In the realm of human anatomy, the fascinating and mystifying nature of the female reproductive system continues to astound us.
Among the myriad of conditions that can affect this intricate network lies the enigmatic world of the longitudinal vaginal septum.
A vertical divide that discretely cleaves the vagina into two distinct realms, this condition holds the power to disrupt the lives of those affected.
Join us as we venture further into this captivating realm, unraveling the complexities, symptoms, and potential treatment options that lie within.
longitudinal vaginal septum
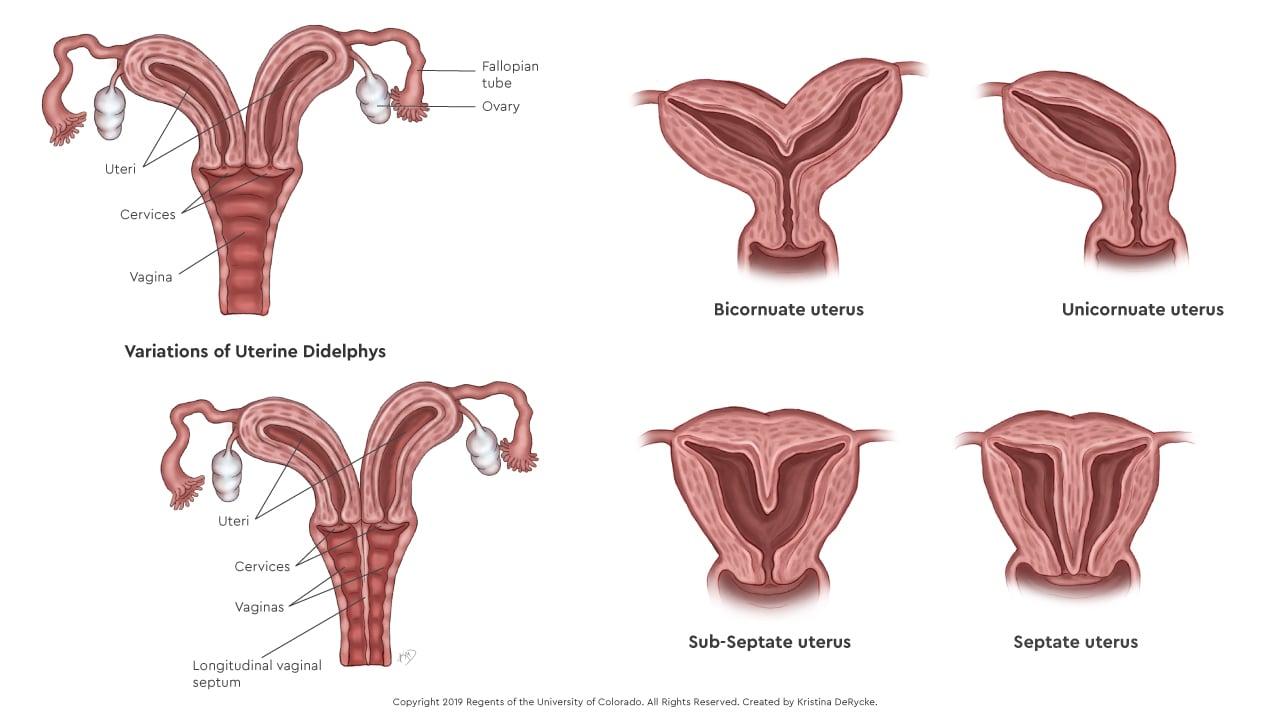
A longitudinal vaginal septum refers to a vertical or complete division of the vagina into two cavities.
This condition, also known as “double vagina” or longitudinal vaginal septum (LVS), occurs when the two parts of the vagina that should join together during development do not properly fuse.
The cause of this abnormal fetal development is unknown.
Girls with this condition may not have symptoms and may not be aware of it until puberty.
However, symptoms such as difficulty using tampons, discomfort during intercourse, pain when inserting or removing a tampon, menstrual blood leakage even when using a tampon, and pain during intercourse may arise during puberty.
Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical exam, and additional testing such as imaging.
Treatment strategies for longitudinal vaginal septum vary.
Additional testing such as ultrasound or MRI may be used for diagnosis before determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Key Points:
- Longitudinal vaginal septum involves a vertical or complete division of the vagina into two cavities.
- The condition occurs when the two parts of the vagina do not properly fuse during development.
- The cause of this abnormal fetal development is unknown.
- Girls with this condition may not have symptoms until puberty.
- Symptoms may include difficulty using tampons, discomfort during intercourse, and pain when inserting or removing a tampon.
- Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical exam, and additional testing such as imaging.
- Treatment strategies can vary and may involve additional testing such as ultrasound or MRI.
longitudinal vaginal septum – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. A longitudinal vaginal septum is a rare anatomical variation in which a membrane or wall divides the vagina into two separate compartments, each with its own opening.
2. The occurrence of a longitudinal vaginal septum can be congenital, meaning it is present at birth, or acquired due to conditions like trauma or surgery.
3. Women with a longitudinal vaginal septum may experience symptoms such as pain during intercourse, difficulty using tampons, or even bladder and bowel problems.
4. Surgery can be performed to correct a longitudinal vaginal septum and restore normal vaginal function. However, the decision to undergo surgery is typically based on the severity of symptoms and the impact on the individual’s quality of life.
5. While a longitudinal vaginal septum can be challenging to diagnose, a gynecological examination, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI, and consultation with a specialist are typically used to confirm the condition.
1. Introduction To Longitudinal Vaginal Septum
Longitudinal Vaginal Septum: Longitudinal vaginal septum, also referred to as “double vagina” or longitudinal vaginal septum (LVS), is a unique condition in which a girl’s vagina is divided into two cavities by a vertical wall of tissue. This condition is present from birth and occurs when the two parts that should normally join together during development fail to properly fuse. The exact cause of this abnormal fetal development is currently unknown, which further complicates the treatment and management of this condition.
Symptoms: Many girls with longitudinal vaginal septum may not experience any noticeable symptoms until they reach puberty. However, difficulties using tampons or discomfort during intercourse may arise during this transitional period.
To summarize in bullet points:
- Longitudinal vaginal septum is a condition where a girl’s vagina is divided into two cavities by tissue.
- It is present from birth and occurs due to the failure of proper fusion during development.
- The cause of this condition is unknown.
- Symptoms may arise during puberty, including difficulties using tampons or discomfort during intercourse.
2. Definition And Terminology
The longitudinal vaginal septum, also known as a vertical or complete vaginal septum, is a condition in which a girl’s vagina is divided into two separate cavities by a vertical wall of tissue. It is sometimes referred to as “double vagina” or longitudinal vaginal septum (LVS). The severity of the division can vary, ranging from a partial septum to a complete separation of the vaginal canal. Medical professionals may use different terms to describe this condition, leading to interchangeable usage.
A few important points about longitudinal vaginal septum are:
- It is a condition where the vagina is divided into two cavities by a vertical tissue wall.
- The severity of the division can range from partial to complete separation.
- Medical professionals may use different terms to describe this condition.
“Knowledge about the longitudinal vaginal septum is crucial in understanding and addressing this condition.”
3. Development And Causes
The development and causes of longitudinal vaginal septum remain unclear. It is believed to arise due to a failure in the fusion of the two parts of the vagina during fetal development. The exact mechanisms that lead to this abnormality are unknown, and further research is needed to determine the specific genetic or environmental factors involved. Currently, there is no conclusive evidence to pinpoint the exact cause of this condition, posing a challenge for both diagnosis and treatment.
- Longitudinal vaginal septum is a condition in which the two parts of the vagina fail to fuse during fetal development.
- The precise genetic or environmental factors that contribute to this abnormality are still unknown.
- Further research is required to uncover the underlying causes of this condition.
- The lack of conclusive evidence makes both diagnosis and treatment challenging for healthcare professionals.
“The development and causes of longitudinal vaginal septum remain unclear.”
4. Asymptomatic Presentation And Lack Of Awareness
One of the intriguing aspects of longitudinal vaginal septum is that girls with this condition may not experience any symptoms and may be unaware of their condition until puberty. This lack of awareness and symptomatology can make diagnosis and treatment challenging. As a result, it is essential for medical professionals to be knowledgeable about this condition and actively inquire about any potential reproductive health concerns during routine check-ups.
- Girls with longitudinal vaginal septum may not experience any symptoms until puberty.
- Lack of awareness and symptomatology can make diagnosis and treatment challenging.
- Medical professionals need to be knowledgeable about this condition and inquire about reproductive health concerns during routine check-ups.
5. Puberty Symptoms And Challenges
During puberty, girls with longitudinal vaginal septum may begin to experience symptoms and face unique challenges. The most common symptoms reported include pain during tampon insertion or removal, menstrual blood leakage even when using a tampon, and discomfort during sexual intercourse. These symptoms can be distressing for young girls who are navigating the changes and challenges of adolescence. Proper management and treatment are crucial to ensure the overall wellbeing and quality of life of affected individuals.
6. Common Symptoms: Tampon Use And Intercourse Discomfort
Two of the most prevalent symptoms experienced by girls with a longitudinal vaginal septum involve tampon use and discomfort during intercourse. The presence of a vertical wall of tissue can make it difficult to insert or remove tampons, leading to pain and discomfort. Additionally, sexual intercourse can also be problematic due to the division of the vaginal canal. This can cause pain and discomfort during sexual activity, affecting both physical and emotional wellbeing. The management of these symptoms requires careful consideration and individualized treatment approaches.
- Difficulty with tampon insertion and removal
- Pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse
The presence of a vertical wall of tissue in girls with longitudinal vaginal septum can lead to difficulties in tampon use and discomfort during intercourse. These symptoms can negatively impact both physical and emotional wellbeing. It is important to carefully consider and tailor treatment approaches to address these challenges.
7. Diagnosis Methods: Medical History, Physical Exam, And Imaging
Diagnosing longitudinal vaginal septum involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a thorough medical history, physical exam, and additional testing. Understanding the patient’s medical history can provide valuable insights into potential risk factors and underlying conditions.
During the physical examination, a healthcare professional will assess the anatomical structures of the reproductive system, looking for any signs of a vertical or complete vaginal septum. However, imaging techniques such as ultrasound or MRI may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the septum.
8. Testing Modalities: Ultrasound And MRI
To accurately diagnose longitudinal vaginal septum and determine the severity of the condition, additional testing modalities such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are often employed.
Ultrasound imaging can provide detailed visualization of the reproductive organs, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the presence and extent of the vaginal septum.
MRI offers a more comprehensive evaluation, providing high-resolution images that aid in treatment planning and defining the anatomy of the condition.
9. Treatment Approaches And Options
The treatment approaches for longitudinal vaginal septum vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors. In cases where the septum does not cause significant symptoms or interfere with reproductive health, conservative management may be recommended, focusing on symptom alleviation and education on sexual health. Surgical intervention is often necessary for severe cases or when symptoms significantly impact the patient’s quality of life. Surgical options include septoplasty to remove or reshape the septum and restore normal vaginal anatomy.
10. Conclusion: Variability In Longitudinal Vaginal Septum Treatment Strategies
Longitudinal vaginal septum, also known as “double vagina” or LVS, is an uncommon condition where a girl’s vagina is divided into two cavities by a vertical wall of tissue. The causes of this condition remain unknown, and many girls may be unaware of their condition until they reach puberty. Symptoms can include difficulty using tampons and discomfort during intercourse. Diagnosing longitudinal vaginal septum involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a medical history, physical exam, and imaging. Treatment approaches vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors, with surgery often being necessary for significant symptoms. Understanding this condition and its treatment strategies is essential for healthcare professionals to provide appropriate care and support to affected individuals.
💡
You may need to know these questions about longitudinal vaginal septum
What is longitudinal Vagunal septum?
A longitudinal vaginal septum is a condition where a septum, or a dividing wall, runs along the length of the vagina, creating two separate canals within the vagina. Unlike an obstructed hemi vagina where the septum partially blocks and divides half of the vagina, a longitudinal vaginal septum does not impede menstrual outflow. This unique anatomy can present various challenges and considerations in terms of sexual intercourse and reproductive health.
What is the recovery time for longitudinal septum surgery?
Recovery time for longitudinal septum surgery can vary depending on the extent of the procedure and individual healing factors. However, similar to other septum surgeries, patients can generally expect a relatively quick recovery. Most individuals are usually able to resume their daily activities within a few days following surgery, with complete recovery expected within a period of two to four weeks. While mild discomfort may be expected post-surgery, it is important to closely follow post-operative care instructions to ensure a smooth and successful healing process.
What are the complications of longitudinal uterine septum?
Longitudinal uterine septum can lead to various complications. One common complication is dystocia during delivery, which refers to difficult or prolonged labor. This can pose risks for both the mother and the baby. Another complication is dyspareunia, which is the medical term for painful intercourse. This can negatively impact a person’s sexual health and overall well-being. Additionally, hygienic problems may arise, necessitating a surgical incision of the longitudinal vaginal septum. It is worth noting that this anomaly is often associated with unilateral vaginal obstruction and ipsilateral renal agenesis in some cases, particularly in individuals with a didelphic or bicornuate uterus.
What does it mean to have a septum in your uterus?
Having a septum in your uterus means that there is a wall of tissue dividing your uterus into two separate cavities. This condition, known as a septate uterus, is characterized by a normal-shaped uterus with this additional tissue. Interestingly, some women may not be aware of having a septate uterus, as it can go unnoticed even during pregnancy and childbirth. In most cases, treatment is not necessary unless there are issues with recurrent pregnancy loss.
Reference source
https://www.texaschildrens.org/health/vertical-or-complete-vaginal-septum
https://www.childrenscolorado.org/conditions-and-advice/conditions-and-symptoms/conditions/vaginal-septum/
https://www.draliabadi.com/surgeries/vaginal-and-uterine-septums-surgery/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0015028205039683