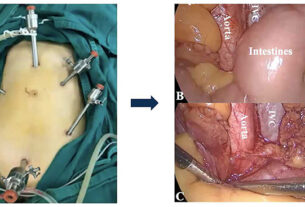
Are you familiar with the term “ovariosalpingectomy”?
If not, prepare to be captivated by a world of surgical precision, medical advancements, and the well-being of our furry friends.
This introduction explores the fascinating realm of reproductive surgeries for animals, delving into a spectrum of topics ranging from uterine diseases to postoperative pain management.
Discover the intricacies of these procedures and their significance across different regions of the world.
Join us on this enlightening journey into the realm of ovariosalpingectomy.
ovariosalpingectomy
Ovariosalpingectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing both the ovaries and the fallopian tubes from the female reproductive system.
This procedure is also commonly referred to as spaying in female dogs and cats.
Ovariosalpingectomy is performed for various reasons, including preventing reproduction, reducing the risk of certain uterine diseases, and treating or preventing tumors in the ovaries or fallopian tubes.
This surgery eliminates the source of hormones produced by the ovaries, which can help prevent the development of both benign and malignant tumors.
Ovariosalpingectomy is typically carried out under general anesthesia, and surgical times vary depending on the patient and the surgeon’s experience.
After the procedure, postoperative pain management is provided to ensure a comfortable recovery.
Ovariosalpingectomy is a commonly performed procedure in many countries, including the US, Canada, and Europe, and is considered the gold standard for spaying female dogs and cats.
Key Points:
- Ovariosalpingectomy is a surgical procedure that removes both the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- It is commonly referred to as spaying in female dogs and cats.
- This procedure is performed to prevent reproduction, reduce the risk of uterine diseases, and treat or prevent tumors in the reproductive organs.
- The surgery eliminates the source of hormones produced by the ovaries, which can help prevent the development of tumors.
- Ovariosalpingectomy is typically done under general anesthesia and surgical times vary.
- Postoperative pain management is provided to ensure a comfortable recovery.
ovariosalpingectomy – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Ovariosalpingectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of both the ovaries and the fallopian tubes, often performed as a treatment for certain gynecological conditions, such as ovarian or fallopian tube cancer.
2. In ancient Egypt, the removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes was a form of punishment reserved for women accused of adultery. This extreme procedure, known as ovariosalpingectomy, was intended to ensure their infertility.
3. The first successful ovariosalpingectomy surgery was performed in the late 19th century by renowned gynecologist Dr. Howard Kelly. The innovative procedure revolutionized the field of gynecological surgery and opened new possibilities for treating various reproductive disorders.
4. Ovariosalpingectomy has also been used in the past as a method of forced sterilization, particularly against marginalized groups such as people with disabilities or those considered “undesirable” by eugenicists. These unethical practices were thankfully discontinued in most countries during the 20th century.
5. Ovariosalpingectomy is sometimes performed as a preventive measure to reduce the risk of ovarian and fallopian tube cancers in individuals with a high genetic predisposition, such as those with a mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes. This proactive surgical intervention can significantly decrease the chances of developing these types of cancers in the future.
Importance Of Ovariosalpingectomy In Female Dogs And Cats
Ovariosalpingectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the ovaries and fallopian tubes in female dogs and cats, also known as spaying. This procedure is important for several reasons and plays a crucial role in reproductive choices.
One primary reason for performing ovariosalpingectomy is to prevent unwanted pregnancies in female pets. By removing the ovaries and fallopian tubes, the animal’s ability to reproduce is eliminated. This helps prevent overpopulation and reduces the risk of complications associated with pregnancy and birth.
Apart from preventing unwanted pregnancies, ovariosalpingectomy brings various health benefits for female dogs and cats. It significantly reduces the risk of uterine diseases, such as pyometra (a life-threatening infection of the uterus). Removing the reproductive organs also minimizes the risk of both benign and malignant tumors.
Ovariosalpingectomy Vs. Ovariectomy: Which Procedure Is Better?
When it comes to spaying female dogs and cats, there are two main procedures to consider: ovariosalpingectomy and ovariectomy. Ovariosalpingectomy involves removing both the ovaries and the fallopian tubes, while ovariectomy solely removes the ovaries.
Although both procedures effectively prevent unwanted pregnancies and offer similar health benefits, there are some key differences. Ovariosalpingectomy is considered the gold standard as it completely eliminates the reproductive organs, reducing the risk of reproductively related diseases. Ovariectomy, on the other hand, is a less invasive procedure and may have a faster recovery time for the pet.
Ultimately, the choice between ovariosalpingectomy and ovariectomy depends on various factors, such as the age and health of the animal, as well as the veterinarian’s recommendation. An informed discussion with a trusted veterinarian can help pet owners make the best decision for their furry companions.
Key Details About Ovariosalpingectomy: Insights Into Surgical Techniques
Ovariosalpingectomy is a surgical procedure that is performed under general anesthesia to remove the ovaries and fallopian tubes. The procedure involves making an incision in the abdominal area and carefully removing these organs.
The goal of ovariosalpingectomy is to minimize surgical trauma and ensure a smooth recovery for the animal. Minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery, are gaining popularity because they allow for smaller incisions and faster recovery times.
The duration of the surgery can vary depending on the size of the animal and the specific technique used. In general, an ovariosalpingectomy takes about 30 to 60 minutes to complete. However, it is important to note that surgical times may be longer in complex cases or if additional procedures are required.
Tackling Uterine Diseases With Ovariosalpingectomy
Uterine diseases, such as pyometra, can pose serious health risks to female dogs and cats. Pyometra is a life-threatening infection that occurs when the uterus becomes filled with pus. An effective way to prevent pyometra and other uterine diseases is through ovariosalpingectomy, which involves removing the uterus.
By removing the uterus through ovariosalpingectomy, the risk of developing pyometra is eliminated. Spaying the animal can be a life-saving measure, as pyometra mainly occurs when the uterus remains intact. In cases where pyometra has already developed, emergency ovariosalpingectomy is often the treatment of choice to prevent further complications.
Ovariosalpingectomy not only reduces the risk of pyometra, but also other uterine diseases, such as uterine tumors and uterine infections. By removing the uterus and the ovaries, the potential for these diseases to develop is significantly decreased, providing better long-term health outcomes for the animal.
Benefits of ovariosalpingectomy include:
- Elimination of the risk of pyometra
- Reduced risk of uterine tumors and infections
In conclusion, ovariosalpingectomy is an effective preventive measure and treatment for uterine diseases in dogs and cats, particularly pyometra. Removing the uterus and ovaries through this procedure can greatly improve the long-term health of the animal.
“By removing the uterus through ovariosalpingectomy, the risk of developing pyometra is eliminated.”
Addressing Tumors Through Ovariosalpingectomy: Benign Vs. Malignant
Tumors can have a significant impact on the reproductive organs of female dogs and cats, posing potential health risks. Ovariosalpingectomy offers an effective solution for addressing both benign and malignant tumors in these animals.
Benign tumors refer to non-cancerous growths that do not spread to other parts of the body. Although not life-threatening, they can still cause discomfort and impact the overall health of the animal. Ovariosalpingectomy is a procedure that completely removes these tumors, preventing further growth and potential complications.
In the case of malignant tumors, which are cancerous growths, ovariosalpingectomy is also beneficial. By removing the affected reproductive organs, the spread of cancer cells can be prevented, thereby reducing the risk of metastasis. Ovariosalpingectomy is often combined with other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, to offer the best chance of recovery for the animal.
It’s important to emphasize the significance of early detection and prompt treatment when dealing with tumors. Regular veterinary check-ups and proactive monitoring of the animal’s reproductive health play a crucial role in identifying any abnormalities or growths during their early stages. This allows for timely intervention and increases the likelihood of successful treatment through ovariosalpingectomy.
Minimizing Surgical Trauma: A Look At Ovariosalpingectomy Incisions
Surgical trauma, including incisions and tissue damage, is an inherent part of any surgical procedure, including ovariosalpingectomy. However, advancements in surgical techniques and technology have allowed for the minimization of surgical trauma, optimizing the recovery process for female dogs and cats.
Ovariosalpingectomy is typically performed through a ventral midline incision, running along the abdominal area of the animal. This incision allows the surgeon to have clear access to the reproductive organs and ensures efficient removal. The length of the incision may vary depending on the size of the animal.
In recent years, minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy, have become increasingly popular for ovariosalpingectomy. These techniques involve small incisions and the use of specialized surgical instruments and cameras to perform the surgery. Minimally invasive approaches offer several advantages, including reduced postoperative pain, smaller scars, and faster recovery times.
The choice of surgical technique depends on various factors, including the veterinarian’s expertise, the complexity of the case, and the overall health of the animal. Discussing different approaches and their potential benefits with a qualified veterinarian can help pet owners make an informed decision and ensure the best possible outcome for their furry companions.
- Surgical trauma can be minimized through advancements in surgical techniques and technology.
- Ovariosalpingectomy is typically performed through a ventral midline incision.
- Minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy, offer advantages like reduced postoperative pain and faster recovery times.
- The choice of surgical technique depends on various factors and should be discussed with a qualified veterinarian.
Anesthetic Considerations For Ovariosalpingectomy In Female Pets
Anesthesia plays a vital role in ensuring the comfort and safety of animals undergoing ovariosalpingectomy. Since the procedure involves a surgical incision and the removal of reproductive organs, it is essential to have the animal under general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and free from pain during the surgery.
Before the surgery, a thorough pre-anesthetic evaluation is conducted to assess the animal’s health and determine the most suitable anesthesia protocol. Factors such as age, breed, weight, and any underlying health conditions are taken into consideration to tailor the anesthesia to the individual animal.
During the surgery, the anesthesia team monitors the animal’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, to ensure their stability throughout the procedure. The anesthetic drugs used are carefully selected to provide the necessary level of anesthesia while minimizing the risk of complications.
Postoperatively, the animal is closely monitored during the recovery phase until they regain consciousness. Pain management is an essential aspect of the postoperative period, and appropriate analgesics are administered to ensure the animal’s comfort and well-being.
It is crucial for pet owners to discuss any concerns or questions regarding anesthesia with the veterinary team before the surgery. Open communication, coupled with the expertise of the anesthesia team, helps ensure the safety and overall success of the ovariosalpingectomy procedure.
Optimizing Surgical Times For Ovariosalpingectomy: What To Expect
The duration of an ovariosalpingectomy procedure can vary depending on several factors, including:
- The size of the animal
- The specific surgical technique used
- The complexity of the case
While each surgery is unique, there are general timeframes that pet owners can expect when their female dogs or cats undergo ovariosalpingectomy.
On average, an ovariosalpingectomy surgery can be completed within 30 to 60 minutes. However, it is essential to note that more complex cases or concurrent procedures may require additional time. The exact duration will be determined by the veterinarian based on the individual needs of the animal.
To ensure a smooth and successful surgery, it is essential for pet owners to follow all pre-operative instructions provided by the veterinary team. This may include:
- Fasting the animal prior to the surgery
- Discontinuing certain medications
- Scheduling the procedure at an optimal time
During the surgery, the veterinary team will closely monitor the animal’s vital signs and ensure their stability. The expertise and efficiency of the surgeon and support staff play a crucial role in minimizing surgical times while maintaining a high standard of care.
After the surgery, the animal will be closely monitored during the recovery phase until they regain consciousness. It is important for pet owners to follow all post-operative instructions provided by the veterinary team to facilitate a smooth recovery and ensure the best possible outcome for the animal.
Managing Postoperative Pain After Ovariosalpingectomy: Best Practices
Postoperative pain management is a critical aspect of ensuring the comfort and well-being of animals that have undergone ovariosalpingectomy. While the surgical procedure itself may cause some discomfort, appropriate pain management strategies can help minimize the pain experienced by the animal and promote a smoother recovery.
Immediately following ovariosalpingectomy, veterinarians typically administer pain medication to help control any surgical pain and discomfort. These medications may include both non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids, depending on the needs and condition of the animal.
In addition to pharmacological pain management, other interventions such as the use of warm compresses, minimizing physical activity, and providing a comfortable resting area can also contribute to the animal’s comfort. Regular monitoring and assessment of the animal’s pain levels are crucial to ensure that pain management protocols can be adjusted as needed.
Pet owners play a vital role in helping manage postoperative pain in their furry companions. Following all post-operative instructions provided by the veterinary team, including medication administration, wound care, and activity restrictions, is essential to facilitate proper healing and minimize discomfort.
Regular communication with the veterinary team is crucial during the recovery period. Pet owners should not hesitate to reach out to the veterinary team if they have any concerns or questions regarding their pet’s postoperative pain management. Prompt and appropriate pain management contributes to a smoother recovery and a better overall experience for the animal.
- Administer pain medication immediately after ovariosalpingectomy
- Use warm compresses to alleviate discomfort
- Minimize physical activity to promote healing
- Provide a comfortable resting area for the animal
“Following all post-operative instructions provided by the veterinary team, including medication administration, wound care, and activity restrictions, is essential to facilitate proper healing and minimize discomfort.”
Preserving A Healthy Uterus: Ovariosalpingectomy As A Preventive Measure
Ovariosalpingectomy (removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes) is an effective solution for addressing reproductive health issues in female dogs and cats while also playing a preventive role in preserving a healthy uterus. By completely removing the reproductive organs, the risk of uterine diseases, including infections and tumors, is significantly reduced.
Prevention is always better than cure, and ovariosalpingectomy offers pet owners the ability to proactively protect their pets from potential reproductive health issues. By spaying female dogs and cats at a suitable age, often before their first heat cycle, the risk of complications such as pyometra or uterine tumors is greatly minimized.
In addition to preventing potential health issues, ovariosalpingectomy can also provide behavioral benefits. Spayed animals are less likely to exhibit certain behaviors associated with their reproductive cycle, such as aggression during heat cycles, roaming, and marking territory with urine. This can greatly improve the pet’s overall quality of life and enhance the owner-pet relationship.
It is important for pet owners to consult with their veterinarian and discuss the optimal timing for ovariosalpingectomy for their female dogs and cats. Early intervention and preventive measures can help ensure the overall well-being and longevity of these beloved pets.
In conclusion, ovariosalpingectomy is a crucial procedure for female dogs and cats, offering numerous benefits such as preventing unwanted pregnancies, reducing the risk of uterine diseases and tumors, minimizing surgical trauma, and preserving a healthy uterus. By understanding the importance of this procedure and partnering with trusted veterinarians, pet owners can make informed decisions that empower women’s reproductive choices for their furry companions.
💡
You may need to know these questions about ovariosalpingectomy
What is the difference between Ovariohysterectomy and ovariectomy?
While both ovariectomy (OVE) and ovariohysterectomy (OVH) are surgical procedures for female sterilization, the main distinction lies in the organs that are removed. During ovariectomy, only the ovaries are removed, eliminating the source of reproductive hormones. On the other hand, ovariohysterectomy involves the removal of both the ovaries and the uterus, rendering the female incapable of reproducing as well as eliminating the possibility of certain reproductive-related health issues. This differentiation highlights the importance of understanding the specific procedure when discussing spaying options for female animals.
How do they do an ovariectomy on a dog?
During an ovariectomy in dogs, the ovarian pedicle is carefully clamped to secure it. Transfixing sutures are used to permanently ligate the ovarian artery and blood vessels, ensuring proper blood flow control. Next, a clamp is applied between the ovary and the uterine horn, and the vessels are ligated. Finally, the isolated ovary is surgically removed, completing the procedure.
What is removed during an Ovariohysterectomy?
During an ovariohysterectomy, the reproductive organs targeted for removal are either the ovaries or the uterus. These organs are carefully brought outside of the body and blood vessels supplying them are secured with ligatures before being excised. Once the ovaries and/or uterus are removed, the layers of the incision are meticulously closed, including the body wall, subcutaneous tissue, and skin. This surgical procedure effectively eliminates the designated reproductive structures, serving various purposes such as sterilization, treatment of certain conditions, or prevention of reproductive diseases.
What is another name for Ovariohysterectomy?
Another term used to refer to an ovariohysterectomy is simply spaying. Spaying involves the removal of both the ovaries and the uterus, effectively sterilizing a female dog. However, some veterinarians now perform a similar procedure called ovariectomy, which involves the removal of only the ovaries.
Reference source
https://www.friendshiphospital.com/friendship-news/spaying-your-pet-ovariectomy-versus-ovariohysterectomy/
https://wagwalking.com/treatment/ovariectomy
https://www.acvs.org/small-animal/ovariohysterectomy/
https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/spaying-in-dogs