Oxytocin: a seemingly unassuming hormone with a much deeper story than meets the eye.
Behind its unpronounceable name lies a captivating tale of childbirth, maternal bonding, and the intricacies of human social behavior.
But there’s more to this hormone than meets the eye.
Delve into the world of oxytocin as we uncover its secrets and explore its potential role in the realm of disorders and conditions.
Prepare to be amazed by the power of this tiny molecule.
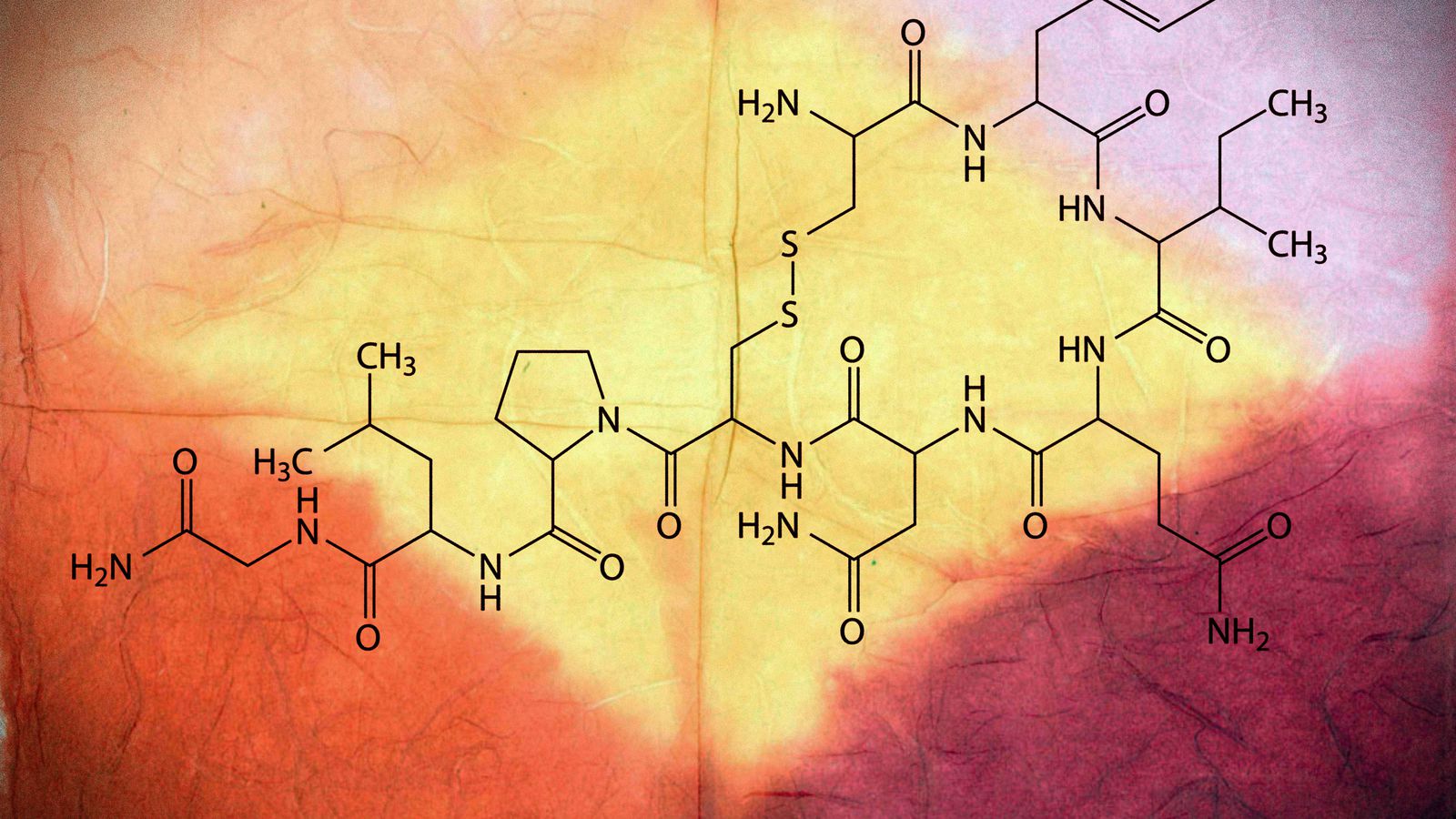
oxytocin
Oxytocin is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus and secreted into the bloodstream by the posterior pituitary gland.
It plays a crucial role in various physiological and psychological processes.
In women, oxytocin stimulates contractions of the uterus during childbirth and promotes milk movement in breastfeeding.
It is also used medically to induce labor, strengthen contractions, and reduce bleeding during childbirth.
In men, oxytocin is involved in sperm transport and testosterone production.
Furthermore, oxytocin acts as a chemical messenger in the brain, influencing sexual arousal, recognition, trust, attachment, and bonding.
It is often referred to as the “love hormone” or “cuddle chemical.” Oxytocin is regulated by positive feedback mechanisms and can be metabolized by oxytocinase.
It is released from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, with levels in the brain sometimes higher than peripheral levels.
Oxytocin has peripheral hormonal actions and actions in the brain.
Its effects can be influenced by context and the presence of familiar or unfamiliar individuals.
Research has shown that oxytocin is associated with various disorders such as addiction, depression, post-traumatic stress, anxiety, and anorexia.
Moreover, it has been found to have cognitive benefits, delay cognitive decline, and promote neural growth.
Oxytocin plays a crucial role in social bonding, pair bonding, and maternal behavior across different species.
It is also related to social emotions, fear, and anxiety.
Oxytocin levels and effects differ between males and females, with estrogen stimulating its release and testosterone suppressing it.
With its unique structure and important physiological and psychological impacts, oxytocin has become a subject of interest in various fields of research and has even been mentioned in songs and literature.
Key Points:
- Oxytocin is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland.
- It plays a crucial role in physiological and psychological processes.
- In women, it stimulates contractions during childbirth and promotes milk movement in breastfeeding.
- In men, it is involved in sperm transport and testosterone production.
- Oxytocin acts as a chemical messenger in the brain, influencing sexual arousal, trust, attachment, and bonding.
- It is associated with various disorders such as addiction, depression, anxiety, and anorexia, but also has cognitive benefits and promotes neural growth.
oxytocin – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone,” is also produced in men. Unlike some misconceptions, oxytocin is not solely produced by women.
2. Did you know that oxytocin can have a positive impact on our immune system? Research has shown that this hormone has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help in fighting off infections.
3. Oxytocin is not just responsible for promoting feelings of love and attachment. Studies have suggested that it may also play a role in promoting trust and strengthening social bonds between individuals.
4. In addition to its role in social bonding, oxytocin has a fascinating effect on our brain’s reward system. It can increase the release of dopamine, the neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, leading to a sense of happiness and contentment.
5. Many people are aware of the role oxytocin plays during childbirth and breastfeeding, but few know that it can also influence our behavior around money. Studies have indicated that oxytocin can make individuals more likely to be generous and generous when it comes to sharing their resources.
Function Of Oxytocin: Uterine Contractions And Milk Production
Oxytocin, a hormone produced in the hypothalamus and secreted into the bloodstream by the posterior pituitary gland, plays a crucial role in women’s reproductive functions.
- One of its primary functions is to stimulate contractions of the uterus during childbirth and lactation.
- During labor, oxytocin acts on the smooth muscles of the uterus, promoting strong contractions necessary for the birthing process.
- Additionally, oxytocin aids in lactation by promoting the movement of milk through the mammary glands in breastfeeding women.
In men, oxytocin also serves various purposes:
- It is involved in sperm transport, assisting the movement of sperm through the male reproductive system.
- Furthermore, oxytocin contributes to testosterone production, playing a role in the regulation of male reproductive functions.
Medical Uses Of Oxytocin: Inducing Labor And Reducing Bleeding
Oxytocin in Obstetrics
Oxytocin plays a crucial role in the field of obstetrics, where it is widely used by healthcare professionals. Its ability to induce labor and strengthen contractions has made it an integral tool in managing delays or complications during pregnancy.
In cases where labor needs to be induced, synthetic forms of oxytocin are administered by healthcare providers. This helps initiate contractions, kick-starting the labor process. By facilitating labor, oxytocin helps ensure a safe delivery for both the mother and the baby.
Furthermore, oxytocin is also employed to reduce bleeding during and after childbirth. This important function contributes to minimizing the risk of complications, promoting a positive outcome for both the mother and the baby.
Oxytocin And Brain Chemistry: A Key Chemical Messenger
Beyond its reproductive functions, oxytocin acts as a crucial chemical messenger in the brain. It plays a significant role in various psychological processes, including sexual arousal, recognition, trust, attachment, and bonding. Oxytocin is often referred to as the “love hormone” or “cuddle chemical” due to its involvement in emotional bonding and social interactions.
Oxytocin receptors are expressed in different areas of the brain, allowing oxytocin to influence behavior, emotions, and social cognition. The release of oxytocin during sexual activity, childbirth, and breastfeeding enhances bonding between individuals. Furthermore, it affects fetal brain activity during delivery, emphasizing the importance of oxytocin in early development.
- Oxytocin plays a crucial role in psychological processes, including sexual arousal, recognition, trust, attachment, and bonding.
- Oxytocin is known as the “love hormone” or “cuddle chemical”.
- Oxytocin receptors in the brain allow it to influence behavior, emotions, and social cognition.
- Oxytocin release is associated with enhanced bonding between individuals during sexual activity, childbirth, and breastfeeding.
- Oxytocin also affects fetal brain activity during delivery, highlighting its importance in early development.
“Oxytocin acts as a crucial chemical messenger in the brain, playing a significant role in various psychological processes.”
Oxytocin’S Role In Bonding And Attachment
Oxytocin, a hormone, is closely associated with human bonding and attachment. Studies indicate that the presence of oxytocin can enhance the likelihood of forming strong bonds between individuals and can even impact personal preferences, ultimately strengthening social connections. Notably, oxytocin has been observed to play a role in pair bonding among prairie voles, and it serves a similar function in fostering social bonds across various species, including humans and dogs.
Although oxytocin is implicated in initiating maternal behavior in humans, its role in maintaining this behavior is less significant. Nevertheless, oxytocin contributes to the emotional bond between a mother and her child during breastfeeding, fostering a sense of closeness and attachment.
Oxytocin As The “Love Hormone” Or “Cuddle Chemical”
Nicknamed the “love hormone” or “cuddle chemical,” oxytocin stands as a symbol of the emotional connection between individuals. Its role in promoting trust, recognition, and bonding has earned it this endearing title. Oxytocin is released during moments of intimacy, such as hugging, cuddling, and other physical touch experiences.
Songs and literature often mention oxytocin, highlighting its significance in human relationships and emotional experiences. It represents the chemical underpinning of love, comfort, and emotional well-being.
- Oxytocin is known as the “love hormone” or “cuddle chemical.”
- It plays a crucial role in promoting trust, recognition, and bonding between individuals.
- The release of oxytocin occurs during moments of intimacy, such as hugging and cuddling.
- Songs and literature often emphasize the importance of oxytocin in human relationships and emotional well-being.
- It forms the chemical foundation of love, comfort, and emotional connections.
Ongoing Research: Oxytocin And Disorders
The potential role of oxytocin in various disorders has sparked significant interest among researchers. Oxytocin is currently being studied for its impact on addiction, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and anorexia. Understanding the role of oxytocin in these conditions could pave the way for new treatments and therapeutic interventions.
Preliminary findings suggest that oxytocin possesses antidepressant-like effects and may be involved in depression. Oxytocin levels and effects also differ between males and females due to the influence of hormones such as estrogen and testosterone.
Regulation Of Oxytocin: Positive Feedback Mechanisms
The regulation of oxytocin involves positive feedback mechanisms. During childbirth, as contractions intensify, oxytocin levels rise, leading to stronger contractions, further increasing oxytocin release. This positive feedback loop ensures the progression of labor. Additionally, oxytocinase metabolizes oxytocin, limiting its duration of action.
Oxytocin’S Effects On The Brain And Peripheral Tissues
Oxytocin’s Role in Brain Chemistry and Peripheral Hormonal Actions
Oxytocin plays a crucial role not only in brain chemistry but also in peripheral hormonal actions. While most commonly known for its involvement in reproductive functions, oxytocin extends beyond that. Under normal conditions, it contributes to water regulation and may even suppress appetite. Additionally, oxytocin interacts with various tissues outside the brain, further contributing to reproductive functions in vertebrates.
What’s particularly interesting is that oxytocin levels in the brain can be significantly higher than those in the periphery. This highlights the importance of central oxytocin in mediating behavior and emotions.
Oxytocin In Social Bonding And Emotional Responses
Oxytocin’s impact on social bonding and emotional responses is multifaceted. It has been associated with both positive and negative emotions, demonstrating its complex role in human behavior. While oxytocin promotes trust, attachment, and ingroup bonding, it can also be implicated in social emotions such as envy and fear.
Moreover, nasal application of oxytocin has shown promise in alleviating impaired learning and promoting neural growth in animals. In a mouse model of early onset Alzheimer’s, oxytocin delays cognitive decline, offering potential therapeutic avenues for neurodegenerative disorders.
- Oxytocin has a complex role in human behavior, encompassing both positive and negative emotions.
- It promotes trust, attachment, and ingroup bonding.
- However, it can also be implicated in social emotions such as envy and fear.
- Nasal application of oxytocin has shown promise in alleviating impaired learning and promoting neural growth in animals.
- In a mouse model of early onset Alzheimer’s, oxytocin delays cognitive decline, offering potential therapeutic avenues for neurodegenerative disorders.
Various Forms And Historical Significance Of Oxytocin
Oxytocin has a unique structure and can exist in different forms, including both synthetic and naturally occurring variations. Its isolation and synthesis in 1954 led to significant advancements in our understanding of the hormone’s functions and paved the way for its use in medicine. Vincent du Vigneaud was awarded the Nobel Prize for his groundbreaking work on oxytocin.
Throughout history, oxytocin has held cultural and literary significance, appearing in songs and literature, symbolizing love, intimacy, and emotional connection. Its fascinating properties continue to captivate scientists, poets, and lovers alike, uncovering the power of the “love hormone.”
Oxytocin, the hormone produced in the hypothalamus and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland, holds great importance in the realms of reproductive functions, brain chemistry, bonding, and emotional attachment. Its impact on various disorders and its role in social interactions continue to be subjects of extensive research. With its unique structure and historical significance, oxytocin truly represents the intricate web of emotions and connections that define our human experience.
💡
You may need to know these questions about oxytocin
Why is oxytocin called the love drug?
Oxytocin has earned the nickname “love drug” due to its involvement in various behaviors associated with love and social bonding. It is often referred to as the “love hormone” because recent studies have shown its role in orgasm, social recognition, bonding, and maternal behavior. The release of oxytocin during intimate moments enhances the feeling of connection and trust between individuals, leading to the association of this hormone with love. Additionally, oxytocin promotes maternal behavior, strengthening the bond between mother and child, further supporting its association with love and nurturing relationships.
What triggers the release of oxytocin?
Oxytocin, a hormone known for its various physiological functions, is triggered to release in response to certain stimuli. One of the primary triggers for oxytocin release occurs during labor, breastfeeding, and sexual activity, where sensory nerves are activated, leading to the release of this hormone. Furthermore, oxytocin can also be released in response to low intensity stimulation of the skin, such as gentle touch, stroking, or exposure to warm temperature. These pleasant sensations can activate the release of oxytocin, contributing to feelings of relaxation and well-being.
Is oxytocin a happy drug?
Oxytocin is often associated with positive emotions, earning it the nickname “love drug” or “love hormone.” While its main function is to facilitate childbirth, oxytocin also promotes feelings of happiness and connection. When released in the body, oxytocin can enhance feelings of trust, bonding, and pleasure, contributing to an overall sense of well-being. Consequently, oxytocin can be considered a “happy drug” due to its ability to promote positive feelings and strengthen social connections.
Does oxytocin make you love?
Oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone,” indeed plays a significant role in fostering feelings of love and attachment. It acts as a powerful catalyst for pair bonding by enhancing one’s emotional state and promoting a sense of connection with their romantic partner. When oxytocin is released during moments of physical intimacy, such as hugging or kissing, it reinforces the bond between individuals, deepening their affection and love for one another.
Reference source
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/22618-oxytocin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3183515/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4290532/
https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/oxytocin-the-love-hormone