In the realm of medical marvels and perplexing conditions, one particular ailment captivates researchers and clinicians alike: metastatic choriocarcinoma.
This enigmatic adversary, with its intricate nature and elusive prognosis, has both perplexed and fascinated the scientific community.
Join me as we delve into the depths of this complex condition, unearthing its secrets and exploring the uncharted territories of medical science.
metastatic choriocarcinoma
Metastatic choriocarcinoma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that originates in the placenta during pregnancy.
It is characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal trophoblastic cells, which can spread to other parts of the body.
This type of cancer is considered highly malignant and can metastasize to the lungs, brain, liver, and other organs.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing metastatic choriocarcinoma, often involving a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Key Points:
- Metastatic choriocarcinoma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that starts in the placenta during pregnancy.
- Abnormal trophoblastic cells grow rapidly and can spread to other parts of the body.
- This type of cancer is highly malignant and can metastasize to the lungs, brain, liver, and other organs.
- Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing metastatic choriocarcinoma.
- Treatment often involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
metastatic choriocarcinoma – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Metastatic choriocarcinoma is an extremely rare and aggressive form of cancer that originates in the cells that would normally develop into the placenta during pregnancy.
2. Choriocarcinoma cells can produce high levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone typically secreted during pregnancy. As a result, patients with metastatic choriocarcinoma can have elevated hCG levels, which can aid in diagnosis and monitoring of the disease.
3. Despite its rarity, metastatic choriocarcinoma is considered one of the most curable types of cancer. This is primarily due to the fact that it is highly sensitive to chemotherapy, even when it has spread to other parts of the body.
4. Metastatic choriocarcinoma can occur in males, although it is much more common in females. In males, the tumor usually arises from abnormal testicular tissue called testicular germ cell tumors.
5. Choriocarcinoma cells have the ability to mimic the cells of the early embryo, which enables them to invade blood vessels and spread to distant organs through the bloodstream. This aggressive behavior makes early detection and aggressive treatment crucial for improving the chances of successful treatment.
Introduction To Metastatic Choriocarcinoma
Metastatic choriocarcinoma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that originates in the cells of the placenta during pregnancy. It is categorized as a gestational trophoblastic disease, meaning it develops from abnormal fertilization of an egg and is characterized by the rapid growth and proliferation of abnormal trophoblastic cells.
While choriocarcinoma occurs most commonly during pregnancy, it can also develop after a molar pregnancy, a miscarriage, or even without a previous pregnancy.
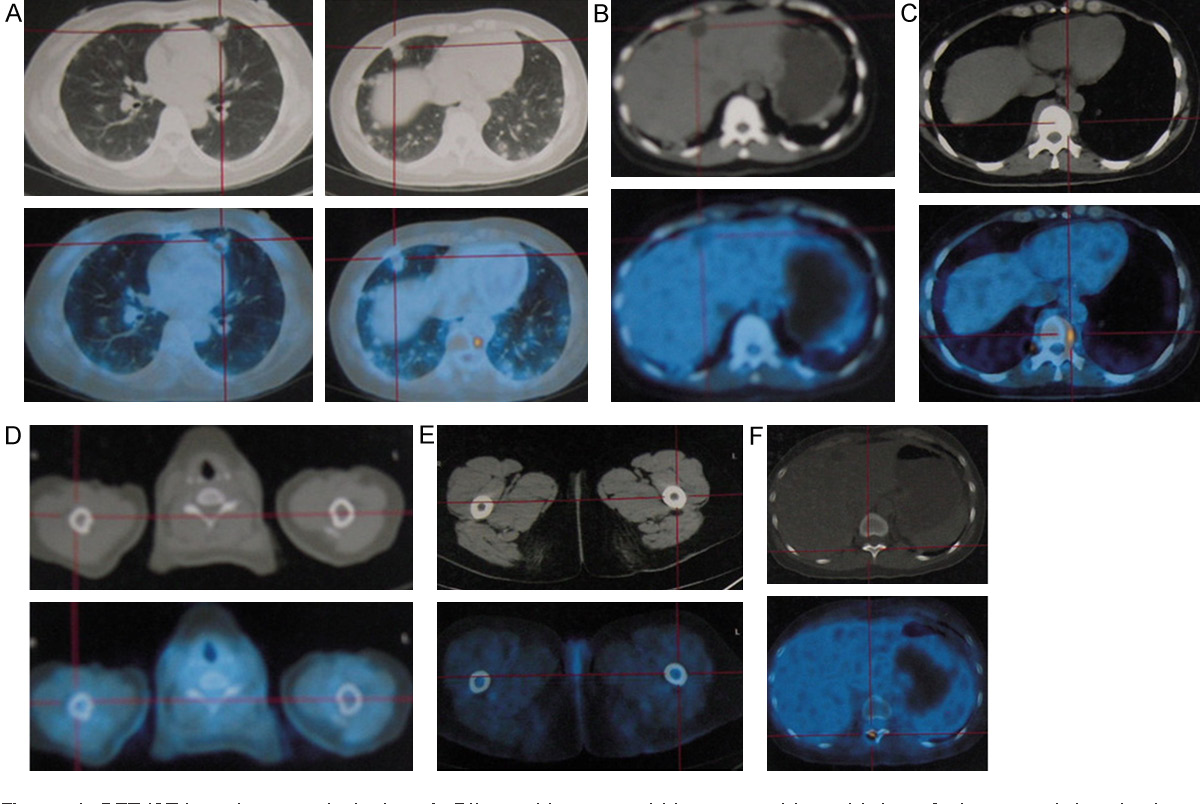
Metastatic choriocarcinoma is particularly concerning because it has the capacity to spread to other organs, including the lungs, liver, and brain, leading to life-threatening complications.
Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for improving the outcomes of patients with metastatic choriocarcinoma.
- Early detection is key
- Spread to lungs, liver, and brain
- risks of life-threatening complications
Understanding The Pathogenesis Of Metastatic Choriocarcinoma
The pathogenesis of metastatic choriocarcinoma involves the abnormal proliferation of trophoblastic cells. These cells typically form the placenta, but in choriocarcinoma, they grow uncontrollably and invade nearby tissues. This abnormal growth is thought to be due to genetic mutations that affect the regulation of cell growth and division. The exact causes of these mutations are still not fully understood, but factors such as genetic predisposition, hormonal factors, and environmental influences may play a role.
The rapid growth of choriocarcinoma cells also leads to angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, which provides the tumor with nutrients and oxygen necessary for its survival and spread to distant organs.
Key points:
- Metastatic choriocarcinoma involves abnormal proliferation of trophoblastic cells
- Genetic mutations contribute to uncontrolled growth and invasion
- Potential factors include genetic predisposition, hormonal factors, and environmental influences
- Angiogenesis supports tumor growth and spread to distant organs.
“The pathogenesis of metastatic choriocarcinoma involves the abnormal proliferation of trophoblastic cells.”
Diagnosing Metastatic Choriocarcinoma: Key Indicators
Diagnosing metastatic choriocarcinoma involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Doctors typically look for specific signs and symptoms, such as vaginal bleeding after a pregnancy, persistent elevated levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy, and the presence of certain ultrasound findings, such as molar changes within the uterus or metastatic lesions in other organs. However, these indicators are not definitive and require further confirmation through diagnostic procedures, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as CT scans or MRI scans), and biopsy of suspicious tissues. It is crucial to perform a thorough evaluation and accurate diagnosis to determine the extent of the disease and plan appropriate treatment strategies.
💡
You may need to know these questions about metastatic choriocarcinoma
What is the survival rate for choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma is a highly treatable form of cancer, especially when detected early. The survival rates for this condition are promising, with nearly all individuals with low-risk gestational choriocarcinoma surviving the disease. Even for those with high-risk gestational choriocarcinoma, the survival rate remains high at 94%. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment significantly contribute to positive outcomes for individuals with choriocarcinoma.
What is the 5-year survival rate of metastatic choriocarcinoma?
The 5-year survival rate of metastatic choriocarcinoma is challenging to determine precisely due to various contributing factors. However, based on the provided background information, the 5-year survival rate for postterm choriocarcinoma patients in the mentioned cohorts is approximately 86.7%. This survival rate reflects the success of complete remission achieved in 87.9% of cases, indicating an encouraging prognosis for patients. However, certain risk factors such as resistance to multiagent chemotherapy, liver metastasis, and a FIGO score greater than 12 may reduce survival rates in specific cases. Therefore, individual patient characteristics and response to treatment should be considered for a more accurate assessment of the 5-year survival rate in metastatic choriocarcinoma.
What is the most common site of metastatic spread of choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma, a fast-growing cancer that develops from trophoblastic cells, tends to metastasize to various sites in the body. Among these locations, the lungs and vulvovaginal region are frequently affected. This aggressive malignancy can also spread to the brain and liver, although they are slightly less common sites of metastatic involvement.
How quickly does choriocarcinoma spread?
Choriocarcinoma, a rare form of cancer that can emerge after pregnancy, has a propensity to spread rapidly. Although it may take several months or even years to manifest, once it does, it can progress swiftly, causing noticeable symptoms within a short span of time. This aggressive tumor has the capacity to metastasize and invade other organs, necessitating prompt intervention such as chemotherapy or surgical procedures. Fortunately, with appropriate treatment, a choriocarcinoma can often be effectively cured.
Reference source
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24863-choriocarcinoma
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4890243/
https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/gestational-trophoblastic-disease-gtd/invasive-mole-choriocarcinoma/symptoms
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4665990/