Are you tired of dealing with unpleasant side effects caused by various forms of contraception?
Well, what if I told you there was one tiny pill that could revolutionize your birth control experience?
That’s right, we’re talking about the oral contraceptive pill.
In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of this little wonder and explore how it has become a game-changer for women worldwide.
So, buckle up and get ready to discover the secrets behind this contraceptive marvel.
oral conrtaceptive pill
The oral contraceptive pill, commonly known as “the pill,” is a medication taken by women to prevent pregnancy.
It is a form of hormonal contraception that contains synthetic versions of the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
When taken consistently and correctly, the pill effectively inhibits ovulation, making it difficult for sperm to fertilize an egg.
Additionally, it thickens the cervical mucus, which further prevents sperm from reaching the egg.
The pill is considered a reliable and convenient method of birth control, but it does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Key Points:
- The oral contraceptive pill is a medication taken by women to prevent pregnancy.
- It contains synthetic versions of the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- It effectively inhibits ovulation, making it difficult for sperm to fertilize an egg.
- It also thickens cervical mucus, preventing sperm from reaching the egg.
- The pill is reliable and convenient birth control but does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
- Consistent and correct use of the pill is important for its effectiveness.
oral conrtaceptive pill – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The oral contraceptive pill was first introduced in the United States in 1960, but it was initially prescribed for the treatment of menstrual disorders rather than as a birth control method.
2. The development of the oral contraceptive pill was made possible due to the work of Gregory Pincus, a biologist and endocrinologist, along with his colleagues Min Chueh Chang and John Rock. They conducted extensive research on the effects of synthetic hormones on fertility.
3. The oral contraceptive pill is estimated to be as much as 99% effective when taken correctly. However, it is important to note that certain medications, such as antibiotics, can interfere with its effectiveness, so it’s always recommended to consult a healthcare professional.
4. Even though the oral contraceptive pill is commonly referred to as “the pill,” there are actually different types available, such as combination pills (containing estrogen and progestin) and progestin-only pills. The choice depends on a person’s medical history and individual needs.
5. In addition to preventing pregnancy, the oral contraceptive pill has several other health benefits. It can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers, and alleviate symptoms of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis.
History Of Oral Contraceptive Pill
The oral contraceptive pill, commonly known as “the pill,” has a long and fascinating history. It was first developed in the 1950s and gained popularity in the 1960s. The research leading to the development of the pill began in the early 20th century when scientists started exploring the potential of hormonal contraception. The breakthrough came in 1951 when scientists managed to synthesize a progestin hormone, which laid the foundation for the first contraceptive pill.
The first oral contraceptive pill, called Enovid, was approved by the FDA in 1960. It contained both estrogen and progestin hormones and was initially intended to treat menstrual disorders. However, it quickly gained recognition as a highly effective contraceptive method. Over the years, advancements in technology and medical research have led to the development of various formulations and types of oral contraceptive pills, providing women with more options and greater control over their reproductive health.
How Oral Contraceptive Pill Works
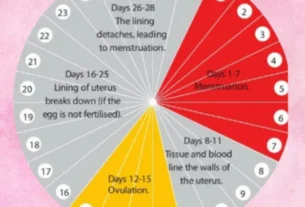
Understanding how the oral contraceptive pill works is crucial for anyone considering its use. The pill primarily works by preventing ovulation, the release of an egg from the ovaries, which is essential for pregnancy. Combination pills, which contain both estrogen and progestin hormones, function by suppressing the hormones responsible for stimulating the release of an egg. By inhibiting ovulation, the contraceptive pill significantly reduces the chances of pregnancy.
In addition to preventing ovulation, the pill also thickens the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to penetrate and reach the egg. Furthermore, some types of oral contraceptive pills alter the lining of the uterus, making it less receptive to implantation of a fertilized egg. It is essential to note that the effectiveness of the pill depends on consistent and correct usage. Missing pills or not taking them at the same time every day may decrease its contraceptive efficacy.
Common Side Effects Of Oral Contraceptive Pill
While the oral contraceptive pill is generally safe and well-tolerated, it can have side effects like any medication. It is important to discuss these potential side effects with a healthcare provider before starting any contraceptive method.
Some common side effects of the pill include:
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Spotting between periods
- Changes in menstrual flow
These side effects are typically mild and transient, and they often improve after a few months of use.
Other possible side effects can include:
- Headache
- Weight gain or loss
- Changes in mood
- Reduced libido
It is important to note that not all individuals experience these side effects, and they can vary from person to person. If any side effects persist or become severe, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for guidance and possible adjustments in the chosen contraceptive method.
Advantages Of Using Oral Contraceptive Pill
The oral contraceptive pill offers several advantages that make it a popular choice among women worldwide.
- Firstly, it is highly effective when used correctly, with a failure rate of less than 1% with perfect use.
- It provides women with control over their reproductive health and allows them to plan their pregnancies.
- The pill also offers additional benefits such as making periods more regular, reducing menstrual pain and heavy bleeding, and reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, such as ovarian and endometrial cancer.
Furthermore, the pill is easily reversible, meaning that fertility returns promptly after discontinuation. This makes it a convenient option for women who may want to conceive in the near future.
Additionally, some types of oral contraceptive pills are known to improve acne and reduce the symptoms of conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
However, it is important to note that individual experiences and benefits may vary, and it is crucial to choose the right pill in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Different Types Of Oral Contraceptive Pills Available
The availability of different types of oral contraceptive pills provides women with options to choose the one that best suits their needs and preferences. These pills can be categorized into two main types: combination pills and progestin-only pills.
Combination pills contain both estrogen and progestin hormones and are available in various formulations, such as monophasic, biphasic, and triphasic pills. These formulations differ in the levels of hormones they deliver during the menstrual cycle.
On the other hand, progestin-only pills, also known as mini-pills, only contain a progestin hormone. These are suitable for women who cannot or prefer not to take estrogen-containing pills due to certain health conditions or other considerations.
Progestin-only pills are taken continuously without a break, making them an option for women who wish to minimize or eliminate menstrual bleeding.
It is crucial to discuss the different types of pills with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate choice based on individual needs and medical history.
- Combination pills contain both estrogen and progestin hormones
- Progestin-only pills only contain a progestin hormone
- Combination pills are available in monophasic, biphasic, and triphasic formulations
- Progestin-only pills can be taken continuously without a break to minimize or eliminate menstrual bleeding
“It is crucial to discuss the different types of pills with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate choice based on individual needs and medical history.”
💡
You may need to know these questions about oral conrtaceptive pill
What is oral contraceptive pill?
The oral contraceptive pill, also known as OCP, is a medication that contains progestin and estrogen, or only progestin, and is taken orally once daily to prevent pregnancy. There are three types of OCP available: the combination pill, which contains both progestin and estrogen; the progestin-only pill, which only contains progestin; and the continuous use pill, which is taken without breaks. These pills work by suppressing ovulation and thickening the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. OCPs are a widely used and effective form of contraception, offering women a convenient and reliable option to help prevent unintended pregnancies.
What is the difference between birth control pills and oral contraceptives?
The term “birth control pills” and “oral contraceptives” are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference between the two. While birth control pills specifically refer to the hormonal pills taken orally to prevent pregnancy, oral contraceptives encompass a broader range of contraceptive methods that are administered orally. Oral contraceptives can include not only the pill but also other forms such as mini-pills, emergency contraception pills, and combination hormone patches or rings that are inserted in the mouth.
The main distinction lies in the comprehensiveness of the term “oral contraceptives,” which accounts for various methods of preventing pregnancy that are taken orally. On the other hand, “birth control pills” specifically refers to the oral contraceptive pills that contain hormones and are primarily used to prevent pregnancy. Thus, birth control pills can be seen as a subset of oral contraceptives, focusing solely on the oral hormonal contraception method in a pill form.
Which oral contraceptive pills are most common?
Monophasic 21-day pills are the most common type of oral contraceptive pills. These pills contain the same amount of hormone and are taken for 21 days, followed by a 7-day break. Examples of monophasic pills include Microgynon, Marvelon, and Yasmin. These pills provide a consistent hormone level throughout the cycle, offering effective contraception for users.
What are the three types of oral contraceptive pills?
Currently, there are three types of oral contraceptive pills available to women. The first is the combined estrogen-progesterone pill, which contains both hormones and works by suppressing ovulation and thickening cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg. The second type is the progesterone-only pill, also known as the mini-pill, which only contains progestin hormone and is suitable for women who are sensitive to estrogen. Lastly, the continuous or extended use pill allows women to skip their menstrual periods by taking active pills without the week of placebo pills, providing greater convenience and reducing the frequency of menstruation. These three types of pills offer different options for women, ensuring they can choose the most suitable oral contraceptive method for their needs.
Reference source
https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/fact-sheet/oral-contraceptive-pills/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/3977-birth-control-the-pill
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/combined-contraceptive-pill/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430882/