Pregnancy, a time filled with boundless anticipation and joy, can also bring some unexpected surprises.
Imagine the shock and concern that washes over a woman upon discovering she has partial placenta previa.
What does this mean?
What are the implications?
In this article, we delve deeper into this mysterious condition, exploring the risks, treatments, and the importance of medical intervention.
Brace yourself for a journey of understanding that will leave you enlightened and amazed.
partial placenta praevia
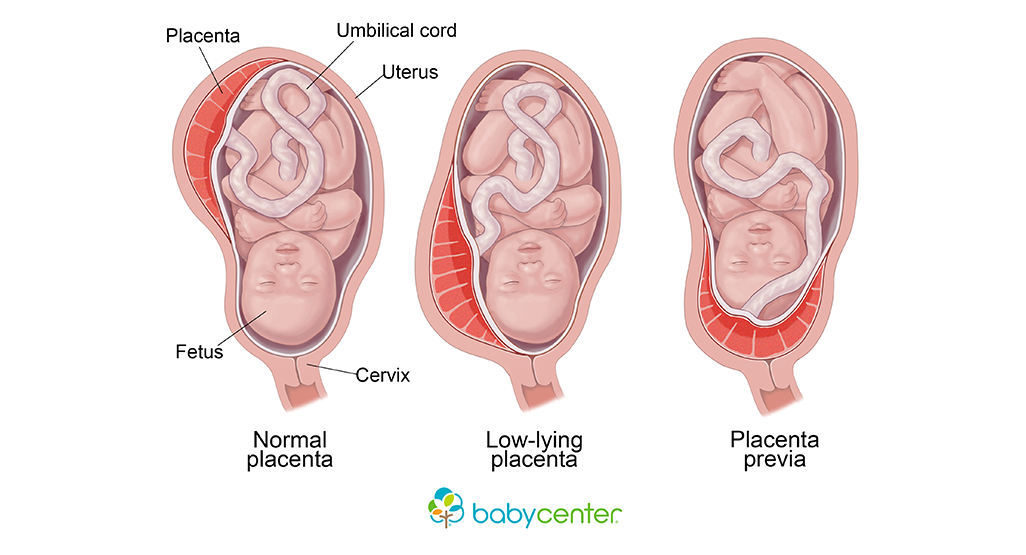
Partial placenta previa is a condition where the placenta implants at the bottom of the uterus, partially covering the cervix.
It is characterized by painless vaginal bleeding after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
This condition affects approximately 1 in every 200 pregnancies.
Some causes of vaginal bleeding during pregnancy include thinning and spreading of the bottom part of the uterus, sexual intercourse, and other complications such as placental abruption.
Diagnosis of partial placenta previa involves ultrasound scans and gentle speculum vaginal examination.
Treatment options depend on various factors, including the type and location of the placenta, amount of blood loss, gestational age of the baby, and the health of both the baby and mother.
Medical treatment during pregnancy may include bed rest, hospitalization, close monitoring, blood transfusion, and avoiding activities that trigger contractions.
Delivery is usually done through a caesarean section, and postpartum monitoring is necessary for potential complications.
It is important to seek prompt medical attention if experiencing vaginal bleeding during pregnancy.
Key Points:
- Partial placenta previa is when the placenta partially covers the cervix at the bottom of the uterus.
- It is characterized by painless vaginal bleeding after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- This condition affects about 1 in every 200 pregnancies.
- Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can be caused by thinning and spreading of the uterus, sexual intercourse, and other complications like placental abruption.
- Diagnosis is made through ultrasound scans and vaginal examination.
- Treatment options depend on factors such as placenta type and location, blood loss, gestational age, and the health of both mother and baby.
partial placenta praevia – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Due to the increased risk of bleeding during pregnancy, women with partial placenta praevia are advised to avoid strenuous activities that involve heavy lifting or intense physical exertion.
2. Research has shown that the majority of cases of partial placenta praevia resolve on their own as the pregnancy progresses, as the placenta gradually moves away from the cervix.
3. Partial placenta praevia is more commonly diagnosed during the second trimester of pregnancy, usually around 18 to 20 weeks.
4. Women with a history of previous cesarean section or multiple pregnancies are at a higher risk of developing partial placenta praevia.
5. In some cases of partial placenta praevia, a procedure called amniocentesis may be necessary to assess the levels of amniotic fluid and determine the best course of action for managing the condition.
Placenta Previa Explained
Placenta previa is a condition that occurs during pregnancy when the placenta implants at the bottom of the uterus, covering the cervix. The placenta, which is responsible for nourishing and oxygenating the developing fetus, typically attaches to the upper part of the uterus. However, in the case of placenta previa, it attaches to the lower part of the uterus, leading to potential complications.
Symptoms Of Placenta Previa
One of the primary symptoms of placenta previa is painless vaginal bleeding after 20 weeks of pregnancy. This bleeding occurs because when the placenta is anchored to the bottom of the uterus, any thinning or spreading of this area can cause bleeding. In some cases, sexual intercourse can also trigger bleeding.
Incidence Of Placenta Previa In Pregnancies
Placenta previa is a condition that affects about 1 in every 200 pregnancies. While it can occur in any woman, certain factors increase the risk. These include:
- Previous cesarean sections
- Previous surgeries on the uterus
- Multiple pregnancies (such as twins or triplets)
- Advanced maternal age
- Maternal smoking
It is important to be aware of these risk factors and seek appropriate medical care during pregnancy if any of these apply to you.
Other Causes Of Vaginal Bleeding During Pregnancy
It’s crucial to differentiate between vaginal bleeding caused by placenta previa and vaginal bleeding caused by other factors during pregnancy. Vaginal bleeding can occur due to various reasons such as hormonal changes, implantation bleeding, cervical changes, infections, miscarriage, or ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, it is important for pregnant women experiencing vaginal bleeding to seek medical attention to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Effects Of Thinning And Spreading Of The Uterus During Placenta Previa
When the bottom part of the uterus thins and spreads during placenta previa, it can lead to the following complications:
- Major bleeding: The thinning and spreading of the uterus can cause significant bleeding.
- Shock: The excessive bleeding may lead to shock, a life-threatening condition.
- Fetal distress: Placenta previa can cause distress to the fetus due to impaired blood flow.
- Premature labor or delivery: The condition may trigger early labor or result in a premature delivery.
- Health risks to the baby: The compromised blood supply can pose risks to the baby’s health.
- Emergency cesarean delivery: In some cases, an emergency cesarean delivery may be necessary to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases, the removal of the uterus may be required to control bleeding.
- Blood loss for the baby: Excessive bleeding can lead to blood loss for the baby, which can be dangerous.
- Maternal death: Placenta previa can be a life-threatening condition for the mother.
These potentially life-threatening complications highlight the importance of early detection and management of placenta previa.
- It is crucial to detect and manage placenta previa early to prevent complications.
- Prompt medical intervention should be sought if any symptoms or risk factors are present.
- Regular prenatal care and check-ups can help in early detection of placenta previa.
- Healthcare professionals should closely monitor pregnancies with a high risk of placenta previa.
“Early detection and management of placenta previa is vital to prevent severe complications.”
The Role Of Sexual Intercourse In Causing Bleeding
Sexual intercourse can cause bleeding in cases of placenta previa. The physical act of intercourse can disrupt the delicate balance of the placenta, leading to bleeding. It is crucial for healthcare providers to inform patients with placenta previa about the potential risks associated with sexual intercourse during pregnancy, ensuring they understand the importance of avoiding activities that may cause bleeding.
- Sexual intercourse can lead to bleeding in cases of placenta previa.
- The placenta can be disrupted during intercourse, resulting in bleeding.
- Healthcare providers must inform patients about the risks of sexual intercourse during pregnancy.
- Patients with placenta previa should understand the importance of avoiding activities that can cause bleeding.
“It is crucial for healthcare providers to inform patients with placenta previa about the potential risks associated with sexual intercourse during pregnancy, ensuring they understand the importance of avoiding activities that may cause bleeding.”
Complications Of Placenta Previa
Placenta previa is a condition that can have significant implications for both the mother and the baby. One of the most serious complications is major bleeding, which can lead to shock and may require immediate medical attention. The baby may experience fetal distress as a result of compromised blood supply, and in some cases, early labor or delivery may be necessary to ensure the well-being of both the baby and the mother. It is important to note that placenta previa can also have long-term health effects on the baby, so close monitoring and appropriate interventions after birth are essential.
Causes And Risk Factors For Placenta Previa
The exact causes of placenta previa are not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified. These risk factors include:
- Low implantation of the fertilized egg
- Abnormalities of the uterine lining
- Scarring of the uterine lining due to previous surgeries or infections
- Abnormalities of the placenta itself
- Multiple pregnancies
It is important for healthcare providers to evaluate these factors during prenatal care to assess the risk of placenta previa and provide appropriate monitoring and interventions.
Diagnostic Tests For Placenta Previa
Diagnosing placenta previa involves the use of various tests. Ultrasound scans are the most common and effective method to evaluate the location of the placenta and diagnose placenta previa. Additionally, healthcare providers may also perform a gentle speculum vaginal examination to assess the cervix and observe any signs of bleeding. Prompt diagnosis is crucial to ensure timely management and decrease the risk of complications.
- Ultrasound scans are the most common and effective method for diagnosing placenta previa.
- A gentle speculum vaginal examination is also used to assess the cervix and look for signs of bleeding.
“Prompt diagnosis is crucial to ensure timely management and decrease the risk of complications.”
Differentiating Placenta Previa From Placental Abruption
Placenta previa should be differentiated from another condition called placental abruption. Placental abruption occurs when the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery, causing painful vaginal bleeding.
While both conditions can cause bleeding during pregnancy, they have different causes and require different management strategies. Accurate diagnosis through ultrasound scans and clinical evaluation is essential to distinguish between the two conditions and provide appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, placenta previa is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires early diagnosis and careful management. Pregnant women experiencing painless vaginal bleeding should seek prompt medical attention to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Important factors that influence treatment options include:
- Type and location of the placenta
- Amount of blood loss
- Gestational age of the baby
- Health of both the baby and mother
Through close monitoring, careful management, and proper medical interventions, the risks associated with placenta previa can be minimized, ensuring the best possible outcomes for both the mother and baby.
💡
You may need to know these questions about partial placenta praevia
How serious is partial placenta previa?
Partial placenta previa is a concerning condition, as it has the potential to lead to serious complications. While placenta previa in the early stages of pregnancy may resolve on its own, if it persists into later stages, it can cause significant bleeding and other complications. Typically, the placenta is expected to grow away from the cervix and into the upper part of the uterus wall. Therefore, the presence of partial placenta previa warrants close monitoring and medical intervention to mitigate potential risks.
Can you deliver with partial placenta previa?
Partial placenta previa can still pose a risk for vaginal delivery. Although the degree of risk may vary depending on the severity of the condition, any amount of placenta covering the cervix increases the chance of severe bleeding. In most cases, healthcare providers will schedule a planned C-section to avoid complications. However, if the bleeding becomes too severe at any point, an emergency C-section may be necessary to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.
What are the 4 types of placenta previa?
There are two main types of placenta previa: complete and marginal previa. A complete previa occurs when the placenta fully covers the cervical os. On the other hand, a marginal previa is when the placenta is located near the edge of the cervical os but does not completely cover it. These classifications help healthcare professionals determine the severity of the condition and guide appropriate management and treatment strategies.
How often does partial placenta previa resolve?
Based on the background information provided, partial placenta previa has a relatively high resolution rate. Approximately 84% of complete placenta previas and 98% of marginal placenta previas resolved by a mean gestational age of 28.6 ±5.3 weeks. This suggests that the majority of cases of partial placenta previa tend to resolve spontaneously during pregnancy, providing a positive outlook for affected individuals.
Reference source
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/placenta-previa
https://www.marchofdimes.org/find-support/topics/pregnancy/placenta-previa
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24211-placenta-previa
https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/p/placenta-previa.html