Placental retention, a condition that affects some women after childbirth, can be a distressing and potentially dangerous experience.
With symptoms ranging from excessive bleeding to intense pain and fever, it’s crucial to understand the treatment options available to prevent complications.
This article delves into the world of placental retention, shedding light on medical interventions, such as ultrasound scans and anesthesia procedures, that can swiftly alleviate this worrisome condition.
Read on to discover how proactive measures can safeguard against life-threatening infections and bring peace of mind to new mothers.
placental retention
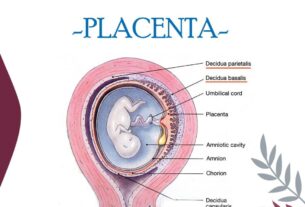
Placental retention refers to the condition where the placenta, the organ that develops during pregnancy to provide nutrients and oxygen to the baby, is not completely expelled from the uterus after childbirth.
This can lead to various symptoms such as fever, bad smelling discharge, heavy bleeding, and pain.
Placental retention can result in severe complications including severe infection, life-threatening blood loss, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Early diagnosis through a postpartum ultrasound scan is crucial in order to implement prompt management options.
Treatment options for placental retention include emptying the bladder, pulling on the umbilical cord, or performing a procedure under anesthesia.
It is important to be aware of the potential complications associated with placental retention, such as life-threatening infection, and to ensure proper management to prevent further harm.
Key Points:
- Placental retention is when the placenta is not fully expelled from the uterus after childbirth.
- Symptoms of placental retention include fever, bad smelling discharge, heavy bleeding, and pain.
- Complications of placental retention can include severe infection, life-threatening blood loss, and postpartum hemorrhage.
- Early diagnosis through a postpartum ultrasound scan is essential for prompt management.
- Treatment options for placental retention include emptying the bladder, pulling on the umbilical cord, or performing a procedure under anesthesia.
- Proper management of placental retention is crucial to prevent further harm and potential life-threatening complications.
placental retention – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Placental retention, also known as retained placenta, is a rare condition where the placenta remains inside the uterus after childbirth instead of being expelled naturally.
2. While often associated with human childbirth, placental retention can also occur in other mammals such as dogs, cats, and horses.
3. Placental retention can lead to severe complications like postpartum hemorrhage, infection, or the development of uterine abnormalities.
4. In ancient times, placental retention was believed to have medicinal properties. It was sometimes consumed, believed to promote fertility, ensure a healthy pregnancy, or be used as a treatment for certain ailments.
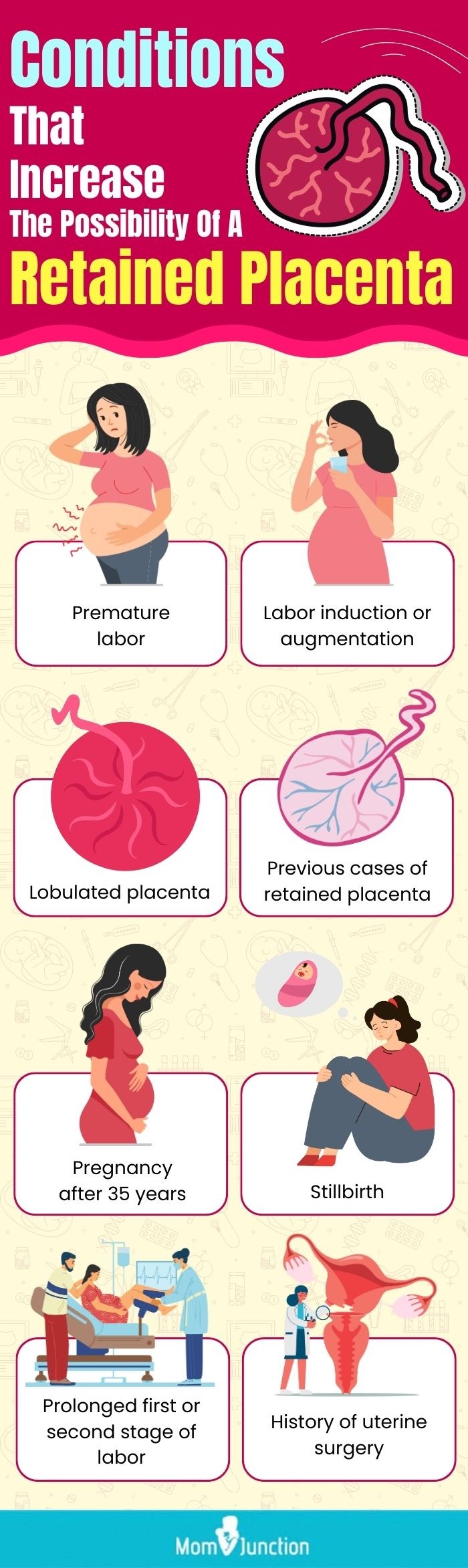
5. Placental retention is more likely to occur in women who have previously experienced the condition, have had multiple pregnancies, or have had cesarean sections in the past. Close monitoring and timely medical intervention are necessary to prevent complications.
Placental Retention
Placental retention is a condition in which the placenta, the organ responsible for nourishing the baby during pregnancy, fails to naturally deliver after childbirth. The placenta should normally be expelled within 30 minutes to an hour after the baby’s birth. However, in certain cases, it can remain in the uterus, resulting in complications and potential health risks for the mother. Placental retention can be caused by several factors, including:
- Uterine abnormalities.
- The baby’s position.
- Issues with the placenta itself.
If placental retention occurs, it is important for medical professionals to intervene and safely remove the placenta to prevent further complications. Failure to remove the retained placenta can lead to infections, excessive bleeding, and other serious health issues. Immediate medical attention is essential in such cases.
In summary, placental retention is a condition that requires prompt medical intervention when the placenta fails to naturally deliver after childbirth. It is crucial to address this concern to avoid potential health risks for the mother.
Uterus
The uterus, or womb, is an essential organ during pregnancy as it is where the baby grows and develops. During labor, the uterus contracts to push the baby through the birth canal. Additionally, after the baby is born, the uterus contracts again to expel the placenta. However, placental retention can occur when the uterus fails to contract effectively or the contractions are not strong enough. This can result in the placenta remaining attached to the uterine wall.
Some key points about the uterus and placental retention include:
- The uterus is responsible for housing and nourishing the growing baby during pregnancy.
- During labor, the uterus contracts to facilitate the birth process.
- The uterus also contracts postpartum to eliminate the placenta.
- Placental retention can occur when the uterus fails to contract properly or when the contractions are weak.
- Placental retention can lead to complications and may require medical intervention.
“In cases of placental retention, the uterus fails to contract properly or the contractions are not strong enough, leading to the placenta remaining attached to the uterine wall.”
Baby
The role of the baby in placental retention may be indirect but significant. The position of the baby during delivery can have an impact on the uterus’ ability to contract and expel the placenta. For instance, if the baby is in a breech position (feet or buttocks first), it can exert pressure on the cervix, hindering effective uterine contractions. Moreover, a large or abnormally positioned placenta can raise the likelihood of placental retention.
Symptoms
Placental retention can lead to a range of symptoms, including:
- Fever
- Bad smelling discharge
- Heavy bleeding
- Large pieces of tissue
- Pain
- Severe infection
These symptoms can manifest immediately after delivery or within a few days. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare providers to closely monitor the postpartum period to promptly identify any signs of placental retention.
Take note: Placental retention is a condition that requires careful attention to prevent complications.
Fever
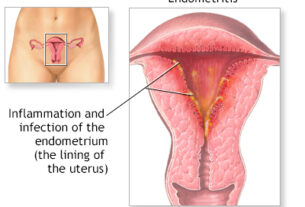
Fever is a common symptom associated with placental retention. It is often caused by an infection in the uterus called endometritis, which arises from retained placental tissue. This infection can result in inflammation and an increase in body temperature, necessitating prompt medical intervention.
Bad Smelling Discharge
Another significant symptom of placental retention is the presence of a foul-smelling discharge. This odor is caused by an infection resulting from the retained placental tissue. The bacteria present in the uterus produce a strong and unpleasant smell, which serves as a clear indication for immediate medical intervention.
- Foul-smelling discharge: One of the key symptoms of placental retention.
- Infection: Retained placental tissue can lead to an infection in the uterus.
- Bacteria and odor: The bacteria in the uterus create a strong and unpleasant smell, highlighting the need for medical attention.
Heavy Bleeding
Postpartum Hemorrhage: Heavy bleeding, also known as postpartum hemorrhage, can occur due to placental retention. When the placenta remains attached to the uterine wall, it prevents the uterus from contracting properly, leading to uncontrolled bleeding. This complication is potentially life-threatening due to the risk of severe blood loss.
- Causes:
- Placental retention
-
Inefficient uterine contractions
-
Consequences:
- Excessive bleeding
- Risk of severe blood loss
- Potential harm to the mother’s health
It is crucial to address postpartum hemorrhage promptly to prevent complications and ensure the well-being of the mother.
Large Pieces Of Tissue
During placental retention, large pieces of placental tissue may not be expelled naturally from the mother’s body. These pieces of tissue can cause discomfort and increase the risk of infection. Healthcare providers must remove these retained tissue fragments to prevent complications.
Pain
Women with placental retention often experience pain in the abdomen or pelvic area. This pain can range from mild to severe, depending on the individual and the specific circumstances. The pain may be associated with the uterus attempting to expel the retained placenta or the presence of infection.
Severe Infection
One of the most severe complications of placental retention is the development of a life-threatening infection. When the placenta remains in the uterus, it can serve as a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to infections such as endometritis or sepsis. Immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent the spread of infection and its potential consequences.
Overall, placental retention can pose significant risks to the mother’s health. Prompt diagnosis, early intervention, and appropriate management are crucial to minimize the complications associated with this condition. Healthcare providers play a vital role in ensuring the safe and effective management of placental retention through careful monitoring and appropriate treatment options.
- Placental retention can lead to a life-threatening infection
- Immediate medical attention is crucial
- Prompt diagnosis, early intervention, and appropriate management are necessary
- Healthcare providers play a vital role in monitoring and treating this condition
💡
You may need to know these questions about placental retention
What is the most common cause of placental retention?
The most common cause of placental retention is insufficient contractions in the uterus, which can occur due to various reasons. Large babies are often associated with this complication, as their size can put additional strain on the uterus and hinder effective contractions. Additionally, other factors such as hormonal imbalances or uterine abnormalities can also contribute to the retention of the placenta. Understanding and addressing these underlying causes are essential for preventing and managing this issue during childbirth.
How do you get rid of placenta retention?
In cases of placenta retention, medical intervention is crucial. One approach involves the manual removal of the placenta by a doctor, although this carries a potential risk of infection. An alternative method involves the administration of medications that help relax the uterus, facilitating the expulsion of the placenta from the womb. These approaches aim to safely remove the placenta and mitigate any associated complications.
How common is retained placenta?
Retained placenta, while relatively uncommon in high-resource countries, affects approximately 2.7% of vaginal deliveries. Several factors contribute to its occurrence, including previous endometrial trauma like cesarean deliveries, curettage, high parity, and a history of retained placenta. Recurrence rates of around 12.5% further emphasize the role of these risk factors in the development of retained placenta. While relatively low in prevalence, these statistics highlight the importance of identifying and addressing these risk factors to minimize the occurrence of retained placenta during childbirth.
Is a retained placenta the doctors fault?
Determining liability for a retained placenta involves a careful assessment of the specific circumstances. While medical professionals are responsible for the management of a retained placenta, it is essential to consider various factors before attributing fault solely to the doctor. The successful delivery of the placenta relies on a collaborative effort between the healthcare team and the mother’s unique physiological response. Factors such as abnormal placental attachment, uterine inertia, or unforeseen complications can play a role in the retention, making it challenging to attribute blame to any one party. Medical malpractice claims related to retained placenta necessitate a thorough examination of the individual case to ascertain the exact causes and identify any negligence.
It is important to note that medical malpractice laws differ across jurisdictions, and specific guidelines may vary. These complexities underscore the significance of conducting a comprehensive investigation and seeking expert opinions in cases involving retained placenta. Only with a thorough assessment and understanding of the circumstances can a determination be made concerning whether the medical professionals involved can be held accountable for the harm suffered by the mother.
Reference source
https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/retained-placenta
https://www.webmd.com/baby/what-is-retained-placenta
https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/pregnancy-complications/retained-placenta
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/labor-and-birth/retained-placenta/