular 28-day cycle, which may not be applicable for all women.
-
Any significant variations in cycle length or irregularities should be reported to the healthcare provider for a more precise calculation.
-
Communicate any variations in cycle length or irregularities to the healthcare provider.
- LMP helps estimate delivery date due to the challenges in determining ovulation and conception dates accurately.
- Calculation assumes a regular 28-day cycle, which may not apply to all women.
6. How Many Weeks Is A Human Pregnancy?
A human pregnancy typically lasts around 40 weeks, counting from the first day of the last menstrual period until the birth of the baby. This timespan is equivalent to approximately 9 months or 280 days. It is important to note that the duration of pregnancy can vary slightly, and pregnancies reaching 42 weeks are still considered within the normal range.
- A normal human pregnancy lasts around 40 weeks.
- The period begins from the first day of the last menstrual period.
- The duration of pregnancy is approximately 9 months or 280 days.
- Pregnancies reaching 42 weeks are still considered normal.
“The duration of pregnancy can vary slightly, with pregnancies reaching 42 weeks still considered within the normal range.”
7. Factors Affecting Pregnancy Duration
Although the average duration of pregnancy is 40 weeks, several factors can influence the length of gestation.
- First-time mothers often experience a longer pregnancy compared to women who have previously given birth.
- Age also plays a role, as women over the age of 35 tend to have shorter pregnancies than their younger counterparts.
- Additionally, genetics, ethnicity, and general health conditions can affect pregnancy duration.
It is important to note that the length of gestation can vary for each individual and should be monitored by healthcare professionals.
- Factors affecting pregnancy duration:
- First-time mothers
- Age (women over 35)
- Genetics
- Ethnicity
- General health conditions
8. The 40 ?? 2 Weeks Pregnancy Rule
The 40 ?? 2 weeks rule is a general guideline for calculating a woman’s due date. It suggests that childbirth is most likely to occur between 38 and 42 weeks of pregnancy. However, it is important to note that this is just an estimate, and the timing of birth can vary. Only about 5% of babies are born on their exact due date, so flexibility and patience are crucial during this period of anticipation.
Some key points to remember are:
- The 40 ?? 2 weeks rule is a general guideline for estimating due date
- Childbirth can occur between 38 and 42 weeks of pregnancy
- The timing of birth can vary
- Only about 5% of babies are born on their exact due date
“Flexibility and patience are key during this exciting period of anticipation.”
9. Tracking LMP For Accurate Due Date Calculation
To ensure an accurate calculation of the due date, expectant mothers should diligently track their LMP. This involves marking the date the menstrual cycle begins on a calendar or in a dedicated app. By providing this information to healthcare providers, they can make a more precise estimation of the gestational age and expected delivery date. Regular prenatal check-ups and ultrasounds further assist in monitoring the growth and development of the baby.
10. Using LMP To Plan For The Arrival Of Your Baby
Knowing the expected due date based on the LMP allows pregnant women and their families to prepare for the arrival of the little one. From organizing the nursery and gathering essential baby supplies to arranging maternity leave and notifying employers or clients, having a target date in mind helps in managing logistics and reducing stress.
While the actual day of delivery may differ, having a plan in place ensures a smoother transition into parenthood.
- Being aware of the expected due date helps in organizing the nursery and gathering essential baby supplies.
- It allows pregnant women to arrange maternity leave and notify employers or clients in advance.
- Having a target date in mind helps in managing logistics effectively.
- Although the actual day of delivery may vary, having a plan in place contributes to a smoother transition into parenthood.
“Having a due date in mind not only helps with planning but also eases the stress associated with the arrival of a new member in the family.”
💡
You may need to know these questions about lmp
What is the LMP?
The LMP, short for last menstrual period, is a crucial reference point used in pregnancy calculations. It marks the beginning of your menstrual cycle immediately before conceiving. This date is utilized in estimating the expected delivery date, typically falling 40 ?? 2 weeks from the LMP. By knowing the LMP, healthcare providers can track pregnancy milestones and ensure proper prenatal care for both the mother and the baby.
What is the LMP date for pregnancy?
The Last Menstrual Period (LMP) date for pregnancy is determined by adding 280 days (40 weeks) to the first day of the woman’s last menstrual period. This method is commonly used for estimating the due date of a pregnancy. It is calculated from the first day of the last menstrual period and allows healthcare professionals to determine the gestational age of the fetus.
What is LMP in delivery?
LMP, or Last Menstrual Period, refers to the first day of a woman’s last menstrual cycle before pregnancy. It is commonly used as a reference point to estimate the due date of a pregnancy. By counting 280 days from the LMP, healthcare providers historically determined the expected duration of a pregnancy. However, it is worth noting that while LMP is a widely-used method, it may not be as accurate as other means of determining due dates, such as ultrasound measurements that can provide more precise information about conception.
How do you calculate LMP?
To calculate LMP (last menstrual period), begin by identifying the initial day of the previous menstrual period. Then, subtract 3 months from that date. Finally, add 1 year and 7 days to obtain the LMP.
Reference source
https://healthinfo.healthengine.com.au/medical-glossary/last-menstrual-period-lmp
https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-pt/professional/multimedia/clinical-calculator/pregnancy-gestation-by-lmp-and-ultrasound-biometry
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536986/
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/calculating-a-due-date