In the vast realm of medical knowledge, certain terms hold a mysterious allure, captivating the curious minds of scientists and researchers alike.
One such term, “pelvic axis,” stands out, its significance shrouded in intrigue.
As we embark on a fascinating journey of discovery, we begin to unravel the enigmatic meaning behind this elusive phrase.
Join us as we delve into the depths of the pelvic axis, where understanding awaits.
pelvic axis
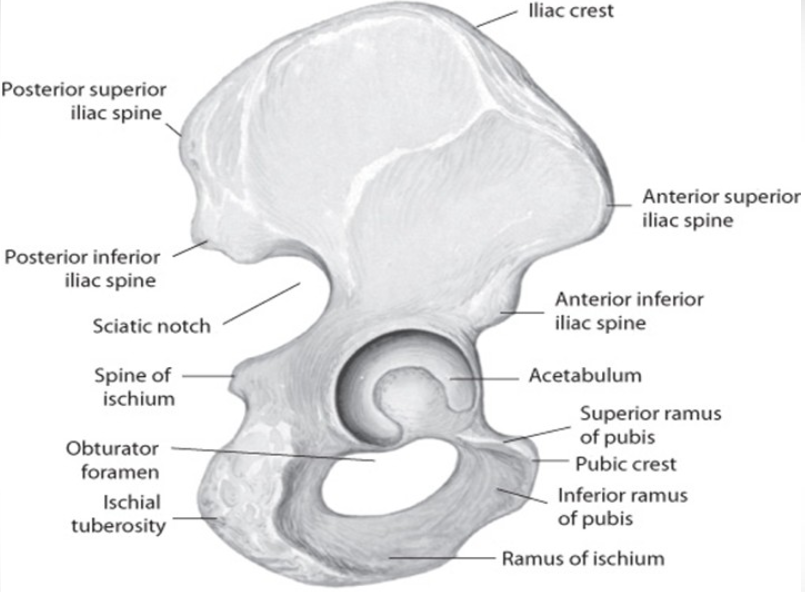
The pelvic axis refers to a line that runs through the center of the pelvis.
It serves as an important reference point for understanding the anatomical positioning and movements of the pelvis.
The pelvic axis is significant in various fields, including orthopedics, obstetrics, and biomechanics, as it helps in assessing and analyzing the alignment and rotation of the pelvis.
In summary, the pelvic axis is a crucial concept in understanding the pelvis’s structure and movement patterns.
Key Points:
- The pelvic axis is a line that runs through the center of the pelvis.
- It is an important reference point for understanding the anatomical positioning and movements of the pelvis.
- The pelvic axis is significant in orthopedics, obstetrics, and biomechanics for assessing and analyzing pelvis alignment and rotation.
- It is a crucial concept in understanding the structure and movement patterns of the pelvis.
pelvic axis – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The pelvic axis is a term used in anatomy to describe the imaginary line passing through the center of the pelvic cavity, from the symphysis pubis to the sacrum.
2. Did you know that the pelvic axis plays a crucial role in childbirth? It is the axis along which the baby rotates during the process of delivery, allowing for a smooth transition through the birth canal.
3. The pelvic axis is also associated with balance and stability. It acts as a central axis for the body, helping to distribute the weight between the legs and providing a point of reference for maintaining equilibrium.
4. In ancient times, the concept of the pelvic axis was not fully understood. It was only in the 16th century that Swiss physician and anatomist Andreas Vesalius accurately described the shape and function of the pelvic axis in his groundbreaking work on human anatomy.
5. Interestingly, the pelvic axis differs between males and females. Due to differences in pelvis shape and size, there are notable variations in the pelvic axis between the two sexes, which can have implications in terms of biomechanics, gait, and overall movement patterns.
1. What Is The Pelvic Axis?
The pelvic axis is a crucial anatomical structure located in the pelvis. It serves as the central reference point for movement and alignment in the human body. This axis is formed by the intersection of three major anatomical landmarks: the pubic symphysis, the sacral promontory, and the hip joint centers.
The pelvic axis is essential for the movement of the entire body, especially in activities involving the lower limbs like walking, running, and squatting. It plays a vital role in maintaining stability, evenly distributing forces, and providing a strong foundation for efficient movement patterns.
Understanding the dynamics of the pelvic axis is crucial for optimizing human performance and minimizing the risk of injuries.
Bullet points:
- The pelvic axis is located in the pelvis.
- It is formed by the pubic symphysis, sacral promontory, and hip joint centers.
- The pelvic axis is important for the movement of the whole body.
- It plays a role in activities like walking, running, and squatting.
- Understanding the pelvic axis is crucial for optimizing human performance and preventing injuries.
2. Importance Of Understanding The Pelvic Axis
Understanding the pelvic axis is crucial in the fields of sports performance, rehabilitation, and overall health. A clear comprehension of the pelvic axis allows healthcare professionals, trainers, and individuals to identify and address imbalances or dysfunctions that may impact movement patterns and cause lower back, hip, or lower extremity pain or discomfort.
By recognizing the significance of the pelvic axis, individuals can proactively enhance their movement quality, boost athletic performance, and prevent injuries associated with pelvic misalignment. A properly aligned pelvic axis enables efficient force transmission throughout the body, resulting in improved power generation, stability, and mobility during physical activities.
3. The Role Of The Pelvic Axis In Body Alignment
The pelvic axis is essential for maintaining body alignment. When properly aligned, it provides a solid foundation for the spine, promoting optimal posture and reducing stress on surrounding structures.
A balanced pelvic axis helps maintain the natural curvature of the spine, also known as the neutral spine position. This alignment ensures proper weight distribution, minimizing the risk of excessive pressure on individual joints and promoting efficient muscle activation patterns. The pelvic axis acts as a stable base, aligning the spine, pelvis, and lower extremities, preventing postural imbalances and reducing the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
4. How To Assess The Pelvic Axis
Assessing the Alignment and Function of the Pelvic Axis
Healthcare professionals and movement specialists employ a systematic approach to assess the alignment and function of the pelvic axis. This involves various assessment techniques, including visual observation, palpation, range of motion tests, and postural analyses.
During a visual assessment, the examiner carefully observes the pelvis for any signs of asymmetry, tilting, or rotation. This is important as these abnormalities can indicate issues with the pelvic axis.
Palpation is another technique used to evaluate the position and movement of the pelvis. Healthcare professionals and movement specialists use their hands to feel the bony landmarks and soft tissues around the pelvis. This helps them identify any irregularities or muscle imbalances that may be contributing to pelvic axis dysfunction.
Range of motion tests are also essential in assessing the mobility and stability of the pelvis. These tests involve moving the pelvis in different directions to gauge its range of motion. They can help identify any restrictions or limitations that may be affecting the alignment and function of the pelvic axis.
In addition to these techniques, postural analyses play a crucial role in evaluating the pelvic axis. By examining the overall body alignment, healthcare professionals and movement specialists can detect any compensatory patterns caused by pelvic axis dysfunction. This comprehensive analysis provides valuable insight into the functional status of the pelvic axis.
Overall, the systematic approach employed by healthcare professionals and movement specialists ensures a thorough assessment of the alignment and function of the pelvic axis. By utilizing visual observation, palpation, range of motion tests, and postural analyses, they can accurately evaluate any issues and develop appropriate treatment plans.
5. Common Misalignments Of The Pelvic Axis
Misalignments of the pelvic axis are relatively common and can result from various factors, including poor posture, repetitive movements, injuries, muscle imbalances, and pregnancy, among others.
Some common misalignments include:
- Anterior pelvic tilt: this refers to a forward rotation of the pelvis, causing an excessive arch in the lower back.
- Posterior pelvic tilt: on the other hand, this involves a backward rotation of the pelvis, resulting in a flattened or rounded lower back.
- Lateral pelvic tilt: occurs when one side of the pelvis is higher than the other, leading to an uneven weight distribution.
- Rotational imbalances: these refer to the rotation of the entire pelvis in relation to the spine, often causing compensatory movements in other areas of the body.
Misalignments of the pelvic axis can have significant impacts on the musculoskeletal system and overall body mechanics. It is important to address these issues promptly and effectively to prevent further complications.
“Awareness and understanding of these misalignments can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and make necessary adjustments to their posture and movement patterns.”
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified specialist for a comprehensive assessment, diagnosis, and personalized treatment plan.
––-*-
- Anterior pelvic tilt
- Posterior pelvic tilt
- Lateral pelvic tilt
- Rotational imbalances
6. Correcting Imbalances In The Pelvic Axis
Addressing imbalances in the pelvic axis requires a multidimensional approach that incorporates targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, postural awareness, and lifestyle modifications. Strengthening and stretching the muscles surrounding the pelvis, such as the glutes, hip flexors, and abdominals, can help restore balance and alignment.
Manual therapy techniques, including joint mobilization, soft tissue manipulation, and myofascial release, can be employed to address any restrictions or tightness in the muscles and joints surrounding the pelvis. Additionally, individuals should be encouraged to improve postural awareness and make necessary adjustments in their daily activities, such as sitting and standing with proper alignment.
7. Exercises To Strengthen And Stabilize The Pelvic Axis
Regular exercise programs that target the muscles of the pelvic area can help strengthen and stabilize the pelvic axis. It is essential to focus on exercises that promote balance between the muscles, including both the front and back of the body, to ensure proper alignment.
Exercises such as squats, lunges, bridges, and planks can be beneficial in strengthening the muscles supporting the pelvis. Additionally, incorporating exercises that improve core stability and hip mobility, such as bird dogs, clamshells, and hip flexor stretches, can further enhance pelvic alignment and function.
8. Impact Of A Balanced Pelvic Axis On Overall Health
Achieving a balanced pelvic axis has significant implications for overall health and well-being. When the pelvic axis is properly aligned, it facilitates efficient movement patterns, improves posture, and reduces the risk of musculoskeletal injuries. It enhances the performance of daily activities and athletic endeavors alike while minimizing undue stress on the body.
Moreover, a balanced pelvic axis can alleviate pain and discomfort associated with conditions such as lower back pain, hip impingements, and sciatica. It optimizes joint mechanics and reduces the likelihood of degenerative changes in the spine and pelvis. This, in turn, enhances the individual’s quality of life and allows them to engage in physical activities with greater ease and confidence.
9. Pelvic Axis And Its Relationship To Posture
The pelvic axis is intimately connected to posture, as it serves as the foundation upon which proper alignment of the spine and other body segments is built. An optimal pelvic axis ensures that the spine rests in its natural curvature, preventing excessive stress on the surrounding tissues and enhancing postural integrity.
Poor posture, such as slouching or standing with hyperextended knees, can lead to misalignment of the pelvic axis. This, in turn, affects the alignment of the spine and can result in a cascade of postural compensations throughout the body. By addressing any pelvic axis dysfunctions and maintaining proper posture, individuals can promote better spinal alignment, improve breathing mechanics, and reduce the risk of postural-related conditions.
- Proper alignment of the spine is crucial for postural integrity
- Misalignment of the pelvic axis can cause cascading postural compensations
- Addressing pelvic axis dysfunctions is key to improving spinal alignment
- Good posture promotes better breathing mechanics and reduces postural-related risk.
10. Seeking Professional Help For Pelvic Axis Issues
While individuals can perform basic self-assessments and incorporate general exercises to improve pelvic axis alignment, seeking professional help from a qualified healthcare provider or a movement specialist is highly recommended. These professionals have the expertise and knowledge to accurately assess pelvic axis dysfunctions, identify underlying causes, and develop personalized treatment plans based on individual needs.
Collaborating with a healthcare professional ensures a comprehensive evaluation and a targeted approach for correcting imbalances in the pelvic axis. They can provide guidance on proper exercise selection, prescribe specific manual therapy techniques, and offer postural corrections tailored to the individual’s unique circumstances.
By seeking professional help, individuals can optimize their movement quality, minimize the risk of injuries, and improve their overall well-being.
In conclusion, the pelvic axis is a crucial anatomical structure that plays a significant role in human movement and alignment. Understanding its importance allows individuals to recognize imbalances, correct dysfunctions, and optimize movement quality.
Benefits of seeking professional help:
- Comprehensive evaluation
- Targeted approach for correcting imbalances
- Guidance on proper exercise selection
- Specific manual therapy techniques
- Postural corrections tailored to individual circumstances
💡
You may need to know these questions about pelvic axis
What are the abnormalities of pelvis?
The abnormalities of the pelvis can manifest in various forms, such as pelvic floor dysfunction, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and pelvic organ prolapse. Pelvic floor dysfunction refers to the inability to control the muscles of the pelvic floor, leading to issues with urinary or bowel function. PID is an infection of the reproductive organs, usually caused by sexually transmitted infections, which can result in pelvic pain and inflammation. Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the pelvic organs, such as the uterus or bladder, descend or protrude into the vaginal canal due to weakened pelvic floor muscles. These abnormalities can cause discomfort, pain, and impact the overall quality of life for those affected.
What is pelvic inlet and outlet?
The pelvic inlet refers to the upper opening of the pelvic region, formed by the bones. It is the space where the abdominal cavity transitions into the pelvic cavity. This crucial anatomical structure allows for the passage of various structures, such as the intestines and blood vessels, between the abdomen and pelvis. On the other hand, the pelvic outlet is the lower opening of the pelvis, situated between the bones at the base. It serves as the exit for the pelvic cavity, allowing for the passage of structures like the urethra, bladder, and rectum. Understanding the pelvic inlet and outlet is important in comprehending the dynamics of body movements, childbirth, and the diagnosis and management of injuries in this region.
Why is it called false pelvis?
The term “false pelvis” refers to the region above the plane where the true pelvis begins. It is called false pelvis because it is sometimes considered to be a part of the abdominal cavity rather than the pelvic cavity. This distinction is important because the true pelvis, which is below the above-mentioned plane, is where the pelvic cavity is located. The urinary bladder is positioned just above the anterior pelvic brim, highlighting the division between the false and true pelvis.
Where is the pelvic inlet?
The pelvic inlet, also known as the superior aperture of the pelvis, is a crucial anatomical feature that delineates the division between the pelvic and abdominal cavities. Some researchers posit that it represents the partition between the lesser and greater pelvis regions. The pelvic inlet holds significant importance in pelvimetry, where it serves as a primary point of measurement. By accurately locating and assessing the dimensions of this planar surface, it aids in evaluating the adequacy of the pelvis for childbirth.
Reference source
https://www.imaios.com/en/vet-anatomy/anatomical-structure/axis-of-pelvis-11073900984
https://www.templehealth.org/services/conditions/pelvic-disorders
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/pelvic-inlet
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pelvic_brim