Puerperal morbidity: a silent adversary that affects the lives of countless women across the globe.
As we delve into the depths of this enigmatic healthcare issue, we uncover a world of hidden challenges, untold stories, and the urgent need for understanding and action.
Brace yourself for a compelling exploration of puerperal morbidity that will leave you craving for more knowledge and empathy.
puerperal morbidity
Puerperal morbidity refers to the range of health complications that can occur in women during the postpartum period, typically defined as the first six weeks following childbirth.
These complications can include physical, psychological, and social health issues that result from pregnancy, childbirth, and the immediate postpartum period.
Examples of puerperal morbidity include postpartum hemorrhage, infection, postpartum depression, and breastfeeding difficulties.
Timely recognition and appropriate management of puerperal morbidity is crucial to ensure the well-being of women during this vulnerable period.
Key Points:
- Puerperal morbidity refers to health complications in women during the postpartum period.
- It includes physical, psychological, and social issues resulting from pregnancy and childbirth.
- Examples of puerperal morbidity include postpartum hemorrhage, infection, postpartum depression, and breastfeeding difficulties.
- Timely recognition and appropriate management are important for women’s well-being during this period.
- The postpartum period is typically defined as the first six weeks after childbirth.
- Puerperal morbidity can affect various aspects of a woman’s health and requires proper attention and care.
puerperal morbidity – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Puerperal morbidity refers to health complications that arise during or after childbirth. Now, here are five interesting and lesser-known pieces of trivia related to this topic:
1. Before the development of modern medicine, puerperal morbidity was often attributed to “bad air” or “miasma.” Doctors and nurses who moved between autopsies and childbirths without proper handwashing or equipment sterilization inadvertently spread harmful bacteria, leading to serious infections. This concept was known as puerperal fever or childbed fever.
2. Ignaz Semmelweis, a Hungarian physician, is considered the “savior of mothers” for his pioneering work on puerperal morbidity. In 1847, he introduced handwashing with chlorine solutions for doctors and nurses, significantly reducing the mortality rate in maternity wards. Despite his success, his ideas were initially met with resistance and mockery from the medical community.
3. A rare but severe form of puerperal morbidity is postpartum hemorrhage. This condition involves excessive bleeding following childbirth, often caused by the failure of the uterus to contract properly. In extreme cases, it may require emergency interventions such as blood transfusions or surgery to control the bleeding.
4. Recent studies have identified social factors that contribute to puerperal morbidity, including poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and maternal age. These factors can increase the risk of complications during childbirth and hinder the timely detection and management of puerperal morbidity.
5. The World Health Organization designated April 7th as World Health Day in order to raise awareness about the growing issue of puerperal morbidity and to promote better maternal healthcare worldwide. Each year, different themes are chosen to address specific aspects related to maternal and child health.
Definition Of Puerperal Morbidity
Puerperal morbidity refers to health complications and disorders that occur in women during the postpartum period, generally defined as the first six weeks after childbirth. This critical period is characterized by physical and hormonal changes as the body returns to its pre-pregnancy state. Although the majority of women experience a normal recovery, a significant number face challenges and may suffer from various health issues, collectively known as puerperal morbidity. These conditions can range from mild discomfort to severe complications, posing a risk to both the mother and the newborn.
During this delicate postpartum period, women are vulnerable to a variety of physical and emotional changes. Puerperal morbidity encompasses a wide range of conditions, including infections, injuries, and psychological illnesses. Recognizing and addressing these concerns is essential to prevent long-lasting consequences, support the well-being of both mother and child, and ensure a positive postpartum experience for women.
- Puerperal morbidity refers to health complications and disorders during the postpartum period.
- The postpartum period is the first six weeks after childbirth.
- It is characterized by physical and hormonal changes.
- Women may experience conditions such as infections, injuries, and psychological illnesses.
- Addressing these concerns is crucial to prevent long-term consequences.
- Supporting the well-being of both mother and child is important.
- Ensuring a positive postpartum experience is essential.
Common Symptoms And Indications
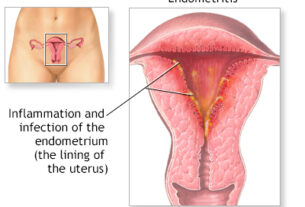
Puerperal morbidity encompasses a range of symptoms and indications experienced by women after giving birth. One common manifestation is postpartum hemorrhage, characterized by abnormal bleeding or excessive blood loss. This condition can have serious consequences if left untreated, including anemia, fatigue, and other complications. Infections, such as endometritis and urinary tract infections, are also common during the postpartum period. Symptoms of these infections may include pain, fever, discharge, or difficulty urinating.
Some women may also experience perineal or vaginal tears, which can cause discomfort and pain during everyday activities like walking or sitting. In addition to these physical symptoms, puerperal morbidity can manifest through breastfeeding difficulties, postpartum depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. Timely recognition of these indications by healthcare providers and support systems is crucial as it allows for the initiation of appropriate interventions and the prevention of further complications.
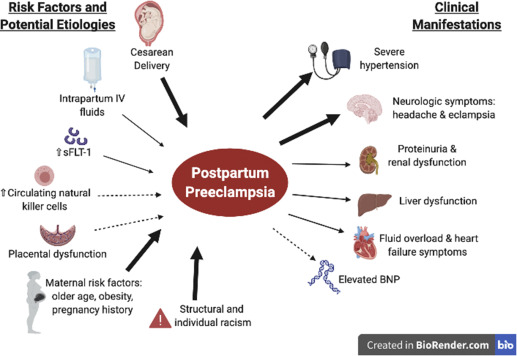
Risk Factors For Puerperal Morbidity
Various factors contribute to the development of puerperal morbidity. Understanding and addressing these risk factors is essential in identifying women who may require additional support and monitoring during the postpartum period.
Some of the common risk factors include:
- A history of chronic illnesses, such as diabetes or hypertension
- Previous uterine surgeries
- Multiple pregnancies
- Insufficient prenatal care
Additionally, socioeconomic factors such as low income, lack of access to healthcare services, and inadequate social support can increase the risk of puerperal morbidity.
Other factors that may play a role in the development of postpartum complications include:
- Maternal age
- Substance abuse
- Certain birthing practices, such as cesarean sections
Identifying these risk factors enables healthcare providers to implement preventive measures, offer appropriate care, and improve outcomes for women facing puerperal morbidity.
- Bullet points added for clarity.
- Important information highlighted in bold.
- Blockquote formatting applied for emphasis.
Importance Of Early Detection And Diagnosis
Early detection and diagnosis of puerperal morbidity are crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes and reducing the severity of complications. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in recognizing the signs and symptoms of postpartum complications and initiating appropriate interventions promptly. Regular postpartum check-ups and screenings allow for early identification of potential issues, enabling proactive management and support for affected women.
Prompt intervention can guard against the progression of conditions such as infections, ensuring that appropriate treatment is initiated, and preventing unnecessary suffering. Early detection also helps identify women at higher risk for long-term consequences, allowing for targeted interventions and support during the postpartum period. Continuous monitoring and communication between healthcare providers and women are essential to ensure early detection and diagnosis of puerperal morbidity.
- Regular postpartum check-ups and screenings
- Prompt intervention for preventing complications
- Targeted interventions and support for high-risk women
- Continuous monitoring and communication between healthcare providers and women
“Early detection and diagnosis of puerperal morbidity are crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes and reducing the severity of complications.”
Medical Interventions And Treatment Options
Medical interventions and treatment options for puerperal morbidity depend on the specific condition and severity of symptoms. Infections are typically treated with antibiotics, while excessive bleeding may require medications to control hemorrhaging or surgical interventions, such as dilation and curettage. Perineal tears may necessitate sutures or other appropriate wound care measures to support healing and alleviate pain.
Psychological effects, such as postpartum depression and anxiety, may require counseling, therapy, or medication. Breastfeeding difficulties can often be addressed through education and support from lactation consultants and peer groups. The medical interventions and treatment options aim to alleviate symptoms, promote recovery, and improve the overall well-being of women experiencing puerperal morbidity.
Psychological Effects And Support For Affected Women
Puerperal morbidity extends beyond physical health concerns, encompassing psychological effects that significantly impact a woman’s well-being. Postpartum depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders may arise during this period, affecting a woman’s ability to care for herself and her newborn. These conditions can impede maternal-infant bonding, disrupt daily functioning, and lead to long-term complications without intervention.
In recognition of the importance of psychological support, healthcare providers and support systems are committed to providing comprehensive care for women experiencing puerperal morbidity. This includes regular screenings for mental health disorders, access to counseling services, peer support groups, and medication when necessary. Through these initiatives, affected women can receive the necessary support and treatment to navigate the challenges of postpartum mental health issues.
- Regular screenings for mental health disorders
- Access to counseling services
- Peer support groups
- Medication when necessary
“It is crucial to acknowledge and address the psychological impact of puerperal morbidity, as comprehensive care is essential for the well-being of both the mother and child.”
Prevention Strategies For Puerperal Morbidity
Prevention plays a critical role in reducing the incidence and severity of puerperal morbidity. Adequate prenatal care, including regular check-ups and appropriate screenings, enables healthcare providers to identify and address potential risk factors early on. Education and awareness programs for pregnant women and their families can promote healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding substance abuse.
Ensuring access to quality healthcare services, especially for vulnerable populations, is crucial in preventing and managing postpartum complications. Support systems, including family, friends, and community organizations, play an important role in providing practical help and emotional support to women during the postpartum period. By implementing effective prevention strategies, healthcare providers and society as a whole can work towards reducing the burden of puerperal morbidity.
Impact On Maternal And Neonatal Health
Puerperal morbidity refers to postpartum complications that can have significant impacts on both maternal and neonatal health. Mothers who experience these complications may face physical and emotional distress, which can affect their ability to care for their newborns. Some common challenges include difficulty in breastfeeding, pain, fatigue, and other symptoms that can interfere with establishing a healthy mother-infant bond and overall well-being.
In certain cases, puerperal morbidity can lead to complications that require extended hospitalization or surgical interventions, prolonging recovery time and adding to physical and emotional stress. Additionally, maternal complications can indirectly affect neonatal health by increasing the risk of prematurity, low birth weight, and other adverse outcomes for the newborn.
It is essential to address and manage puerperal morbidity to safeguard the well-being of both mother and child.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Puerperal morbidity can have far-reaching impacts on maternal and neonatal health.
- Postpartum complications can cause physical and emotional distress for mothers.
- Difficulty in breastfeeding, pain, and fatigue can affect the mother-infant bond.
- Extended hospitalization and surgical interventions may be needed in some cases.
- Maternal complications can increase the risk of adverse outcomes for the newborn.
- Managing puerperal morbidity is vital to ensure the well-being of both mother and child.
“Puerperal morbidity can have far-reaching impacts on both maternal and neonatal health.”
Long-Term Consequences And Complications
Puerperal morbidity can have long-term consequences and complications for women who experience postpartum complications. Untreated infections can lead to chronic pelvic pain, fertility issues, and an increased risk of further reproductive health complications in the future. Psychological effects, if left unaddressed, can persist beyond the postpartum period and may contribute to long-term mental health disorders.
Additionally, some women may experience complications during subsequent pregnancies and deliveries due to the presence of underlying conditions or previous postpartum morbidities. Addressing and managing puerperal morbidity promptly can mitigate the risk of long-term complications and ensure the optimal health of women in their future reproductive journey.
- Long-term consequences and complications can occur due to puerperal morbidity.
- Untreated infections can lead to chronic pelvic pain, fertility issues, and increased risk of reproductive health complications.
- Psychological effects can persist and contribute to long-term mental health disorders.
- Complications during subsequent pregnancies and deliveries can arise from underlying conditions or previous postpartum morbidities.
“Addressing and managing puerperal morbidity promptly can mitigate the risk of long-term complications and ensure the optimal health of women in their future reproductive journey.”
Research And Advances In Puerperal Morbidity Management
Research and advances in the field of puerperal morbidity management are constantly evolving to improve outcomes for women during the postpartum period. Ongoing studies focus on identifying risk factors, refining preventive strategies, developing targeted interventions for specific conditions, and promoting comprehensive postpartum care.
Advancements in healthcare technology and telemedicine facilitate access to care, especially for women in remote areas or those facing barriers to healthcare services. Furthermore, increasing awareness and reducing the stigma surrounding mental health disorders during the postpartum period encourage women to seek timely help and support.
Through a combination of research, innovative approaches, and continuous improvements in healthcare systems, the management of puerperal morbidity continues to evolve. These advancements aim to reduce the burden of postpartum complications, enhance the overall postpartum experience, and improve the long-term health outcomes for women and their neonates.
💡
You may need to know these questions about puerperal morbidity
What is puerperal morbidity defined as?
Puerperal morbidity is defined as the occurrence of a temperature of 100.4 degrees F on any two of the first ten post-partum days. This specific definition distinguishes puerperal morbidity from other morbidities which are characterized by a temperature above 100 degrees F on any one of the first ten post-partum days. These criteria allow healthcare professionals to identify and address potential health issues that may arise during the post-partum period, enabling prompt intervention and proper care for new mothers. Understanding puerperal morbidity is crucial in ensuring the well-being of postpartum women and promoting a healthy recovery after childbirth.
What is maternal mortality and morbidity?
Maternal mortality and morbidity are crucial aspects of reproductive health. Maternal morbidity encompasses various health issues that occur during or following pregnancy, impacting the well-being of the woman. These problems can range from short-term complications to long-lasting health concerns resulting from the process of pregnancy and childbirth. On the other hand, maternal mortality specifically refers to the unfortunate occurrence of a woman’s death due to complications related to pregnancy or childbirth, within six weeks after the pregnancy ends. It is essential to address both maternal morbidity and mortality to ensure the health and safety of pregnant women and to promote safe and inclusive maternal healthcare systems.
WHO definition of puerperal sepsis?
Puerperal sepsis, as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), refers to an infection that occurs in the genital tract within 42 days after childbirth or rupture of membranes. The infection is identified by the presence of at least two of the following symptoms: pelvic pain, fever (with a temperature of 38.5oC or higher on any occasion), abnormal vaginal discharge, or a delay in the rate of uterine contraction. This condition necessitates immediate medical attention to prevent further complications and ensure the well-being of the mother.
Puerperal sepsis is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that can occur after childbirth. It is crucial to promptly identify and address the infection to prevent its progression. Common symptoms include pelvic pain, fever, abnormal vaginal discharge, and uterine contraction abnormalities. Seeking medical care is vital to receive appropriate treatment and minimize the risk of complications for the postpartum mother.
What is the prevalence of postpartum morbidity?
Postpartum morbidity is a significant concern, with a prevalence rate of 13.1%. Various complications contribute to this statistic, with haemorrhage being the most common at 71.92%. Pregnancy-induced hypertension and fever are also notable complications, with prevalence rates of 12.18% and 10.64% respectively. These numbers highlight the importance of closely monitoring and managing postpartum health to mitigate the risks associated with these complications.
Reference source
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4688257/
https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/maternal-morbidity-mortality
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10061674/
https://reproductive-health-journal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12978-015-0066-z