In a world filled with complex biological processes, there are certain mysterious players that hold the key to our understanding.
Enter luteinizing hormone, a captivating enigma that ignites curiosity and leaves scientists eager to unlock its secrets.
Though our quest for information on this fascinating hormone may prove challenging today, rest assured, we are determined to delve deeper into its captivating realm.
Join us on this intellectual expedition as we explore the enigmatic world of luteinizing hormone.
luteinizing hormone
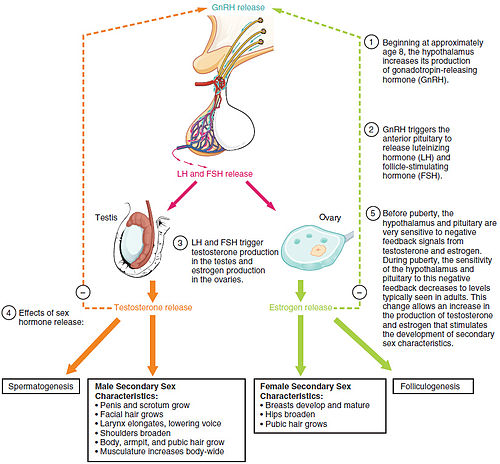
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is a hormone produced and released by the anterior pituitary gland in the brain.
It plays a crucial role in regulating the reproductive system in both males and females.
In females, LH stimulates the release of an egg from the ovary during menstruation.
This process is known as ovulation.
In males, LH stimulates the production and release of testosterone, a hormone responsible for the development and maintenance of male reproductive tissues and secondary sexual characteristics.
Overall, LH is a vital hormone that is essential for proper reproductive function in both sexes.
Key Points:
- LH is produced and released by the anterior pituitary gland in the brain.
- It regulates the reproductive system in males and females.
- In females, LH triggers ovulation and the release of an egg from the ovary.
- In males, LH stimulates the production and release of testosterone.
- Testosterone is responsible for male reproductive tissue development and secondary sexual characteristics.
- LH is crucial for proper reproductive function in both sexes.
luteinizing hormone – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Luteinizing hormone (LH) is responsible for triggering ovulation in women and the production of testosterone in men.
2. LH is also found in both males and females during puberty and helps stimulate the maturation of reproductive organs.
3. Luteinizing hormone levels fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, with a surge in LH indicating the release of an egg during ovulation.
4. In some rare cases, LH levels can rise in men, potentially leading to decreased testosterone production. This condition is known as primary testicular failure.
5. Luteinizing hormone can play a crucial role in diagnosing certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women and hypogonadism in men.
Introduction To Luteinizing Hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is a hormone produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland in both males and females. It is an important player in the complex orchestration of the reproductive system, working in conjunction with other hormones, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), to regulate the menstrual cycle in women and stimulate the production of testosterone in men.
LH is crucial for the proper functioning of the reproductive system and plays a significant role in fertility and hormonal balance.
Bullet points:
- LH is produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
- It works with FSH to regulate the menstrual cycle in women.
- It stimulates testosterone production in men.
“LH is crucial for the proper functioning of the reproductive system and plays a significant role in fertility and hormonal balance.”
Functions And Importance Of Luteinizing Hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH) serves several critical functions in the body. In women, LH plays a pivotal role in regulating the menstrual cycle. It stimulates the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles, preparing them for ovulation. LH also triggers the release of an egg from the dominant follicle during ovulation.
In men, LH stimulates the production of testosterone by the Leydig cells in the testes, ensuring proper sperm production and development.
The importance of LH in reproductive health cannot be overstated. It is necessary for the development and release of eggs in women and the production of testosterone in men. LH also plays a role in maintaining hormonal balance and supporting overall reproductive function. Without adequate LH levels, fertility can be compromised, leading to difficulties in conceiving and maintaining a pregnancy.
Luteinizing Hormone And The Reproductive System
Luteinizing hormone is a crucial hormone in regulating the reproductive system. It works alongside Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) in women to control the menstrual cycle. Initially, an increase in LH levels stimulates the maturation of ovarian follicles. The dominant follicle then starts producing higher levels of estrogen, which results in a surge of LH. This surge is what triggers ovulation, the release of the egg from the follicle. LH also helps the ruptured follicle transform into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone – a hormone necessary for maintaining a pregnancy.
In men, LH stimulates the Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone. Testosterone is essential for proper reproductive function as it promotes the development of sperm cells. By playing a vital role in maintaining adequate testosterone levels, LH ensures healthy sperm production, fertility, and overall reproductive function.
Key points:
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) is crucial for regulating the reproductive system.
- In women, LH works alongside FSH to control the menstrual cycle.
- LH triggers the maturation of ovarian follicles and the release of the egg during ovulation.
- LH also supports the transformation of the ruptured follicle into the corpus luteum.
- In men, LH stimulates the Leydig cells to produce testosterone.
- Testosterone is crucial for proper sperm development and overall reproductive function.
Luteinizing Hormone And Menstrual Cycle Regulation
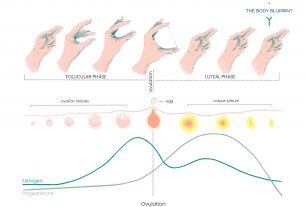
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle in women. It stimulates the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles during the follicular phase (first half of the cycle). The developing follicles produce estrogen, which inhibits the release of LH.
As the cycle progresses, estrogen levels rise, triggering a surge in LH secretion. This surge is responsible for ovulation, the release of the egg from the dominant follicle. After ovulation, LH facilitates the transformation of the ruptured follicle into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone prepares the uterine lining for implantation and provides support for early pregnancy if fertilization occurs.
Luteinizing Hormone And Ovulation
Ovulation is the release of a mature egg from the ovary, which is a crucial event in the menstrual cycle. The role of Luteinizing hormone (LH) is essential in triggering this process. During the follicular phase, estrogen levels gradually increase until they reach a threshold that leads to a surge in LH secretion. This surge stimulates the final maturation of the dominant follicle and ultimately triggers ovulation.
It is important to note that the surge in LH levels precedes ovulation by approximately 24-36 hours, creating optimal conditions for fertilization to occur. Once the egg is released from the ovary, it begins its journey down the fallopian tube, where it can potentially be fertilized by sperm. In the event that fertilization does not take place, the unfertilized egg is eventually expelled from the body during menstruation.
Luteinizing Hormone And Male Reproduction
While often associated with female reproductive health, luteinizing hormone (LH) also plays a crucial role in male reproduction. In men, LH stimulates the Leydig cells in the testes, promoting the production of testosterone. Testosterone is essential for the development and maturation of sperm cells, ensuring optimal fertility and reproductive function.
LH levels in men are relatively stable, with slight fluctuations throughout the day. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland release LH in response to testosterone levels, maintaining a delicate balance. Low levels of LH can lead to decreased testosterone production, affecting sperm development and overall reproductive function. Male fertility can be impacted by abnormalities in LH levels, requiring medical intervention to restore hormonal balance.
Role Of Luteinizing Hormone In Hormonal Balance
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a critical role in maintaining hormonal balance throughout the reproductive system. In women, LH works alongside FSH to ensure proper development and release of eggs. Imbalances in LH levels can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in the body. For example, high LH levels relative to FSH can indicate a condition known as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can result in irregular menstrual cycles and difficulties in conceiving.
In men, LH levels are closely tied to testosterone production. Imbalances in LH can lead to decreased testosterone levels, affecting reproductive health and overall well-being. Hormonal imbalances can have wide-ranging effects on fertility, sexual function, and overall health, highlighting the importance of proper LH regulation.
Luteinizing Hormone And Fertility Treatment
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a significant role in fertility treatment, especially in assisted reproductive technologies such as in-vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI). LH levels are closely monitored and may be supplemented to ensure optimal timing for egg retrieval or artificial insemination.
For women undergoing fertility treatment, medications containing LH or LH-releasing hormones may be prescribed to stimulate follicle development and induce ovulation. These medications help regulate the release of eggs and increase the chances of successful conception.
In men, LH supplementation may be considered if testosterone levels are low. This can help stimulate the production of testosterone, supporting sperm development and overall reproductive function.
- LH plays a significant role in fertility treatment
- LH levels are closely monitored and may be supplemented for optimal timing
- Medications containing LH or LH-releasing hormones stimulate follicle development and induce ovulation
- LH supplementation in men can support sperm development and overall reproductive function
Abnormalities And Disorders Related To Luteinizing Hormone
Abnormalities in luteinizing hormone (LH) levels can give rise to various disorders and conditions. In women, elevated levels of LH compared to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are often associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is a hormonal condition characterized by multiple cysts in the ovaries, menstrual irregularities, and fertility challenges. It can lead to difficulties in ovulation and conception.
Both men and women can experience abnormalities in LH levels due to issues with the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, or other hormonal imbalances. Low LH levels in men can contribute to decreased production of testosterone, affecting fertility and sexual function. In women, abnormalities in LH levels can disrupt the menstrual cycle and impair reproductive health.
- Some key points:
- Abnormalities in LH levels can lead to various disorders and conditions.
- In women, high LH levels relative to FSH are often associated with PCOS.
- PCOS is characterized by multiple ovarian cysts, menstrual irregularities, and fertility challenges.
- PCOS can cause difficulties in ovulation and conception.
- Abnormalities in LH levels can also affect men, contributing to decreased testosterone production and impacting fertility and sexual function.
- Both men and women can experience abnormalities in LH levels due to issues with the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, or other hormonal imbalances.
“Abnormal LH levels can significantly impact reproductive health in both men and women.”
Conclusion And Future Research On Luteinizing Hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is a vital hormone involved in the regulation of the menstrual cycle in women and the production of testosterone in men. It plays a significant role in maintaining hormonal balance, supporting fertility, and ensuring proper reproductive function.
In the future, further research on LH and its role in reproductive health may lead to advancements in fertility treatment, diagnostic methods, and overall understanding of hormonal balance. Improved understanding of LH abnormalities and disorders could potentially help individuals struggling with fertility challenges to conceive and maintain a healthy pregnancy.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of the reproductive system, LH remains a key player in the delicate dance of human reproduction, highlighting its importance in reproductive health and overall well-being.
💡
You may need to know these questions about luteinizing hormone
What happens when luteinizing hormone is low?
When luteinizing hormone is low, it can have significant consequences on reproductive health and development. If left untreated, LH deficiency can lead to infertility, as it impairs the body’s ability to produce testosterone and initiate puberty. This means that individuals with low LH levels may fail to develop secondary sexual characteristics and experience delayed or absent sexual maturation. In men, the decreased testosterone levels can result in a loss of muscle mass, decreased bone density, and a decline in sexual drive. Therefore, low levels of luteinizing hormone can have far-reaching effects on both fertility and hormonal balance.
What does high LH mean in females?
High levels of LH in females can indicate various underlying conditions. A particularly significant finding is that during nonovulatory times in the menstrual cycle, abnormally high LH levels suggest the onset of menopause. Additionally, elevated LH can also point towards the presence of a pituitary disorder or polycystic ovary syndrome. Conversely, low levels of LH may indicate a pituitary disorder, anorexia, malnutrition, or high levels of stress. Monitoring LH levels can therefore provide valuable insights into a woman’s reproductive health and overall well-being.
What happens when luteinizing hormone is high?
When luteinizing hormone levels are high, typically around day 14 of the cycle, the ovarian follicle ruptures, leading to ovulation. This surge in luteinizing hormone triggers the release of a mature egg from the ovary. After ovulation, during weeks three to four of the cycle, the remnants of the ovarian follicle transform into a structure known as the corpus luteum, which plays an essential role in the production of progesterone. Progesterone is necessary for the preparation of the uterus for possible implantation of a fertilized egg.
What is your LH level supposed to be?
The LH level, also known as luteinizing hormone, varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. Typically, during the follicular phase, LH levels can range from 1.9 to 14.6 IU/L, while during the luteal phase, they may vary between 0.7 to 12.9 IU/L. Your doctor would consider any LH level within these ranges to be normal before pregnancy. However, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider for accurate interpretation of your LH levels and their significance in your specific situation.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539692/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562219/
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=167&ContentID=luteinizing_hormone_blood
https://www.yourhormones.info/hormones/luteinising-hormone/